Abstract
The application of modern biochemical techniques has led to a rapid improvement in our knowledge of the molecular biology of CMV. Several coding regions of the DNA genome have been identified with certainty and major virus-coded proteins have been given provisional names. The cascade expression of the CMV genome has been shown to be controlled by mechanisms similar to those found in other herpes viruses, together with novel post-transcriptional controls which remain to be defined. The control of CMV replication by the host involves both non-specific and specific defence mechanisms. The induction of natural killer cells and interferon early after CMV infection appears to be the most important aspects of the non-specific host defence against the virus. The cell-mediated immune response, in particular the generation of Tc cells against CMV early antigens, is probably the most important facet of the specific immune defence against CMV. When intact these defence mechanisms appear to be efficient in restricting viral replication; however, when such immunity is compromised, the balance rapidly swings in favour of the virus. As our understanding of the interaction between the host and the virus increases, it may be possible to redress the balance in such cases in favour of the host.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J. E., Shellam G. R., Grundy J. E. Effect of murine cytomegalovirus infection on mitogen responses in genetically resistant and susceptible mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):235–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.235-242.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders D. G., Irmiere A., Gibson W. Identification and characterization of a major early cytomegalovirus DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):253–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.253-262.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araullo-Cruz T. P., Ho M., Armstrong J. A. Protective effect of early serum from mice after cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):840–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.840-842.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale J. F., Jr, O'Neil M. E., Greiner T. The interaction of murine cytomegalovirus with murine neutrophils: effect on migratory and phagocytic activities. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Dec;38(6):723–734. doi: 10.1002/jlb.38.6.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft G. J., Shellam G. R., Chalmer J. E. Genetic influences on the augmentation of natural killer (NK) cells during murine cytomegalovirus infection: correlation with patterns of resistance. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):988–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomaeus W. N., Shellam G. R., Allan J. E., Reed W. D., Joske R. A. Autoantibodies to liver-specific lipoprotein following hepatitis induced by mouse cytomegalovirus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Apr;52(1):89–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklock H. A., Griffiths P., Stirk P., Prentice H. G. Specific hyperimmune globulin for cytomegalovirus pneumonitis. Lancet. 1985 Jul 20;2(8447):152–153. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton R. A., Tevethia M. J. Immunoprecipitation of virus-specific immediate-early and early polypeptides from cells lytically infected with human cytomegalovirus strain AD 169. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):262–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90631-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldogh I., Gönczöl E., Gärtner L., Váczi G. Expression of the human cytomegalovirus genome in mouse cells and in human-mouse heterokaryons. Arch Virol. 1977;53(1-2):101–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01314851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booss J., Wheelock E. F. Correlation of survival from murine cytomegalovirus infection with spleen cell responsiveness to Concanavallin A. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jun;149(2):443–445. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borysiewicz L. K., Graham S., Sissons J. G. Human natural killer cell lysis of virus-infected cells. Relationship to expression of the transferrin receptor. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Apr;16(4):405–411. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borysiewicz L. K., Morris S., Page J. D., Sissons J. G. Human cytomegalovirus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes: requirements for in vitro generation and specificity. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Oct;13(10):804–809. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830131005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borysiewicz L. K., Rodgers B., Morris S., Graham S., Sissons J. G. Lysis of human cytomegalovirus infected fibroblasts by natural killer cells: demonstration of an interferon-independent component requiring expression of early viral proteins and characterization of effector cells. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2695–2701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britt W. J., Auger D. Synthesis and processing of the envelope gp55-116 complex of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):185–191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.185-191.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britt W. J. Neutralizing antibodies detect a disulfide-linked glycoprotein complex within the envelope of human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski J. F., Warner J. F., Dennert G., Welsh R. M. Adoptive transfer studies demonstrating the antiviral effect of natural killer cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):40–52. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski J. F., Welsh R. M. Inability of interferon to protect virus-infected cells against lysis by natural killer (NK) cells correlates with NK cell-mediated antiviral effects in vivo. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3537–3541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski J. F., Woda B. A., Welsh R. M. Pathogenesis of murine cytomegalovirus infection in natural killer cell-depleted mice. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):119–128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.119-128.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. M., Preston C. M. Comparison of the immediate early polypeptides of human cytomegalovirus isolates. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jun;54(Pt 2):421–424. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-2-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney W. P., Hirsch M. S. Mechanisms of immunosuppression in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. II. Virus-monocyte interactions. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):47–54. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmer J. E., Mackenzie J. S., Stanley N. F. Resistance to murine cytomegalovirus linked to the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):107–114. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman S. H., Rubin R. H., Stewart J. A., Tolkoff-Rubin N. E., Cosimi A. B., Cantell K., Gilbert J., Winkle S., Herrin J. T., Black P. H. Controlled clinical trial of prophylactic human-leukocyte interferon in renal transplantation. Effects on cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus infections. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jun 14;300(24):1345–1349. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197906143002401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba S., Striker R. L., Jr, Benyesh-Melnick M. Microculture plaque assay for human and simian cytomegaloviruses. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Apr;23(4):780–783. doi: 10.1128/am.23.4.780-783.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua C. C., Carter T. H., St Jeor S. Transcription of the human cytomegalovirus genome in productively infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1981 Sep;56(Pt 1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-56-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer N. E., Cossen C. K., Shell G. R., Pereira L. Antibody response to cytomegalovirus polypeptides captured by monoclonal antibodies on the solid phase in enzyme immunoassays. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):517–521. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.517-521.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz J. R., Dammin G. J., Waner J. L. Protective effect of low-dose interferon against neonatal murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):332–342. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.332-342.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
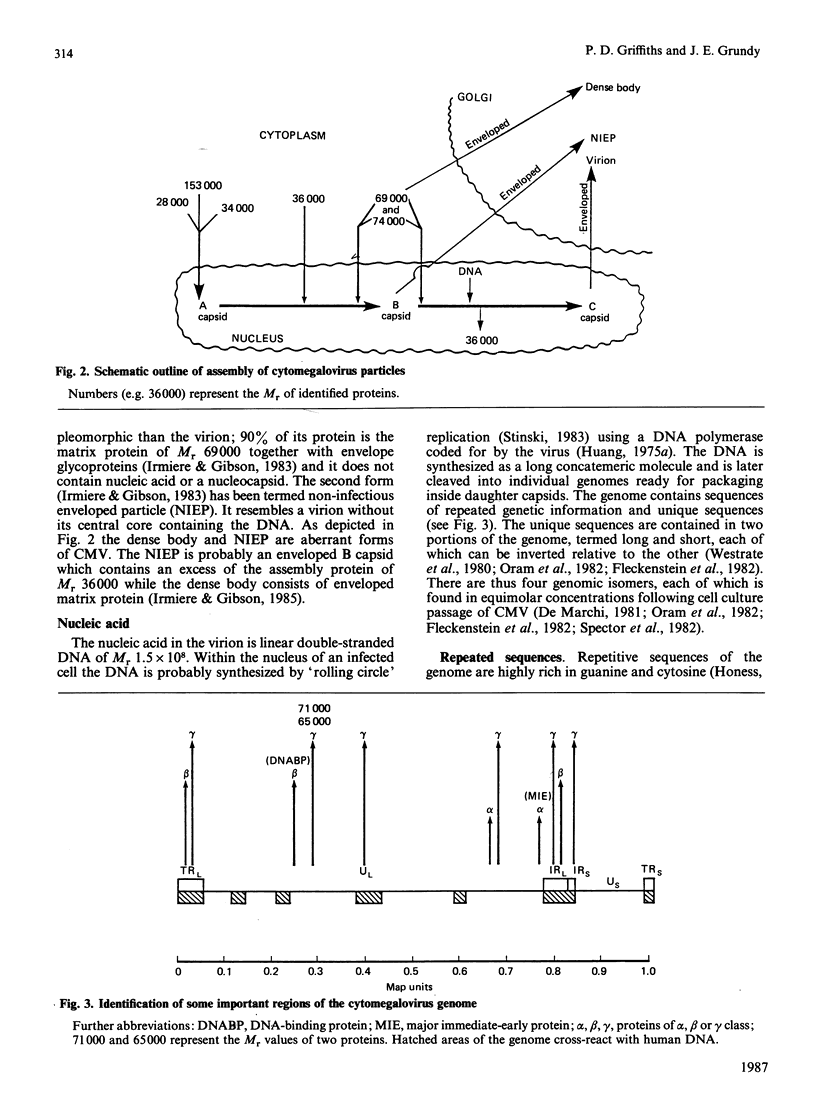
- DeMarchi J. M. Correlation between stimulation of host cell DNA synthesis by human cytomegalovirus and lack of expression of a subset of early virus genes. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):274–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M. Post-transcriptional control of human cytomegalovirus gene expression. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):390–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M., Schmidt C. A., Kaplan A. S. Patterns of transcription of human cytomegalovirus in permissively infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):277–286. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.277-286.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demarchi J. M. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: restriction enzyme cleavage maps and map locations for immediate-early, early, and late RNAs. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diosi P., Moldovan E., Tomescu N. Latent cytomegalovirus infection in blood donors. Br Med J. 1969 Dec 13;4(5684):660–662. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5684.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn L., Ost A. Cytomegalovirus infection of human blood cells. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):207–214. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar G. H., Oram J. D. Characterization of the human cytomegalovirus envelope glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1984 Nov;65(Pt 11):1991–2001. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-11-1991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Honess R. W., Heiner D. C., Heine J. W., Jr, Murnane J., Wallace R., Guze L. B. Cytomegalovirus proteins. I. Polypeptides of virions and dense bodies. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):243–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.243-254.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleckenstein B., Müller I., Collins J. Cloning of the complete human cytomegalovirus genome in cosmids. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman S. J., Zaia J. A., Clark B. R., Wright C. L., Mills B. J., Pottathil R., Racklin B. C., Gallagher M. T., Welte K., Blume K. G. A 64,000 dalton matrix protein of human cytomegalovirus induces in vitro immune responses similar to those of whole viral antigen. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3391–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett H. M. Isolation of human cytomegalovirus from peripheral blood T cells of renal transplant patients. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Jan;99(1):92–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett A. J., Warren D. E. A simple technique for endonuclease mapping of cytomegaloviruses. J Virol Methods. 1985 Mar;10(3):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Leach F. S., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus late gene expression: gamma genes are controlled by posttranscriptional events. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):864–874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.864-874.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehrz R. C., Rutzick S. R. Cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific lysis of CMV-infected target cells can be mediated by both NK-like and virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jul;61(1):80–89. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Immediate-early proteins of human cytomegalovirus strains AD 169, Davis, and Towne differ in electrophoretic mobility. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90641-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Protein counterparts of human and simian cytomegaloviruses. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):391–406. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J. Cytomegalovirus infections following renal transplantation. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1151–1178. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham B. J., Minamishima Y., Dresman G. R., Haines H. G., Benyesh-Melnick M. Complement-requiring neutralizing antibodies in hyperimmune sera to human cytomegaloviruses. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1618–1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths P. D. The presumptive diagnosis of primary cytomegalovirus infection in early pregnancy by means of a radioimmunoassay for specific-IgM antibodies. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1981 Jun;88(6):582–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1981.tb01212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths P., Baboonian C., Ashby D. The demographic characteristics of pregnant women infected with cytomegalovirus. Int J Epidemiol. 1985 Sep;14(3):447–452. doi: 10.1093/ije/14.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy J. E., Mackenzie J. S., Stanley N. F. Influence of H-2 and non-H-2 genes on resistance to murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):277–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.277-286.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy J. E., Melief C. J. Effect of Nu/Nu gene on genetically determined resistance to murine cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jul;61(Pt 50):133–136. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy J. E., Shearer G. M. The effect of cytomegalovirus infection on the host response to foreign and hapten-modified self histocompatibility antigens. Transplantation. 1984 May;37(5):484–490. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198405000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy J. E., Super M., Griffiths P. D. Reinfection of a seropositive allograft recipient by cytomegalovirus from donor kidney. Lancet. 1986 Jan 18;1(8473):159–160. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy J. E., Trapman J., Allan J. E., Shellam G. R., Melief C. J. Evidence for a protective role of interferon in resistance to murine cytomegalovirus and its control by non-H-2-linked genes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):143–150. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.143-150.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSON D., SMITH R. D. INTERFERON PRODUCTION IN VITRO BY CELLS INFECTED WITH THE MURINE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Nov;117:517–520. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett G. B., Shellam G. R. Variation in murine cytomegalovirus replication in fibroblasts from different mouse strains in vitro: correlation with in vivo resistance. J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):39–47. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson D., Smith R. D., Gehrke J. Non-fatal mouse cytomegalovirus hepatitis. Combined morphologic, virologic and immunologic observations. Am J Pathol. 1966 Nov;49(5):871–888. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T., Cosimi A. B., Russell P. S., Delmonico F. L., Tolkoff-Rubin N. E., Herrin J. T., Cantell K., Farrell M. L., Rota T. R. Effects of interferon-alpha on cytomegalovirus reactivation syndromes in renal-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 23;308(25):1489–1493. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306233082501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. Role of specific cytotoxic lymphocytes in cellular immunity against murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):767–776. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.767-776.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W. Herpes simplex and 'the herpes complex': diverse observations and a unifying hypothesis. The eighth Fleming lecture. J Gen Virol. 1984 Dec;65(Pt 12):2077–2107. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-12-2077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Miller J., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus-induced immune suppression. II. Cell-mediated immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):119–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus-induced immune suppression. I. Humoral immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):109–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus. III. Virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1975 Aug;16(2):298–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.2.298-310.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus. IV. Specific inhibition of virus-induced DNA polymerase activity and viral DNA replication by phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1560–1565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1560-1565.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Kilpatrick B. A., Huang Y. T., Pagano J. S. Detection of human cytomegalovirus and analysis of strain variation. Yale J Biol Med. 1976 Mar;49(1):29–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutt-Fletcher L. M., Balachandran N., Elkins M. H. B cell activation by cytomegalovirus. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2171–2176. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irmiere A., Gibson W. Isolation and characterization of a noninfectious virion-like particle released from cells infected with human strains of cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irmiere A., Gibson W. Isolation of human cytomegalovirus intranuclear capsids, characterization of their protein constituents, and demonstration that the B-capsid assembly protein is also abundant in noninfectious enveloped particles. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):277–283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.277-283.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane R. C., Rousseau W. E., Noble G. R., Tegtmeier G. E., Wulff H., Herndon H. B., Chin T. D., Bayer W. L. Cytomegalovirus infection in a volunteer blood donor population. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):719–723. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.719-723.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangro H. O., Griffiths P. D., Huber T. J., Heath R. B. Specific IgM class antibody production following infection with cytomegalovirus. J Med Virol. 1982;10(3):203–212. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890100306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor G. L., Goldberg L. S., Johnson B. L., Jr, Derechin M. M., Barnett E. V. Immunologic abnormalities induced by postperfusion cytomegalovirus infection. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Oct;73(4):553–558. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-4-553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Peitchel R., Goldman J. N., Goldman M. An IgG-Fc receptor induced in cytomegalovirus-infected human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):772–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey D. K., Olsen G. A., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Alteration of host defense mechanisms by murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):754–760. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.754-760.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern E. R., Olsen G. A., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Treatment of a murine cytomegalovirus infection with exogenous interferon, polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid, and polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid-poly-L-lysine complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):344–346. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick B. A., Huang E. S., Pagano J. S. Analysis of cytomegalovirus genomes with restriction endonucleases Hin D III and EcoR-1. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):1095–1105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.1095-1105.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Sapienza V. J., Carp R. I., Moon H. M. Analysis of structural polypeptides of purified human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):604–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.604-611.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landini M. P., Re M. C., Mirolo G., Baldassarri B., La Placa M. Human immune response to cytomegalovirus structural polypeptides studied by immunoblotting. J Med Virol. 1985 Dec;17(4):303–311. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law K. M., Wilton-Smith P., Farrar G. H. A murine monoclonal antibody recognising a single glycoprotein within a human cytomegalovirus virion envelope glycoprotein complex. J Med Virol. 1985 Nov;17(3):255–266. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. D., Keller R. Natural cytotoxicity of murine cytomegalovirus-infected cells mediated by mouse lymphoid cells: role of interferon in the endogenous natural cytotoxicity reaction. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):5–12. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.5-12.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Wilton J. M., Shillitoe E. J. Immunological basis for latency, recurrences and putative oncogenicity of herpes simplex virus. Lancet. 1975 Jul 12;2(7924):60–62. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90499-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley M. D., Torpey D. J., 3rd, Rinaldo C. R., Jr HLA-DR-restricted cytotoxicity of cytomegalovirus-infected monocytes mediated by Leu-3-positive T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):3045–3051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh L., Hudson J. B. Immunosuppressive effect of murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):54–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.54-60.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., Simmons R. L., Mauer S. M., Najarian J. S., Good R. A., Gentry S. Association of renal allograft rejection with virus infections. Am J Med. 1974 Mar;56(3):280–289. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90609-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher A. M., Reichert C. M., Straus S. E., Longo D. L., Parrillo J., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S., Rook A. H., Manischewitz J. F., Quinnan G. V., Jr Death in the AIDS patient: role of cytomegalovirus. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 8;309(23):1454–1454. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312083092312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackowiak P. A., Marling-Cason M., Smith J. W., Luby J. P. Antibody-mediated bacterial adhesion to cytomegalovirus-induced Fc receptors. Potential relationship to secondary infections complicating herpesvirus infections. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):987–991. doi: 10.1172/JCI111324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. H., Staprans S. I., Spector D. H. Analysis of the major transcripts encoded by the long repeat of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):711–718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.711-718.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeating J. A., Grundy J. E., Varghese Z., Griffiths P. D. Detection of cytomegalovirus by ELISA in urine samples is inhibited by beta 2 microglobulin. J Med Virol. 1986 Apr;18(4):341–348. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890180407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. D., McGuffin R. W., Bryson Y. J., Cantell K., Thomas E. D. Treatment of cytomegalovirus pneumonia after marrow transplant with combined vidarabine and human leukocyte interferon. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jul;146(1):80–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson-Fiske S., Horodniceanu F., Guillon J. C. Immediate early antigens in human cytomegalovirus infected cells. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):615–617. doi: 10.1038/270615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovic R., Werch J., South M. A., Benyesh-Melnick M. Incidence of cytomegaloviremia in blood-bank donors and in infants with congenital cytomegalic inclusion disease. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):45–50. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.45-50.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Pereira L., Michael N. Precise localization of genes on large animal virus genomes: use of lambda gt11 and monoclonal antibodies to map the gene for a cytomegalovirus protein family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1266–1270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Post L. E., Roizman B. Molecular engineering of the herpes simplex virus genome: insertion of a second L-S junction into the genome causes additional genome inversions. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):243–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Structure and role of the herpes simplex virus DNA termini in inversion, circularization and generation of virion DNA. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90408-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Stinski M. F. Persistence of the cytomegalovirus genome in human cells. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):761–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.761-775.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak B., Gmeiner A., Sarnow P., Levine A. J., Fleckenstein B. Physical mapping of human cytomegalovirus genes: identification of DNA sequences coding for a virion phosphoprotein of 71 kDa and a viral 65-kDa polypeptide. Virology. 1984 Apr 15;134(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90275-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak B., Sullivan C., Sarnow P., Thomas R., Bricout F., Nicolas J. C., Fleckenstein B., Levine A. J. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies and polyclonal immune sera directed against human cytomegalovirus virion proteins. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):325–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie H. K., Easton J. M., Ablashi D. V., Baron S. Murine cytomegalovirus: induction of and sensitivity to interferon in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1012–1017. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1012-1017.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. D., Downing R. G., Akrigg A., Dollery A. A., Duggleby C. J., Wilkinson G. W., Greenaway P. J. Use of recombinant plasmids to investigate the structure of the human cytomegalovirus genome. J Gen Virol. 1982 Mar;59(Pt 1):111–129. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Blazkovec A. A., Walker D. L. Immunosuppression during acute murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):835–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Medearis D. N., Jr Studies of relationship between mouse cytomegalovirus and interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Mar;121(3):819–824. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Medearis D. N., Jr Suppression of interferon and antibody and multiplication of Newcastle disease virus in cytomegalovirus infected mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Feb;124(2):347–353. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Glycoprotein gE of herpes simplex virus type 1: effects of anti-gE on virion infectivity and on virus-induced fc-binding receptors. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):129–136. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.129-136.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass R. F., Griffiths P. D., August A. M. Antibody response to cytomegalovirus after renal transplantation: comparison of patients with primary and recurrent infections. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):40–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R., Fiala M., Berne V., Chatterjee N. Cytomegalovirus infections in renal allograft recipients: correlative studies with histocompatibility antigens. N Z Med J. 1978 Jun 14;87(613):393–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peckham C. S., Chin K. S., Coleman J. C., Henderson K., Hurley R., Preece P. M. Cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy: preliminary findings from a prospective study. Lancet. 1983 Jun 18;1(8338):1352–1355. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K., Mounts P., Hayward G. S. Homology between mammalian cell DNA sequences and human herpesvirus genomes detected by a hybridization procedure with high-complexity probe. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90406-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Hoffman M., Gallo D., Cremer N. Monoclonal antibodies to human cytomegalovirus: three surface membrane proteins with unique immunological and electrophoretic properties specify cross-reactive determinants. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):924–932. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.924-932.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Hoffman M., Tatsuno M., Dondero D. Polymorphism of human cytomegalovirus glycoproteins characterized by monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90331-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Stagno S., Hoffman M., Volanakis J. E. Cytomegalovirus-infected cell polypeptides immune-precipitated by sera from children with congenital and perinatal infections. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):100–108. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.100-108.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira R. S., James D. C., Stern H. Correlation between cytomegalovirus infection and HLA-BW15. Br Med J. 1978 Jul 8;2(6130):126–126. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6130.126-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin S. A., Smiley M. L., Friedman H. M., Starr S. E., Fleisher G. R., Wlodaver C., Dafoe D. C., Friedman A. D., Grossman R. A., Barker C. F. Towne-vaccine-induced prevention of cytomegalovirus disease after renal transplants. Lancet. 1984 Mar 10;1(8376):528–530. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90930-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postic B., Dowling J. N. Susceptibility of clinical isolates of cytomegalovirus to human interferon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):656–660. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Jr, Kirmani N., Esber E., Saral R., Manischewitz J. F., Rogers J. L., Rook A. H., Santos G. W., Burns W. H. HLA-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte and nonthymic cytotoxic lymphocyte responses to cytomegalovirus infection of bone marrow transplant recipients. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):2036–2041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Manischewitz J. E., Ennis F. A. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to murine cytomegalovirus infection. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):541–543. doi: 10.1038/273541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Manischewitz J. E. The role of natural killer cells and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity during murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1549–1554. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman A. A., Teschner M., Sethi K. K., Brandis H. Appearance of IgG (Fc) receptor(s) on cultured human fibroblasts infected with human cytomegalovirus. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L., Mullenax J., Nelson M., Merigan T. C. Human cytomegalovirus polypeptides stimulate neutralizing antibody in vivo. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddehase M. J., Koszinowski U. H. Significance of herpesvirus immediate early gene expression in cellular immunity to cytomegalovirus infection. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):369–371. doi: 10.1038/312369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. P., Schrier R. D., Oldstone M. B. Cytomegalovirus infects human lymphocytes and monocytes: virus expression is restricted to immediate-early gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6134–6138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Carney W. P., Richter B. S., Black P. H., Hirsch M. S. Mechanisms of immunosuppression in cytomegaloviral mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):488–495. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers B. C., Scott D. M., Mundin J., Sissons J. G. Monocyte-derived inhibitor of interleukin 1 induced by human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):527–532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.527-532.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook A. H., Quinnan G. V., Jr, Frederick W. J., Manischewitz J. F., Kirmani N., Dantzler T., Lee B. B., Currier C. B., Jr Importance of cytotoxic lymphocytes during cytomegalovirus infection in renal transplant recipients. Am J Med. 1984 Mar;76(3):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90655-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell B. B., Betts R. F. Physical properties of cytomegalorvirus immune complexes prepared with IgG neutralizing antibody, anti-IgG, and complement. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüger R., Bornkamm G. W., Fleckenstein B. Human cytomegalovirus DNA sequences with homologies to the cellular genome. J Gen Virol. 1984 Aug;65(Pt 8):1351–1364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-8-1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma S., Furukawa T., Plotkin S. A. The characterization of IgG receptor induced by human cytomegalovirus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jun;155(2):168–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-155-39767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov B., Naggan L., Rosenzveig R., Katz S., Haikin H., Sarov I. Prevalence of antibodies to human cytomegalovirus in urban, kibbutz, and Bedouin children in southern Israel. J Med Virol. 1982;10(3):195–201. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890100305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Abady I. The morphogenesis of human cytomegalovirus. Isolation and polypeptide characterization of cytomegalovirions and dense bodies. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):464–473. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Müller-Lantzsch N., Peteler G. Human immune response to proteins of cytomegalovirus. Intervirology. 1980;13(3):154–161. doi: 10.1159/000149120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Detection of human cytomegalovirus in peripheral blood lymphocytes in a natural infection. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1048–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2997930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Rice G. P., Oldstone M. B. Suppression of natural killer cell activity and T cell proliferation by fresh isolates of human cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1084–1091. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selgrade M. K., Ahmed A., Sell K. W., Gershwin M. E., Steinberg A. D. Effect of murine cytomegalovirus on the in vitro responses of T and B cells to mitogens. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1459–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Brandis H. Induction of virus specific and H-2 restricted cytotoxic T cells by UV inactivated murine cytomegalovirus. Arch Virol. 1979;60(3-4):227–238. doi: 10.1007/BF01317494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanley J. D., Jordan M. C., Stevens J. G. Modification by adoptive humoral immunity of murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):231–237. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanley J. D., Pesanti E. L. Replication of murine cytomegalovirus in lung macrophages: effect of phagocytosis of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1152–1159. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1152-1159.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellam G. R., Allan J. E., Papadimitriou J. M., Bancroft G. J. Increased susceptibility to cytomegalovirus infection in beige mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5104–5108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellam G. R., Flexman J. P., Farrell H. E., Papadimitriou J. M. The genetic background modulates the effect of the beige gene on susceptibility to cytomegalovirus infection in mice. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(2):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellam G. R., Flexman J. P. Genetically determined resistance to murine cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus in newborn mice. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):152–156. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.152-156.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons R. L., Lopez C., Balfour H., Jr, Kalis J., Rattazzi L. C., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus: Clinical virological correlations in renal transplant recipients. Ann Surg. 1974 Oct;180(4):623–634. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197410000-00028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinickas V. G., Ashman R. B., Blanden R. V. The cytotoxic response to murine cytomegalovirus. I. Parameters in vivo. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):747–755. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., De Harven E. Herpes simplex virus and human cytomegalovirus replication in WI-38 cells. I. Sequence of viral replication. J Virol. 1973 Oct;12(4):919–930. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.4.919-930.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus gene expression: alpha and beta promoters are trans activated by viral functions in permissive human fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.135-143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. The alpha sequence of the cytomegalovirus genome functions as a cleavage/packaging signal for herpes simplex virus defective genomes. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):817–824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.817-824.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Hock L., Tamashiro J. C. Cleavage maps for human cytomegalovirus DNA strain AD169 for restriction endonucleases EcoRI, BglII, and HindIII. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):558–582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.558-582.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Vacquier J. P. Human cytomegalovirus (strain AD169) contains sequences related to the avian retrovirus oncogene v-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3889–3893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. A., Neuman T. R., Hirata K. K. Rapid determination of molecular relatedness of isolates of human cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):755–759. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Pass R. F., Dworsky M. E., Alford C. A. Congenital and perinatal cytomegalovirus infections. Semin Perinatol. 1983 Jan;7(1):31–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Pass R. F., Dworsky M. E., Henderson R. E., Moore E. G., Walton P. D., Alford C. A. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: The relative importance of primary and recurrent maternal infection. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 22;306(16):945–949. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204223061601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Reynolds D. W., Huang E. S., Thames S. D., Smith R. J., Alford C. A. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 2;296(22):1254–1258. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706022962203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Reynolds D. W., Pass R. F., Alford C. A. Breast milk and the risk of cytomegalovirus infection. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 8;302(19):1073–1076. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005083021908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder H., Ehrensberger A. Microneutalization of cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):102–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr S. E., Allison A. C. Role of T lymphocytes in recovery from murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):458–462. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.458-462.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr S. E., Dalton B., Garrabrant T., Paucker K., Plotkin S. A. Lymphocyte blastogenesis and interferon production in adult human leukocyte cultures stimulated with cytomegalovirus antigens. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):17–22. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.17-22.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr S. E., Garrabrant T. Natural killing of cytomegalovirus-infected fibroblasts by human mononuclear leucocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):484–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern H., Tucker S. M. Prospective study of cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy. Br Med J. 1973 May 5;2(5861):268–270. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5861.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Human cytomegalovirus: glycoproteins associated with virions and dense bodies. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):594–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.594-609.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Mocarski E. S., Thomsen D. R. DNA of human cytomegalovirus: size heterogeneity and defectiveness resulting from serial undiluted passage. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):231–239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.231-239.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Mocarski E. S., Thomsen D. R., Urbanowski M. L. Membrane glycoproteins and antigens induced by human cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1979 Apr;43(1):119–129. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Roehr T. J. Activation of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus by cis-acting elements in the promoter-regulatory sequence and by virus-specific trans-acting components. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):431–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.431-441.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A., Kern E. R., Kelsey D. K., Glasgow L. A. Suppressed response to interferon inducation in mice infected with encephalomyocarditis virus, Semliki forest virus, influenza A2 virus, Herpesvirus hominis type 2, or murine cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):540–551. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P., Almeida J. D. Human cytomegalovirus: purification of enveloped virions and dense bodies. J Gen Virol. 1977 Aug;36(2):345–349. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-2-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Chiba S., Chiba Y., Nakao T. Virus excretion and neutralizing antibody response in saliva in human cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):842–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.842-845.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr G. C., Armstrong J. A., Ho M. Production of interferon and serum hyporeactivity factor in mice infected with murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):903–907. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.903-907.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Frenkel N. Replication of herpes simplex virus DNA: localization of replication recognition signals within defective virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S., Jacob R. J., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. II. Size, composition, and arrangement of inverted terminal repetitions. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1487–1497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1487-1497.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Ljungman P., Paulin T., Ringdén O. Enhancive and suppressive effects of cytomegalovirus on human lymphocyte responses in vitro. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):909–913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.909-913.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waner J. L., Hopkins D. R., Weller T. H., Allred E. N. Cervical excretion cytomegalovirus: correlation with secretory and humoral antibody. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):805–809. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waner J. L., Nierenberg J. A. Natural killing (NK) of cytomegalovirus (CMV)-infected fibroblasts: a comparison between two strains of CMV, uninfected fibroblasts, and K562 cells. J Med Virol. 1985 Jul;16(3):233–244. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Stinski M. F. Temporal patterns of human cytomegalovirus transcription: mapping the viral RNAs synthesized at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):462–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.462-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Temporal regulation of human cytomegalovirus transcription at immediate early and early times after infection. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):446–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.446-459.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. G. Problems of infection after bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jun;36(6):683–692. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.6.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westmoreland D., St Jeor S., Rapp F. The development by cytomegalovirus-infected cells of binding affinity for normal human immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1976 Jun;116(6):1566–1570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weststrate M. W., Geelen J. L., van der Noordaa J. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: physical maps for restriction endonucleases BglII, hindIII and XbaI. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jul;49(1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Pollard R. B., Ho W. G., Gallagher J. G., Rasmussen L. E., Huang S. N., Lin C. H., Gossett T. G., Merigan T. C., Gale R. P. Cytomegalovirus immune plasma in bone marrow transplant recipients. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jul;97(1):11–18. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi K., Rapp F. Induction of host DNA synthesis and DNA polymerase by DNA-negative temperature-sensitive mutants of human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):237–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaia J. A., Forman S. J., Ting Y. P., Vanderwal-Urbina E., Blume K. G. Polypeptide-specific antibody response to human cytomegalovirus after infection in bone marrow transplant recipients. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):780–787. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]