Abstract
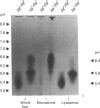
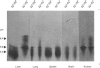
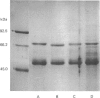
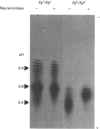
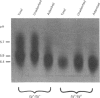
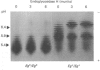
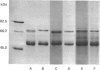
The accumulation of the relatively large amounts of beta-glucuronidase in microsomal fractions of normal mice depends on formation of complexes with the protein egasyn. Unexpectedly, it was found that the egasyn gene also affects the processing of beta-glucuronidase, which is segregated to lysosomes. In egasyn-positive mice lysosomal beta-glucuronidase from liver has a mean pI of 5.9 with a minor proportion at pI 5.4, whereas in egasyn-negative mice the proportion of the two lysosomal forms is reversed. Combined experiments measuring susceptibility to neuraminidase and to endoglycosidase H and specific binding to Ricinus communis lectin-agarose columns showed that the alterations in isoelectric point were associated with a decrease in complex oligosaccharides of lysosomal beta-glucuronidase in egasyn-positive mice. Since this alteration occurs not only in a congenic strain carrying the Eg0 gene but also in several other inbred strains that are homozygous for this gene, it is considered to be a genuine effect of the Eg gene rather than other genes that might regulate oligosaccharide processing. Also, the alteration is likely to be a result of direct physical interaction of the egasyn protein and lysosomal beta-glucuronidase, since a second lysosomal enzyme, beta-galactosidase, which does not form complexes with egasyn, is unaffected. The results suggest a model in which egasyn not only causes accumulation of beta-glucuronidase in the microsomal compartment but also acts upon the precursor to lysosomal beta-glucuronidase to alter its interaction with trans-Golgi-apparatus processing enzymes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann H., Doyle D. Effect of trypsin on the cell surface proteins of hepatoma tissue culture cells. Characterization of a carbohydrate-rich glycopeptide released from a calcium binding membrane glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3935–3946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belinsky S. A., Kauffman F. C., Sokolove P. M., Tsukuda T., Thurman R. G. Calcium-mediated inhibition of glucuronide production by epinephrine in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7705–7711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltramini-Guarini P., Gitzelmann R., Pfister K. Presence and absence of the microsomal beta-glucuronidase in mice correlates with differences in the processing of the lysosomal enzyme. Eur J Cell Biol. 1984 May;34(1):165–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt E. J., Elliott R. W., Swank R. T. Defective lysosomal enzyme secretion in kidneys of Chediak-Higashi (beige) mice. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):774–788. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt E. J., Swank R. T. The Chediak-Higashi (beige) mutation in two mouse strains. Allelism and similarity in lysosomal dysfunction. Am J Pathol. 1976 Mar;82(3):573–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen G. A., Lusis A. J., Paigen K. Linkage of genetic determinants for mouse beta-galactosidase electrophoresis and activity. Genetics. 1977 Jan;85(1):73–84. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. A., Jahreis G. P., Swank R. T. The synthesis and processing of beta-glucuronidase in normal and egasyn deficient mouse kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Mar 31;99(2):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91799-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Farquhar M. G. The mannose-6-phosphate receptor for lysosomal enzymes is concentrated in cis Golgi cisternae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):295–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90223-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S. L., Creek K. E., Merion M., Hirschberg C. B. Subfractionation of rat liver Golgi apparatus: separation of enzyme activities involved in the biosynthesis of the phosphomannosyl recognition marker in lysosomal enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3938–3942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S. L., Nuwayhid N., Stanley P., Briles E. I., Hirschberg C. B. Translocation across Golgi vesicle membranes: a CHO glycosylation mutant deficient in CMP-sialic acid transport. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizik M., Elliott R. W. A second gene affecting the sialylation of lysosomal alpha-mannosidase in mouse liver. Biochem Genet. 1978 Apr;16(3-4):247–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00484082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Fries E., Urbani L. J., Rothman J. E. Early and late functions associated with the Golgi apparatus reside in distinct compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7453–7457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedde K. N., Sly W. S. Ricin-binding properties of acid hydrolases from isolated lysosomes implies prior processing by terminal transferases of the trans-Golgi apparatus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90949-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze H. J., Slot J. W., Strous G. J., Hasilik A., Von Figura K. Ultrastructural localization of the mannose 6-phosphate receptor in rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):2047–2054. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. E., Kornfeld S. Evidence for extensive subcellular organization of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing and lysosomal enzyme phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3159–3165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYASHI M., NAKAJIMA Y., FISHMAN W. H. THE CYTOLOGIC DEMONSTRATION OF BETA-GLUCURONIDASE EMPLOYING NAPHTHOL AS-BI GLUCURONIDE AND HEXAZONIUM PARAROSANILIN; A PRELIMINARY REPORT. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Apr;12:293–297. doi: 10.1177/12.4.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himeno M., Nishimura Y., Takahashi K., Kato K. The synthesis of rat liver lysosomes. III. Chemical composition of microsomal and lysosomal beta-glucuronidases purified from rat liver. J Biochem. 1978 Feb;83(2):511–518. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Rosner M. R., Robbins P. W. Host-dependent variation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides at individual glycosylation sites of Sindbis virus glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2548–2554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Rosner M. R., Robbins P. W. Selective cleavage by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H at individual glycosylation sites of Sindbis virion envelope glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2555–2561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl T. R., Chapman V. M. Linkage and expression of the Eg locus controlling inclusion of beta-glucuronidase into microsomes. Biochem Genet. 1974 May;11(5):367–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00486410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., Paigen K. Properties of mouse alpha-galactosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 21;437(2):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., Paigen K. The large scale isolation of mouse beta-glucuronidase and comparison of allozymes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7336–7345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., Tomino S., Paigen K. Isolation, characterization, and radioimmunoassay of murine egasyn, a protein stabilizing glucuronidase membrane binding. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7753–7760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medda S., Swank R. T. Egasyn, a protein which determines the subcellular distribution of beta-glucuronidase, has esterase activity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15802–15808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medda S., von Deimling O., Swank R. T. Identity of esterase-22 and egasyn, the protein which complexes with microsomal beta-glucuronidase. Biochem Genet. 1986 Apr;24(3-4):229–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00502791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. L., Kress B. C., Stein R., Kinnon C., Kern H., Schneider J. A., Harms E. Properties of N-acetyl-beta-D-hexosaminidase from isolated normal and I-cell lysosomes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9352–9362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuochi T., Nishimura Y., Kato K., Kobata A. Comparative studies of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide structures of rat liver microsomal and lysosomal beta-glucuronidases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jun;209(1):298–303. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens J. W., Gammon K. L., Stahl P. D. Multiple forms of beta-glucuronidase in rat liver lysosomes and microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jan;166(1):258–272. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90387-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potier M., Lu Shun Yan D., Womack J. E. Neuraminidase deficiency in the mouse. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80560-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K., Ganschow R. E. Turnover of murine beta-glucuronidase. Comparison among liver, kidney, and spleen and between lysosomes and microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5437–5442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strawser L. D., Touster O. The cellular processing of lysosomal enzymes and related proteins. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1980;87:169–210. doi: 10.1007/BFb0030898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swallow D. M., West L. F., Van Elsen A. The role of lysosomal sialidase and beta-galactosidase in processing the complex carbohydrate chains on lysosomal enzymes and possibly other glycoproteins. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Jul;48(Pt 3):215–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb01017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Paigen K. Biochemical and genetic evidence for a macromolecular -glucuronidase complex in microsomal membranes. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jul 5;77(3):371–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominco S., Paigen K. Egasyn, a protein complexed with microsomal beta-glucuronidase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):1146–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Six H., Touster O. Rat liver microsomal and lysosomal beta-glucuronidases differ in both carbohydrate and amino acid compositions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3080–3084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varki A., Kornfeld S. The spectrum of anionic oligosaccharides released by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H from glycoproteins. Structural studies and interactions with the phosphomannosyl receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2808–2818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassmer B., de Looze S. M., von Deimling O. H. Biochemistry and genetics of esterase-20 (ES-20), a second trimeric carboxylesterase of the house mouse (Mus musculus). II. A unique recombination reveals ES-20 as a hybrid enzyme. Biochem Genet. 1985 Oct;23(9-10):759–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson G., Davey R. A., Labarca C., Paigen K. Genetic determination of kinetic parameters in beta-glucuronidase induction by androgen. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3005–3011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womack J. E., Yan D. L., Potier M. Gene for neuraminidase activity on mouse chromosome 17 near h-2: pleiotropic effects on multiple hydrolases. Science. 1981 Apr 3;212(4490):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.7209520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]