Abstract
When type II pneumonocytes were exposed to purified lung surfactant that contained 1-palmitoyl-2-[3H]palmitoyl-glycero-3-phosphocholine, radiolabelled surfactant was apparently taken up by the cells since it could not be removed by either repeated washing or exchange with non-radiolabelled surfactant, but was released when the cells were lysed. After 4 h of exposure to [3H]surfactant, more than half of the 3H within cells remained in disaturated phosphatidylcholine. Incorporation of [3H]choline, [14C]palmitate and [14C]acetate into glycerophospholipids was decreased in type II cells exposed to surfactant and this inhibition, like surfactant uptake, was half-maximal when the extracellular concentration of surfactant was approx. 0.1 mumol of lipid P/ml. Inhibition of incorporation of radiolabelled precursors by surfactant occurred rapidly and reversibly and was not due solely to dilution of the specific radioactivity of intracellular precursors. Activity of dihydroxyacetone-phosphate acyltransferase, but not glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, was decreased in type II cells exposed to surfactant and this was reflected by a decrease in the 14C/3H ratio of total lipids synthesized when cells incubated with [U-14C]glycerol and [2-3H]glycerol were exposed to surfactant. Phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylglycerol and cholesterol, either individually or mixed in the molar ratio found in surfactant, did not mimic purified surfactant in the inhibition of glycerophospholipid synthesis. In contrast, an apoprotein fraction isolated from surfactant inhibited greatly the incorporation of [3H]choline into lipids and this inhibitory activity was labile to heat and to trypsin. It is concluded that the apparent uptake of surfactant by type II cells in vitro is accompanied by an inhibition of glycerophospholipid synthesis via a mechanism that involves a surfactant apoprotein.
Full text
PDF


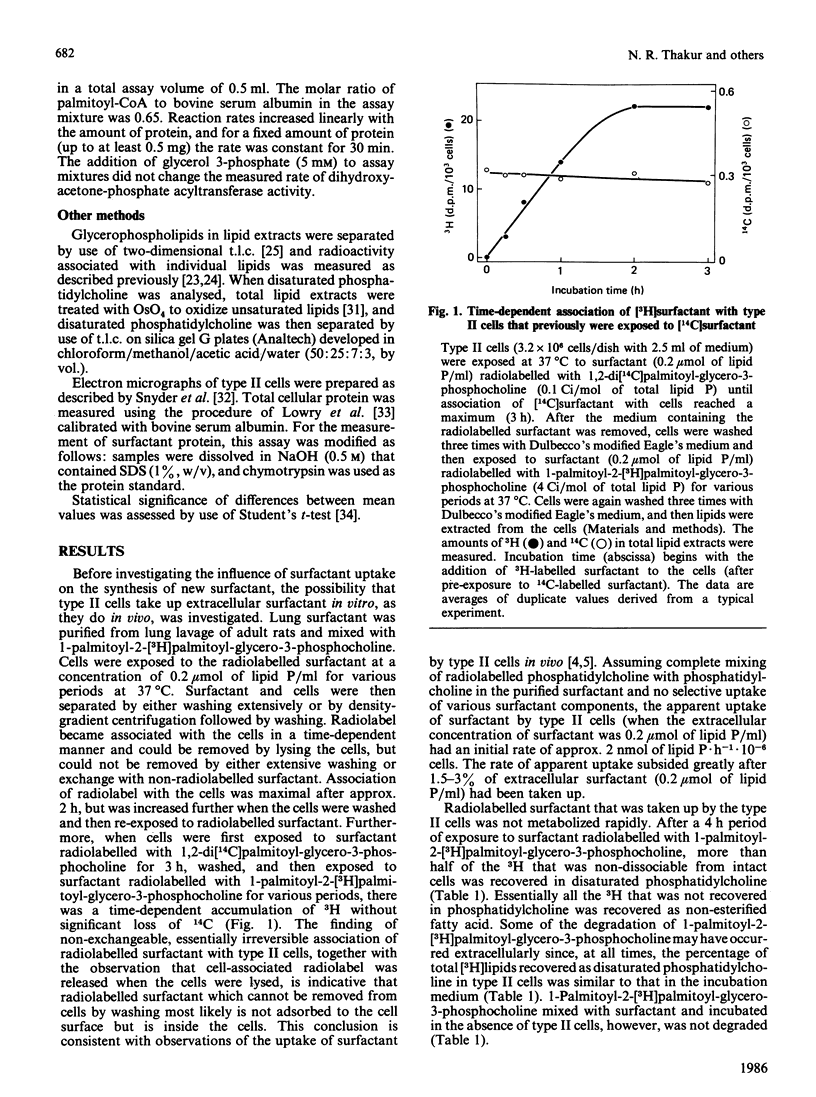
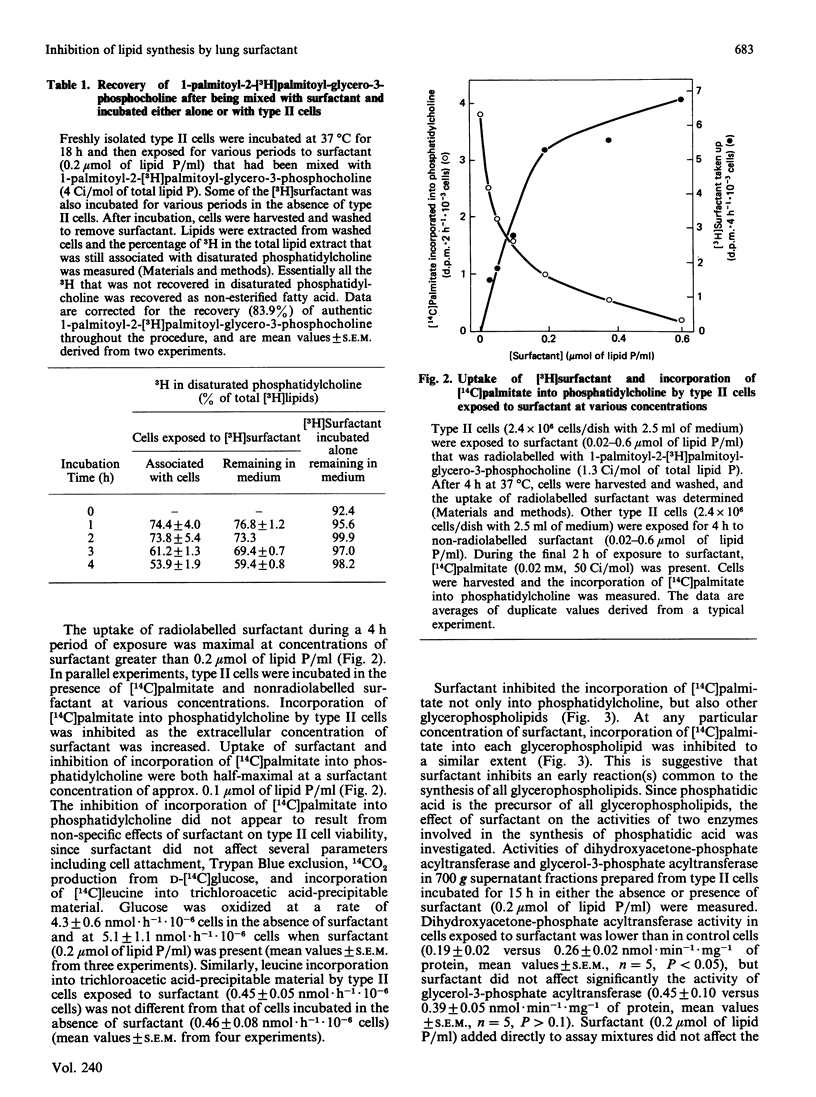
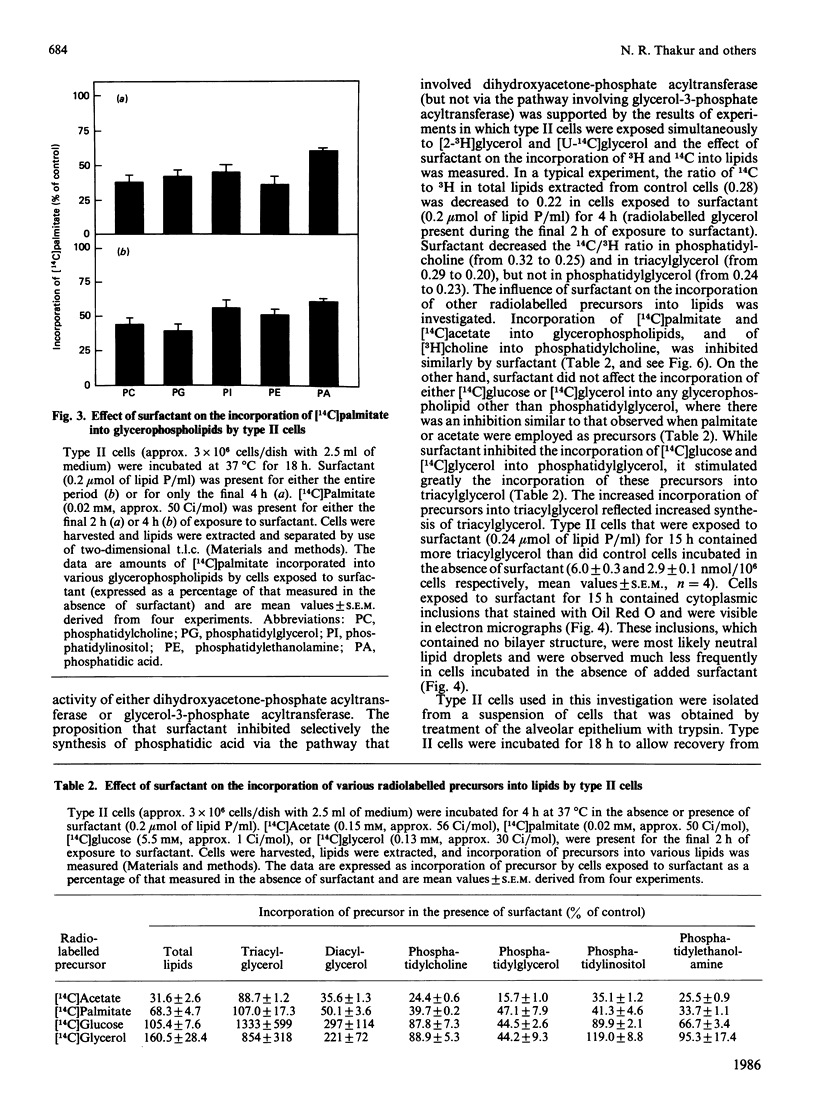



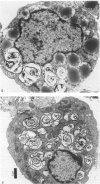
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVERY M. E., MEAD J. Surface properties in relation to atelectasis and hyaline membrane disease. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 May;97(5 Pt 1):517–523. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1959.02070010519001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anceschi M. M., Di Renzo G. C., Venincasa M. D., Bleasdale J. E. The choline-depleted type II pneumonocyte. A model for investigating the synthesis of surfactant lipids. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):253–262. doi: 10.1042/bj2240253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleasdale J. E., Thakur N. R., Rader G. R., Tesan M. Cytidine monophosphate-dependent synthesis of phosphatidylglycerol in permeabilized type II pneumonocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 1;232(2):539–545. doi: 10.1042/bj2320539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleasdale J. E., Tyler N. E., Busch F. N., Quirk J. G. The influence of myo-inositol on phosphatidylglycerol synthesis by rat type II pneumonocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):811–818. doi: 10.1042/bj2120811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleasdale J. E., Tyler N. E., Snyder J. M. Subcellular sites of synthesis of phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylinositol in type II pneumonocytes. Lung. 1985;163(6):345–359. doi: 10.1007/BF02713835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleasdale J. E., Wallis P., MacDonald P. C., Johnston J. M. Characterization of the forward and reverse reactions catalyzed by CDP-diacylglycerol:inositol transferase in rabbit lung tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 26;575(1):135–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casola P. G., Possmayer F. Separation and characterization of the membrane-bound and aqueously dispersed phosphatidate phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase activities in rat lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 22;664(2):298–315. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claypool W. D., Wang D. L., Chander A., Fisher A. B. An ethanol/ether soluble apoprotein from rat lung surfactant augments liposome uptake by isolated granular pneumocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI111483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declercq P. E., Haagsman H. P., Van Veldhoven P., Debeer L. J., Van Golde L. M., Mannaerts G. P. Rat liver dihydroxyacetone-phosphate acyltransferases and their contribution to glycerolipid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9064–9075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Geppert E. F., Williams M. C., Greenleaf R. D., Mason R. J. Metabolic properties and ultrastructure of alveolar type II cells isolated with elastase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 23;618(3):510–523. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein J. N., Mavis R. D. Biochemical evidence for internal proteolytic damage during isolation of type II alveolar epithelial cells. Lung. 1979;156(4):243–254. doi: 10.1007/BF02714018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger K., Gallagher M. L., Hedley-Whyte J. Cellular distribution and clearance of aerosolized dipalmitoyl lecithin. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Nov;39(5):759–766. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.5.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerschenson L. E., Okigaki T., Andersson M., Molson J., Davidson M. B. Fine structural and growth characteristics of cultured rat liver cells. Insulin effects. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Mar;71(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giard D. J., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J., Arnstein P., Kersey J. H., Dosik H., Parks W. P. In vitro cultivation of human tumors: establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1417–1423. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil J., Weibel E. R. Improvements in demonstration of lining layer of lung alveoli by electron microscopy. Respir Physiol. 1969 Dec;8(1):13–36. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(69)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilfillan A. M., Chu A. J., Rooney S. A. Stimulation of phosphatidylcholine synthesis by exogenous phosphatidylglycerol in primary cultures of type II pneumocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 6;794(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilfillan A. M., Smart D. A., Rooney S. A. Phosphatidylglycerol stimulates cholinephosphate cytidylyltransferase activity and phosphatidylcholine synthesis in type II pneumocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 14;835(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman M., Epstein B. L., Gluck L. Analysis of labeling and clearance of lung surfactant phospholipids in rabbit. Evidence of bidirectional surfactant flux between lamellar bodies and alveolar lavage. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):742–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI110310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman M., Merritt T. A., Schneider H., Epstein B. L., Mannino F., Edwards D. K., Gluck L. Isolation of human surfactant from amniotic fluid and a pilot study of its efficacy in respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1983 Apr;71(4):473–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Jobe A., Duane G. Liposomes of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine associate with natural surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 9;835(2):352–359. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90291-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Jobe A., Glatz T. Surface activity following natural surfactant treatment in premature lambs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Aug;51(2):306–312. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.2.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs H., Jobe A., Ikegami M., Conaway D. The significance of reutilization of surfactant phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4159–4165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs H., Jobe A., Ikegami M., Miller D., Jones S. Reutilization of phosphatidylcholine analogues by the pulmonary surfactant system. The lack of specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 18;793(2):300–309. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90333-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katyal S. L., Estes L. W., Lombardi B. Method for the isolation of surfactant from homogenates and lavages of lung of adult, newborn, and fetal rats. Lab Invest. 1977 Jun;36(6):585–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Klass D. J., Gikas E. G., Clements J. A. Isolation of apoproteins from canine surface active material. Am J Physiol. 1973 Apr;224(4):788–795. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.4.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Martin H. Intracellular metabolism of the apoproteins of pulmonary surfactant in rat lung. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 May;48(5):812–820. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Martin H., Mitts D., Holmstrom F. M. Metabolism of the apoproteins in pulmonary surfactant. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Apr;42(4):483–491. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.42.4.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magoon M. W., Wright J. R., Baritussio A., Williams M. C., Goerke J., Benson B. J., Hamilton R. L., Clements J. A. Subfractionation of lung surfactant. Implications for metabolism and surface activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 7;750(1):18–31. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Nellenbogen J., Clements J. A. Isolation of disaturated phosphatidylcholine with osmium tetroxide. J Lipid Res. 1976 May;17(3):281–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Van Keuren M. L. Silver staining methods for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:230–239. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles P. R., Castranova V., Bowman L. Catabolism of rat surfactant disaturated phosphatidylcholines during incubation of alveolar lavage materials in vitro at 37 degrees C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 22;836(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90217-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles P. R., Wright J. R., Bowman L., Castranova V. Incorporation of [3H]palmitate into disaturated phosphatidylcholines in alveolar type II cells isolated by centrifugal elutriation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 29;753(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90104-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo G. A., Nimmo H. G. Studies of rat adipose-tissue microsomal glycerol phosphate acyltransferase. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):101–108. doi: 10.1042/bj2240101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita J. R., Sagawa N., Casey M. L., Snyder J. M. A comparison of human amnion tissue and amnion cells in primary culture by morphological and biochemical criteria. In Vitro. 1983 Feb;19(2):117–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02621895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phizackerley P. J., Town M. H., Newman G. E. Hydrophobic proteins of lamellated osmiophilic bodies isolated from pig lung. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):731–736. doi: 10.1042/bj1830731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed B. C., Lane M. D. Expression of insulin receptors during preadipocyte differentiation. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1980;18:97–117. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(80)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed B. C. Metabolism of covalent receptor-insulin complexes by 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Synthesis and use of photosensitive insulin analogs to study insulin receptor metabolism in cell culture. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4424–4433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. M., Mendelson C. R., Johnston J. M. The effect of cortisol on rabbit fetal lung maturation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1981 Jul 15;85(1):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesan M., Anceschi M. M., Bleasdale J. E. Regulation of CTP: phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase activity in type II pneumonocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):705–713. doi: 10.1042/bj2320705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton P. A., Possmayer F. The role of Mg2+-dependent phosphatidate phosphohydrolase in pulmonary glycerolipid biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 6;796(3):364–372. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. T., Damm D., Miller J., Spratt K., Schilling J., Hawgood S., Benson B., Cordell B. Isolation and characterization of the human pulmonary surfactant apoprotein gene. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):361–363. doi: 10.1038/317361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. C. Uptake of lectins by pulmonary alveolar type II cells: subsequent deposition into lamellar bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yavin E., Zutra A. Separation and analysis of 32P-labeled phospholipids by a simple and rapid thin-layer chromatographic procedure and its application to cultured neuroblastoma cells. Anal Biochem. 1977 Jun;80(2):430–437. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90665-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]