Abstract
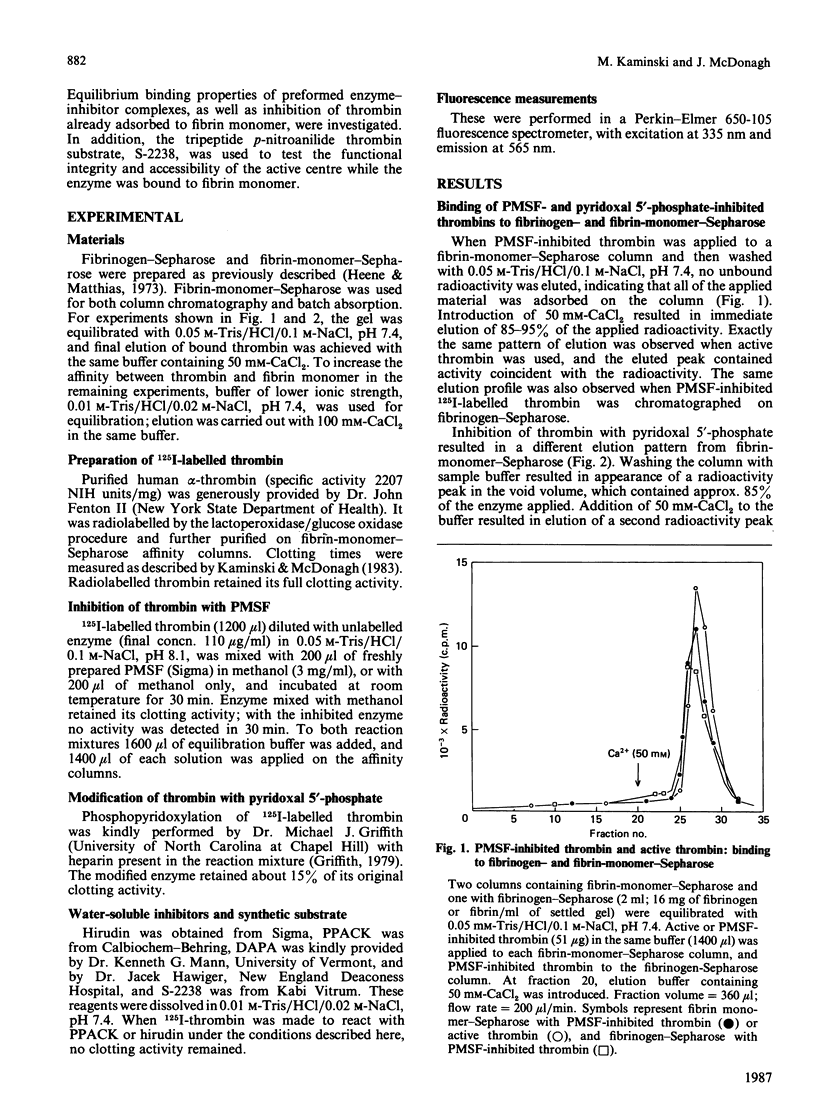
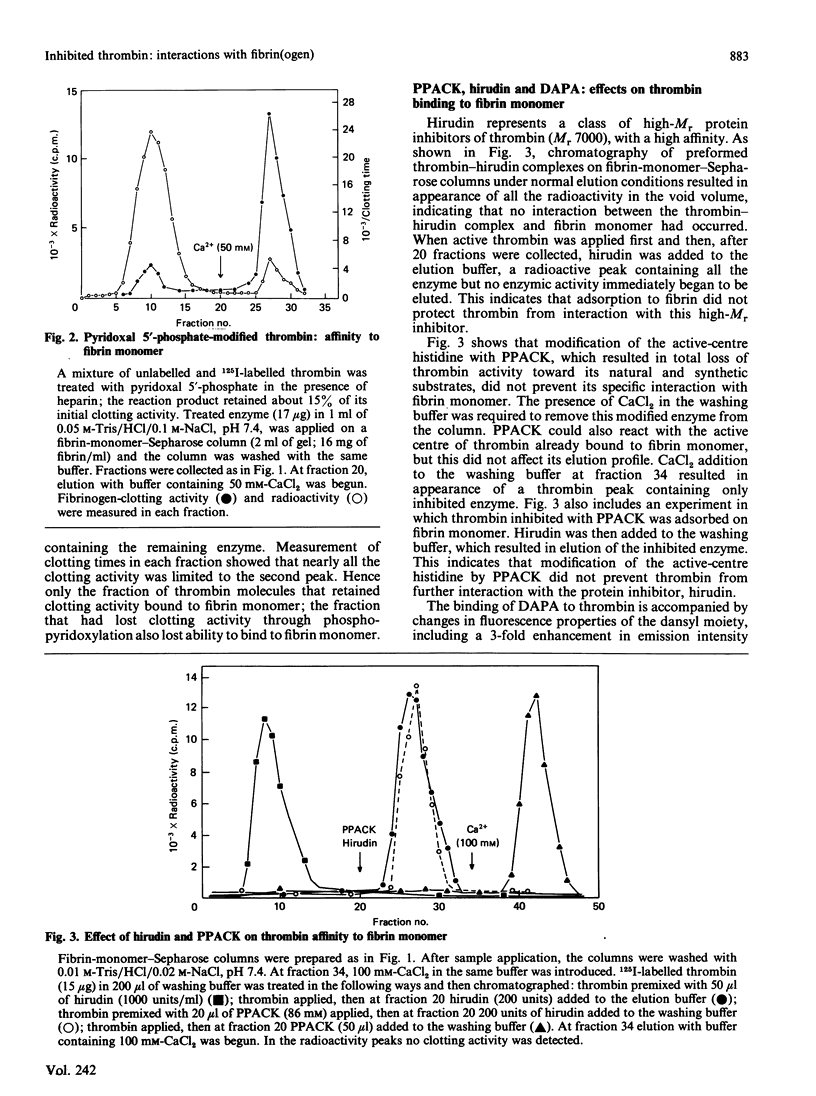
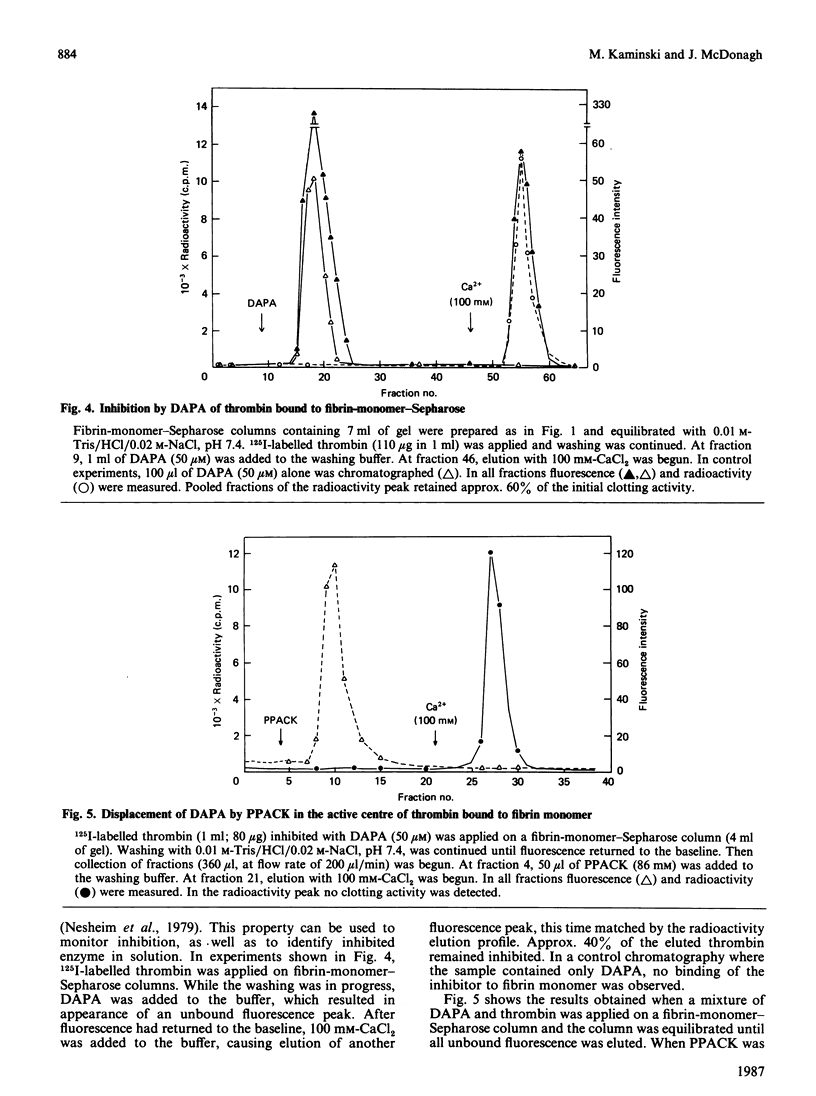
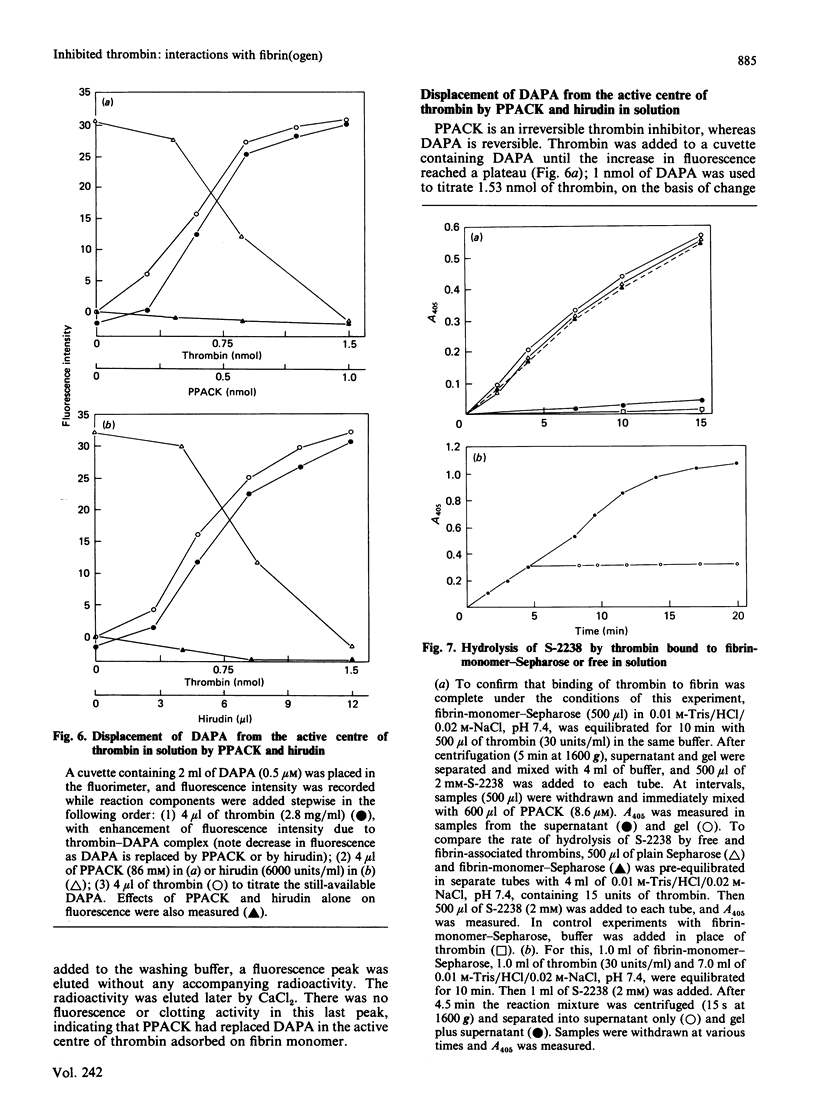
Fibrin-monomer-Sepharose was used to study thrombin binding to fibrin and the role of the enzyme active centre in this interaction. Binding properties of preformed enzyme-inhibitor complexes, as well as inhibition of thrombin already adsorbed to fibrin monomer, were investigated. No apparent difference was found in binding properties of phenylmethanesulphonyl fluoride-, D-Phe-Pro-Arg-CH2Cl- and dansylarginine NN-(3-ethylpentane-1,5-diyl)amide-inhibited thrombins. Also, the elution profile of phenylmethane-sulphonyl fluoride-inhibited thrombin from fibrinogen-Sepharose was identical with that of active thrombin from fibrin-monomer-Sepharose. Thus far the only low-Mr inhibitor that prevents thrombin from binding to fibrin monomer is pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Preformed hirudin-thrombin complexes do not interact with fibrin. The extent to which the active centre of thrombin associated with fibrin is still accessible to substrates and inhibitors was also studied. Thrombin bound to fibrin hydrolyses a synthetic substrate at the same rate as the free enzyme. Water-soluble low-Mr inhibitors such as D-Phe-Pro-Arg-CH2Cl and dansylarginine NN-(3-ethylpentane-1,5-diyl)amide can readily modify the active centre of the fibrin-associated enzyme, and the active centre is exposed to the degree that displacement of dansylarginine NN-(3-ethylpentane-1,5-diyl)amide by D-Phe-Pro-Arg-CH2Cl is possible without disturbing the binding. Hirudin disrupts the affinity between thrombin and fibrin. These data indicate that the active centre of thrombin associated with fibrin through extended binding is fully exposed and freely accessible. It is possible that extended binding may play a regulatory role in the activation of Factor XIII by thrombin, as well as inactivation of this enzyme by antithrombin III.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berliner L. J., Sugawara Y., Fenton J. W., 2nd Human alpha-thrombin binding to nonpolymerized fibrin-Sepharose: evidence for an anionic binding region. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):7005–7009. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Hessel B., Hogg D., Therkildsen L. A two-step fibrinogen--fibrin transition in blood coagulation. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):501–505. doi: 10.1038/275501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Glenn K. C., Cunningham D. D., Das M., Fox C. F., Fenton J. W., 2nd Photoaffinity labeling of a single receptor for alpha-thrombin on mouse embryo cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6244–6247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith M. J. Covalent modification of human alpha-thrombin with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Effect of phosphopyridoxylation on the interaction of thrombin with heparin. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3401–3406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski M., McDonagh J. Studies on the mechanism of thrombin. Interaction with fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10530–10535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. D-Phe-Pro-ArgCH2C1-A selective affinity label for thrombin. Thromb Res. 1979;14(6):969–973. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. Y., Handley D. A., Chien S. Gold labeling of thrombin and ultrastructural studies of thrombin-gold conjugate binding by fibrin. Anal Biochem. 1985 May 15;147(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. Y., Nossel H. L., Kaplan K. L. The binding of thrombin by fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10421–10425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh H. C., Jr, Meinwald Y. C., Lee S., Scheraga H. A. Mechanism of action of thrombin on fibrinogen. Direct evidence for the involvement of phenylalanine at position P9. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6167–6171. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy J. A., Meinwald Y. C., Scheraga H. A. Immunochemical determination of conformational equilibria for fragments of the A alpha chain of fibrinogen. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 13;21(8):1794–1806. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Prendergast F. G., Mann K. G. Interactions of a fluorescent active-site-directed inhibitor of thrombin: dansylarginine N-(3-ethyl-1,5-pentanediyl)amide. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):996–1003. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Danitz M. P., Mudd M. S., Hsieh K. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd Selective immobilization of alpha-thrombin by surface-bound fibrin. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Mar;97(3):403–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


