Abstract
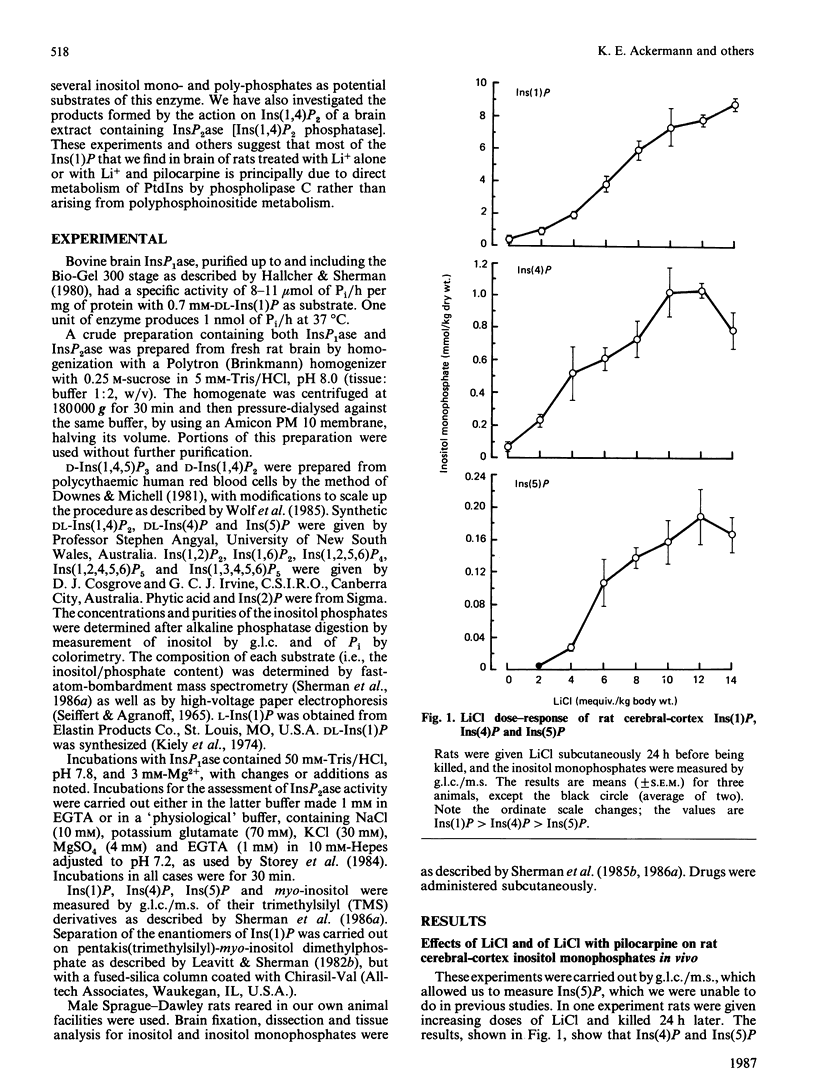
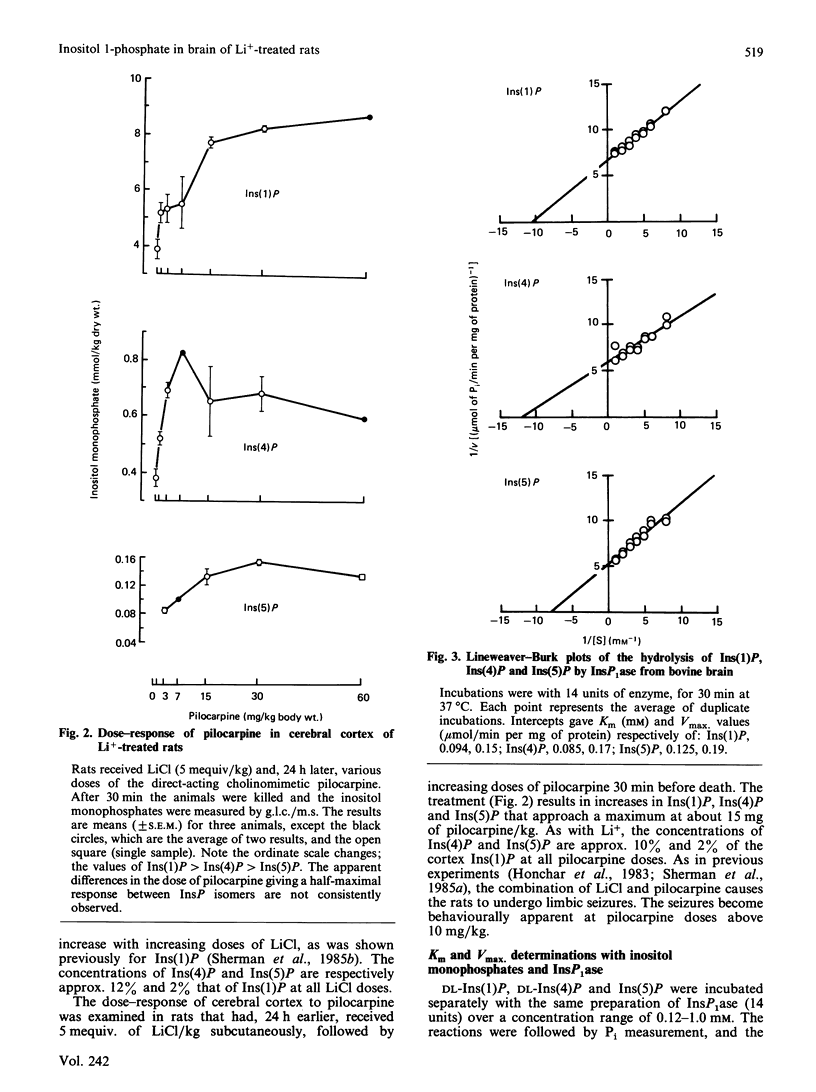
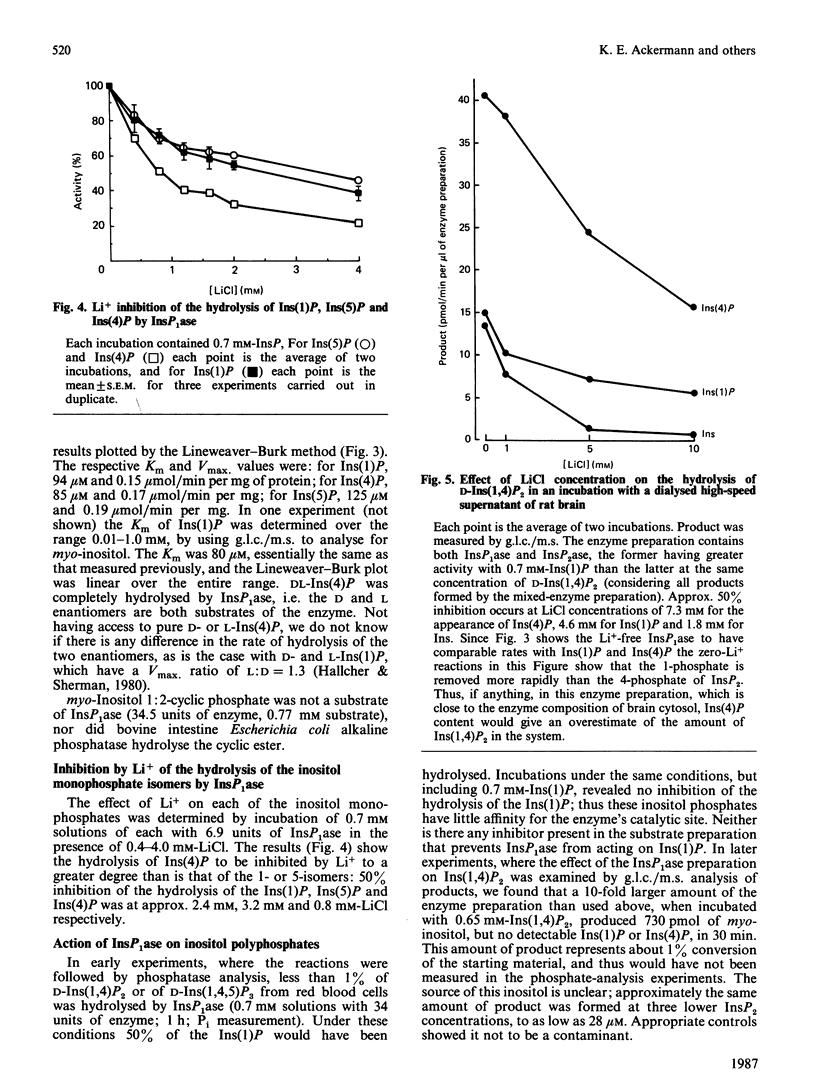
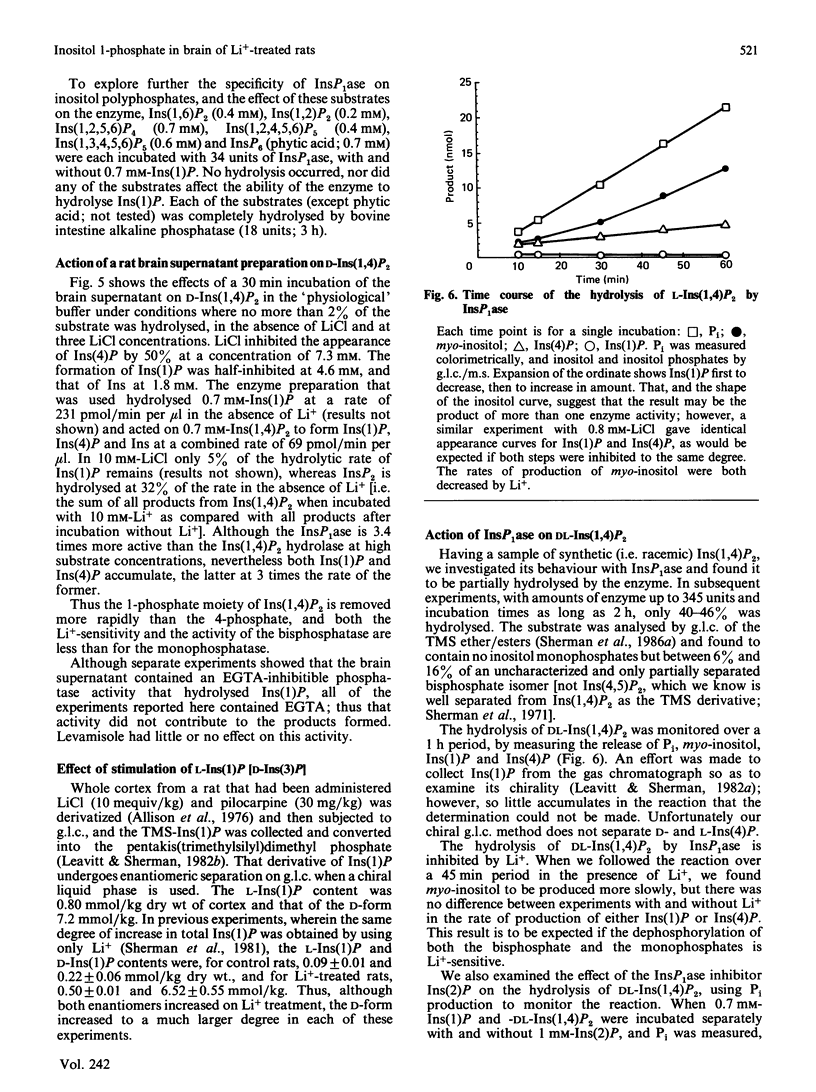
In cerebral cortex of rats treated with increasing doses of LiCl, the relative concentrations of Ins(1)P, Ins(4)P and Ins(5)P (when InsP is a myo-inositol phosphate) are approx. 10:1:0.2 at all doses. In rats treated with LiCl followed by increasing doses of pilocarpine a similar relationship occurs. myo-Inositol-1-phosphatase (InsP1ase) from bovine brain hydrolyses Ins(1)P, Ins(4)P and Ins(5)P at comparable rates, and these substrates have similar Km values. The hydrolysis of Ins(4)P is inhibited by Li+ to a greater degree than is hydrolysis of Ins(1)P and Ins(5)P. D-Ins(1,4,5)P3 and D-Ins(1,4)P2 are neither substrates nor inhibitors of InsP1ase. A dialysed high-speed supernatant of rat brain showed a greater rate of hydrolysis of Ins(1)P than of D-Ins(1,4)P2 and a lower sensitivity of the bisphosphate hydrolysis to LiCl, as compared with the monophosphate. That enzyme preparation produced Ins(4)P at a greater rate than Ins(1)P when D-Ins(1,4)P2 was the substrate. The amount of D-Ins(3)P [i.e. L-Ins(1)P, possibly from D-Ins(1,3,4)P3] is only 11% of that of D-Ins(1)P on stimulation with pilocarpine in the presence of Li+. DL-Ins(1,4)P2 was hydrolysed by InsP1ase to the extent of about 50%; both Ins(4)P and Ins(1)P are products, the former being produced more rapidly than the latter; apparently L-Ins(1,4)P2 is a substrate for InsP1ase. Li+, but not Ins(2)P, inhibited the hydrolysis of L-Ins(1,4)P2. The following were neither substrates nor inhibitors of InsP1ase; Ins(1,6)P2, Ins(1,2)P2, Ins(1,2,5,6)P4, Ins(1,2,4,5,6)P5, Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5 and phytic acid. myo-Inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate was neither substrate nor inhibitor of InsP1ase. We conclude that the 10-fold greater tissue contents of Ins(1)P relative to Ins(4)P in both stimulated and non-stimulated rat brain in vivo are the consequence of a much larger amount of PtdIns metabolism than polyphosphoinositide metabolism under these conditions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. H., Blisner M. E., Holland W. H., Hipps P. P., Sherman W. R. Increased brain myo-inositol 1-phosphate in lithium-treated rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 26;71(2):664–670. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90839-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison J. H., Stewart M. A. Reduced brain inositol in lithium-treated rats. Nat New Biol. 1971 Oct 27;233(43):267–268. doi: 10.1038/newbio233267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., McKinney J. S., Irvine R. F., Putney J. W., Jr Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate formation in Ca2+-mobilizing-hormone-activated cells. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2320237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Michell R. H. The polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1980133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg F., Jr D-myoinositol 1-phosphate as product of cyclization of glucose 6-phosphate and substrate for a specific phosphatase in rat testis. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1375–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallcher L. M., Sherman W. R. The effects of lithium ion and other agents on the activity of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10896–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Mah S., Williamson J. R. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8100–8103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honchar M. P., Olney J. W., Sherman W. R. Systemic cholinergic agents induce seizures and brain damage in lithium-treated rats. Science. 1983 Apr 15;220(4594):323–325. doi: 10.1126/science.6301005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiely D. E., Abruscato G. J., Baburao V. A synthesis of (plus or minus)-myo-inositol 1-phosphate. Carbohydr Res. 1974 Jun;34(2):307–313. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)82905-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccarato W. F., Ray R. E., Wells W. W. Biosynthesis of myo-inositol in rat mammary gland. Isolation and properties of the enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Sep;164(1):194–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert U. B., Agranoff B. W. Isolation and separation of inositol phosphates from hydrolysates of rat tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 1;98(3):574–581. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. R., Ackermann K. E., Berger R. A., Gish B. G., Zinbo M. Analysis of inositol mono- and polyphosphates by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and fast atom bombardment. Biomed Environ Mass Spectrom. 1986 Jul;13(7):333–341. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200130704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. R., Gish B. G., Honchar M. P., Munsell L. Y. Effects of lithium on phosphoinositide metabolism in vivo. Fed Proc. 1986 Oct;45(11):2639–2646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. R., Leavitt A. L., Honchar M. P., Hallcher L. M., Phillips B. E. Evidence that lithium alters phosphoinositide metabolism: chronic administration elevates primarily D-myo-inositol-1-phosphate in cerebral cortex of the rat. J Neurochem. 1981 Jun;36(6):1947–1951. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb10819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. R., Munsell L. Y., Gish B. G., Honchar M. P. Effects of systemically administered lithium on phosphoinositide metabolism in rat brain, kidney, and testis. J Neurochem. 1985 Mar;44(3):798–807. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb12886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. J., Shears S. B., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. Stepwise enzymatic dephosphorylation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to inositol in liver. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):374–376. doi: 10.1038/312374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto K., Okada M., Matsuda Y., Nakagawa H. Purification and properties of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from rat brain. J Biochem. 1985 Aug;98(2):363–370. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Bross T. E., Sherman W. R., Berger R. A., Majerus P. W. Inositol cyclic phosphates are produced by cleavage of phosphatidylphosphoinositols (polyphosphoinositides) with purified sheep seminal vesicle phospholipase C enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4013–4017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Connolly T. M., Bross T. E., Majerus P. W., Sherman W. R., Tyler A. N., Rubin L. J., Brown J. E. Isolation and characterization of the inositol cyclic phosphate products of polyphosphoinositide cleavage by phospholipase C. Physiological effects in permeabilized platelets and Limulus photoreceptor cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13496–13501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Neufeld E. J., Majerus P. W. Phosphoinositide interconversion in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1046–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Comens P. G., Ackermann K. E., Sherman W. R., McDaniel M. L. The digitonin-permeabilized pancreatic islet model. Effect of myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate on Ca2+ mobilization. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):965–969. doi: 10.1042/bj2270965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


