Abstract
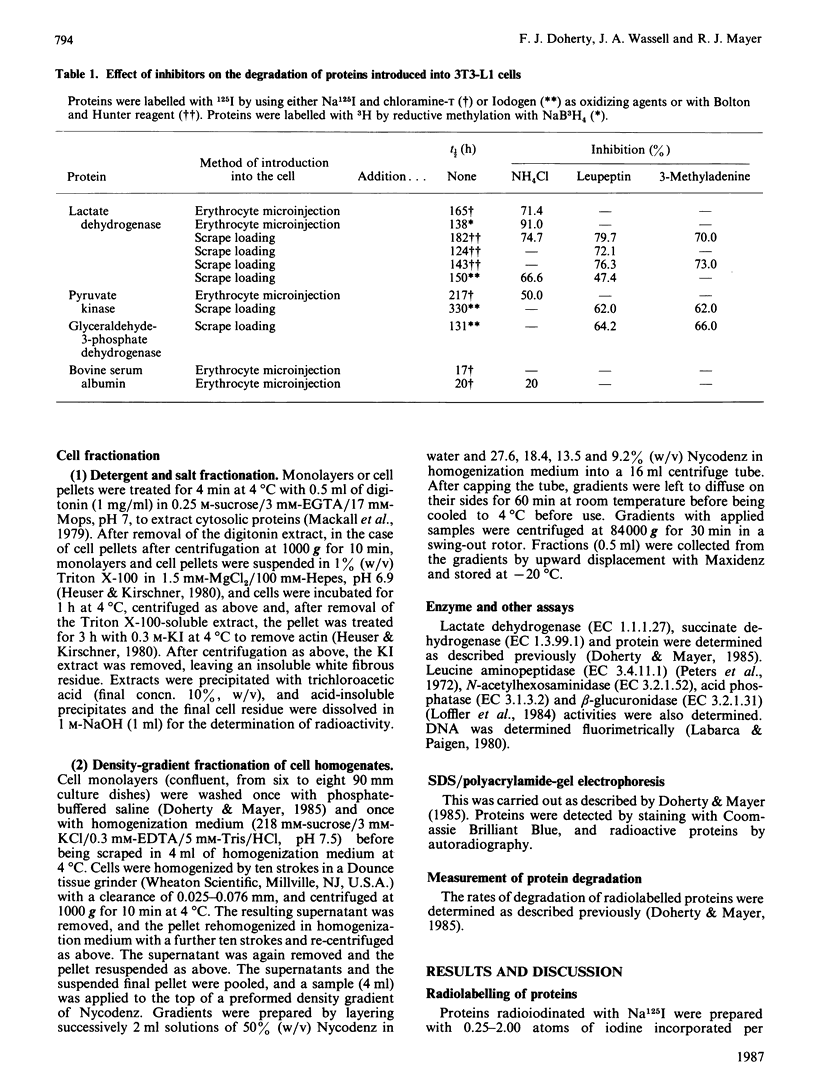
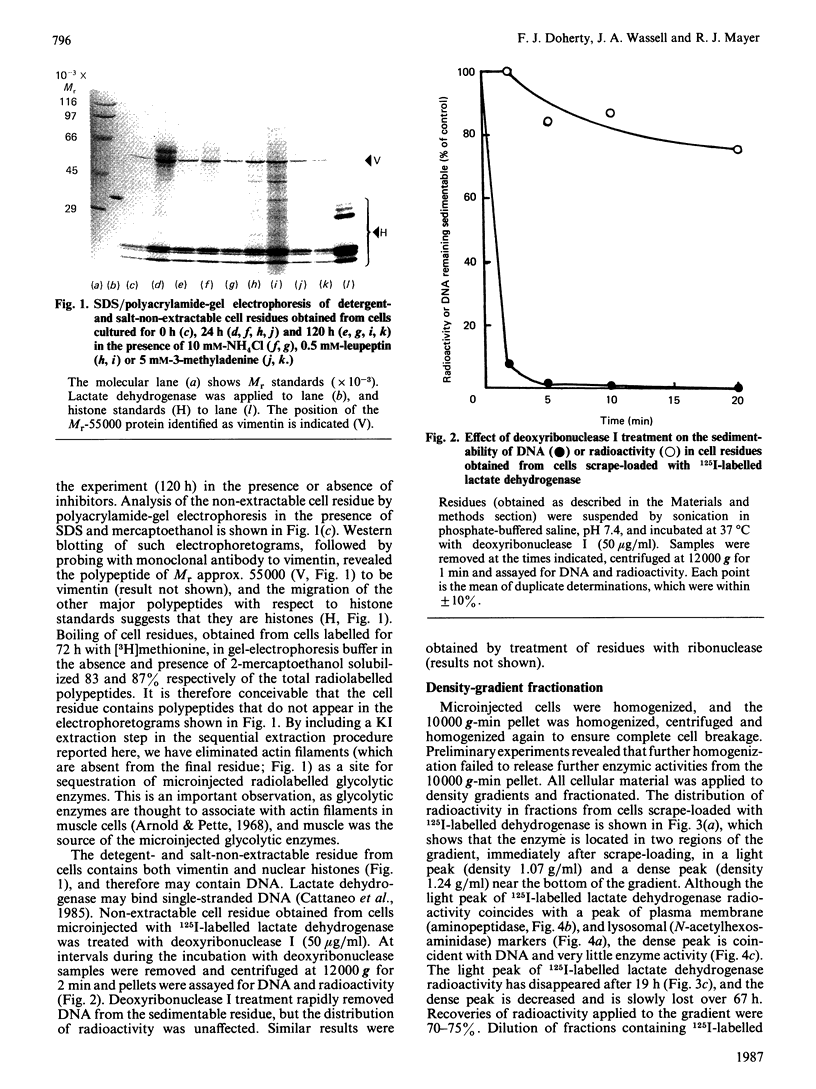
Several glycolytic enzymes (lactate dehydrogenase, pyruvate kinase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) were radiolabelled by [125I]iodination, conjugation with 125I-labelled Bolton & Hunter reagent and reductive [3H]methylation, and their degradative rates after microinjection into 3T3-L1 cells compared with that of the extracellular protein bovine serum albumin. Although the albumin remains largely cytosolic in recipient cells, the glycolytic enzymes rapidly (less than 30 min) become insoluble, as measured by detergent and salt extractions. The microinjected glycolytic enzymes appear to form disulphide-linked aggregates, are found in a cell fraction rich in vimentin-containing intermediate filaments and histones (nuclear-intermediate-filament fraction), and are degraded slowly by a lysosomal mechanism, as judged by the effects of inhibitors (NH4Cl, leupeptin, 3-methyladenine). 125I-labelled bovine serum albumin appears to be degraded rapidly and non-lysosomally. Prolonged treatment (96 h) of cultured cells with leupeptin results in the accumulation of pulse-labelled ([35S]methionine for 24 h) endogenous cell proteins in the detergent-and salt-non-extractable residue, but NH4Cl and 3-methyladenine do not have this effect. The findings are in terms of the interpretation of experiments involving microinjection of proteins to study intracellular protein protein degradation by autophagy.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlberg J., Berkenstam A., Henell F., Glaumann H. Degradation of short and long lived proteins in isolated rat liver lysosomes. Effects of pH, temperature, and proteolytic inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5847–5854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlberg J., Glaumann H. Uptake--microautophagy--and degradation of exogenous proteins by isolated rat liver lysosomes. Effects of pH, ATP, and inhibitors of proteolysis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1985 Feb;42(1):78–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(85)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold H., Pette D. Binding of glycolytic enzymes to structure proteins of the muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Nov;6(2):163–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENESCH R. E., LARDY H. A., BENESCH R. The sulfhydryl groups of crystalline proteins. I. Some albumins, enzymes, and hemoglobins. J Biol Chem. 1955 Oct;216(2):663–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo A., Biocca S., Corvaja N., Calissano P. Nuclear localization of a lactic dehydrogenase with single-stranded DNA-binding properties. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Nov;161(1):130–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90497-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dice J. F., Backer J. M., Miao P., Bourret L., McElligott M. A. Regulation of catabolism of ribonuclease A microinjected into human fibroblasts. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;180:385–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty F. J., Mayer R. J. Degradation of erythrocyte-microinjected and scrape-loaded homologous cytosolic proteins by 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 15;226(3):685–695. doi: 10.1042/bj2260685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl R. T., Billett E. E., Hunneyball I. M., Mayer R. J. Sendai-viral HN and F glycoproteins as probes of plasma-membrane protein catabolism in HTC cells. Studies with fusogenic reconstituted Sendai-viral envelopes. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):801–807. doi: 10.1042/bj2410801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl R. T., Mangiapane E. H., Billett E. E., Mayer R. J. A putative protein-sequestration site involving intermediate filaments for protein degradation by autophagy. Studies with transplanted Sendai-viral envelope proteins in HTC cells. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):809–815. doi: 10.1042/bj2410809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskell M. J., Heinrich P. C., Mayer R. J. Mechanisms of intracellular protein catabolism. Intracellular fate of microinjected polypeptides translated in vitro. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):817–825. doi: 10.1042/bj2410817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendil K. B. Autophagy of metabolically inert substances injected into fibroblasts in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Sep;135(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Kirschner M. W. Filament organization revealed in platinum replicas of freeze-dried cytoskeletons. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):212–234. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliachko O. S., Neifakh A. A. Obnaruzhenie v pecheni krysy kompleksov, soderzhashchikh laktatdegidrogenazu, metodom tsentrifugirovaniia v srede s rastvorennym fermentom. Biokhimiia. 1984 Oct;49(10):1661–1665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löffler B. M., Hesse B., Kunze H. A combined assay of three lysosomal marker enzymes: acid phosphatase, beta-D-glucuronidase, and beta-N-acetyl-D-hexosaminidase. Anal Biochem. 1984 Nov 1;142(2):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90470-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackall J., Meredith M., Lane M. D. A mild procedure for the rapid release of cytoplasmic enzymes from cultured animal cells. Anal Biochem. 1979 May;95(1):270–274. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer R. J., Doherty F. Intracellular protein catabolism: state of the art. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 31;198(2):181–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer R. J., Evans P., Russell S., Amenta J. S. Degradative fate of transplanted proteins. Ciba Found Symp. 1984;103:202–219. doi: 10.1002/9780470720844.ch13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Müller M., De Duve C. Lysosomes of the arterial wall. I. Isolation and subcellular fractionation of cells from normal rabbit aorta. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1117–1139. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Carew T. E., Glass C. K., Green S. R., Taylor C. A., Jr, Attie A. D. A radioiodinated, intracellularly trapped ligand for determining the sites of plasma protein degradation in vivo. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):791–800. doi: 10.1042/bj2120791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M., Chin D., Hough R., McGarry T., Rogers S., Rote K., Wu L. What determines the degradation rate of an injected protein? Ciba Found Symp. 1984;103:181–201. doi: 10.1002/9780470720844.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rote K. V., Rechsteiner M. Degradation of microinjected proteins: effects of lysosomotropic agents and inhibitors of autophagy. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Jul;116(1):103–110. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041160116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]