Abstract
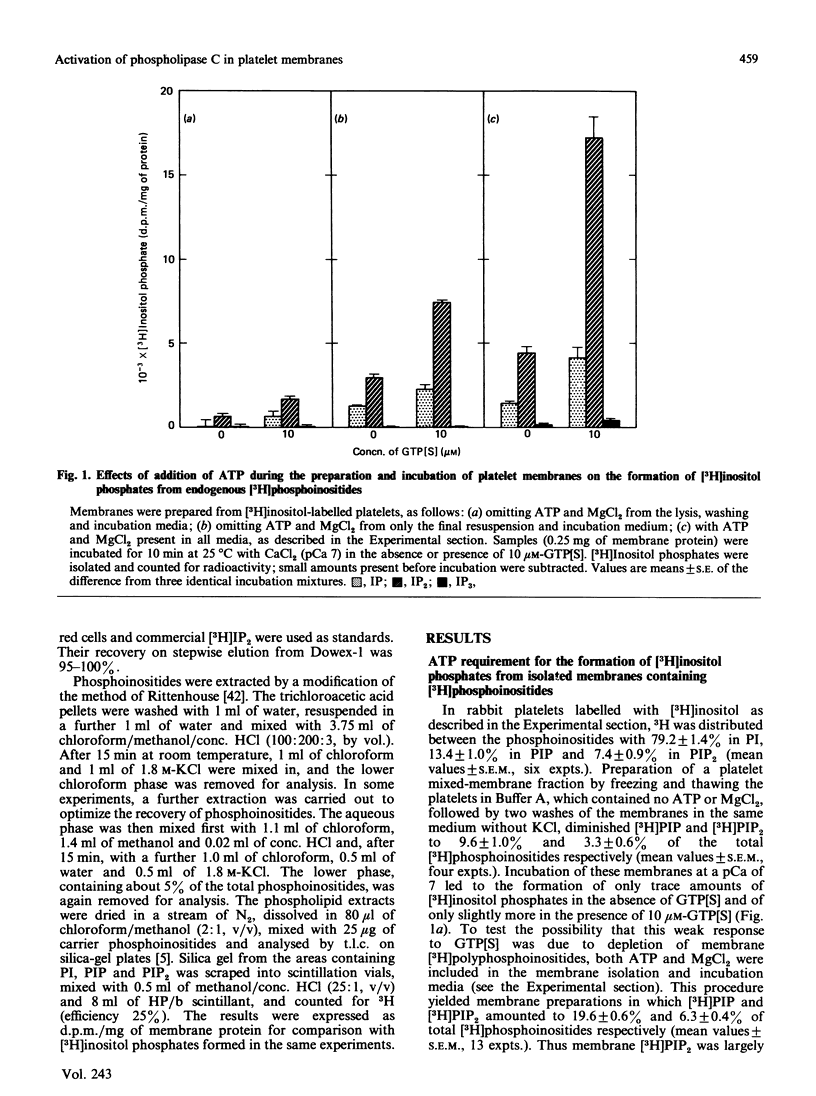
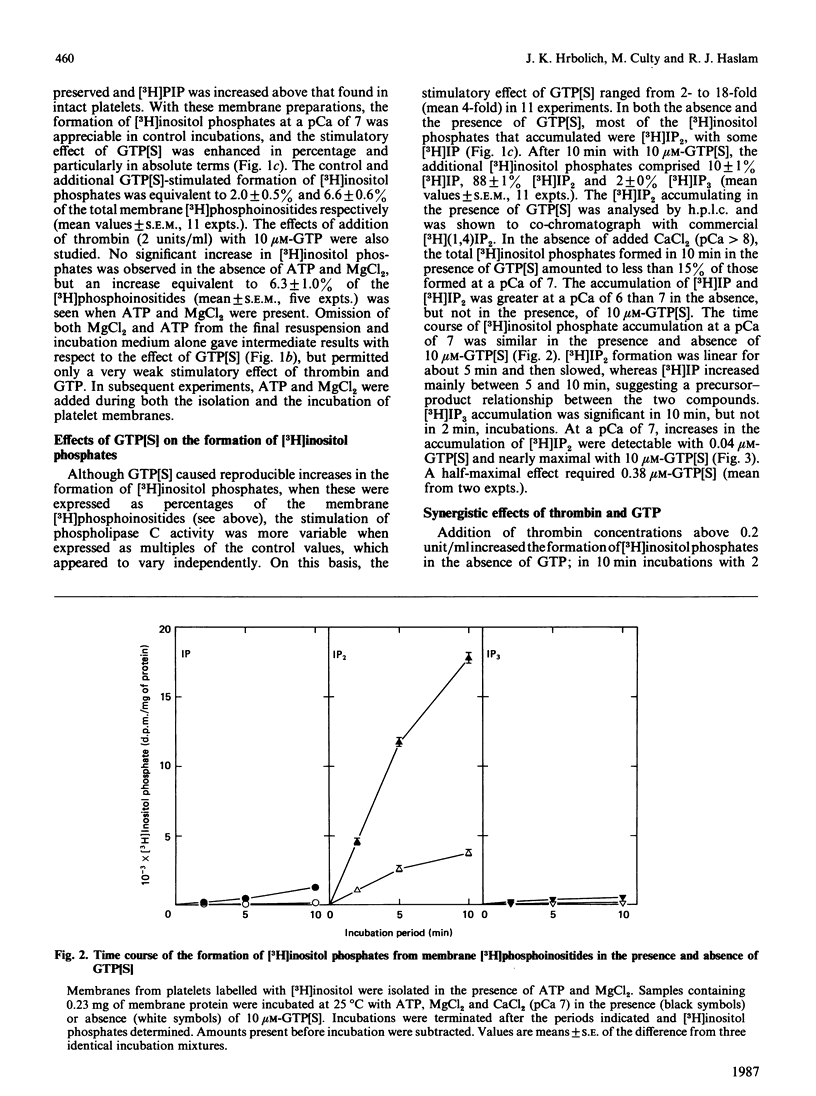
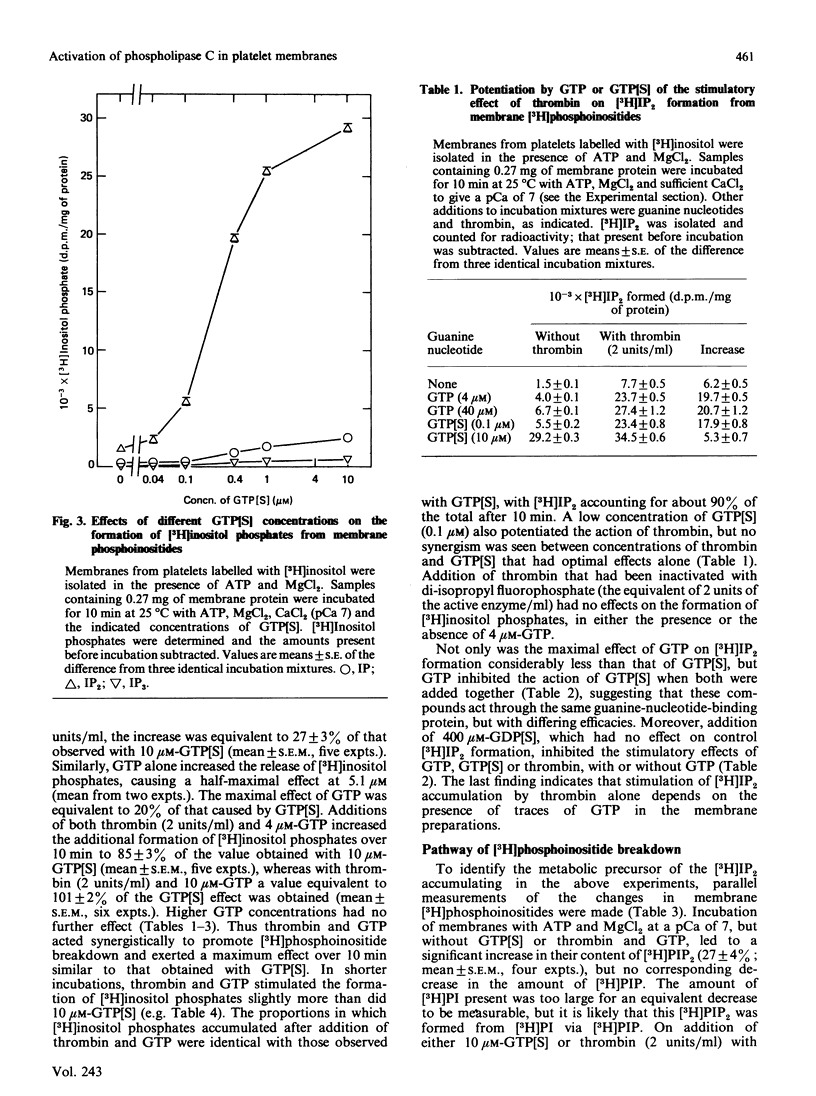
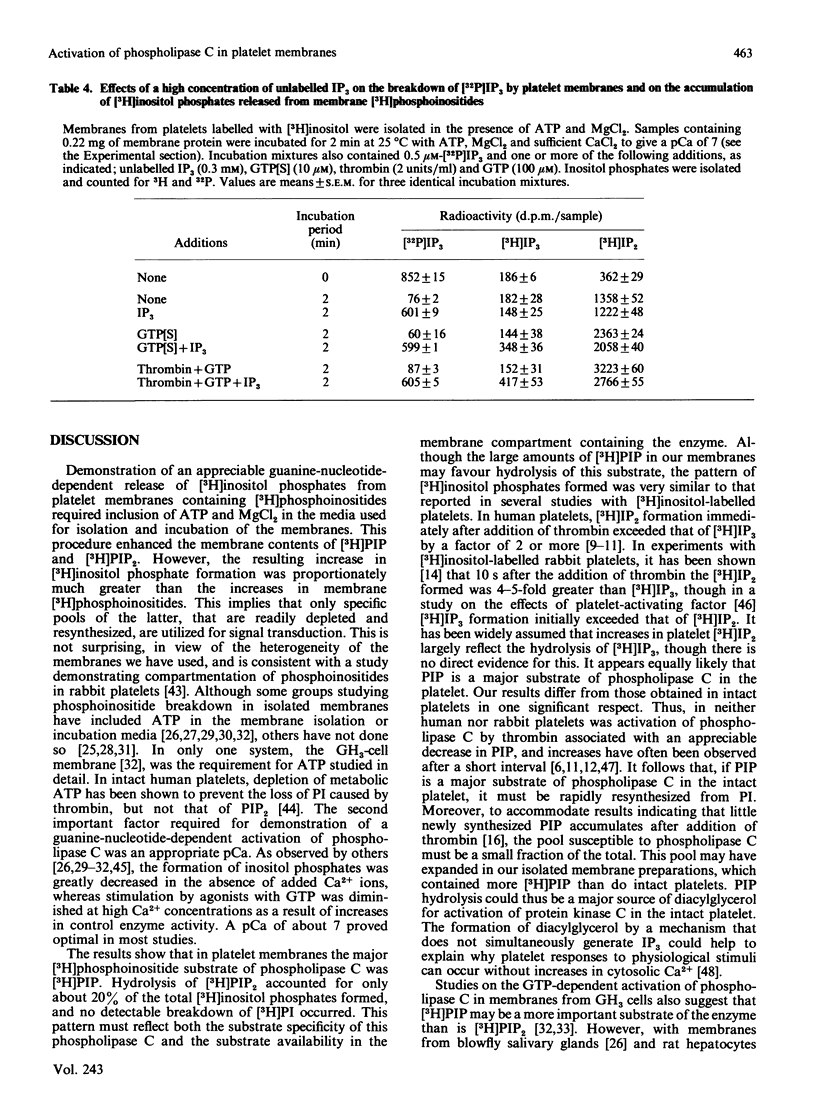
Rabbit platelets were labelled with [3H]inositol and a membrane fraction was isolated in the presence of ATP, MgCl2 and EGTA. Incubation of samples for 10 min with 0.1 microM-Ca2+free released [3H]inositol phosphates equivalent to about 2.0% of the membrane [3H]phosphoinositides. Addition of 10 microM-guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]) caused an additional formation of [3H]inositol phosphates equivalent to 6.6% of the [3H]phosphoinositides. A half-maximal effect was observed with 0.4 microM-GTP[S]. The [3H]inositol phosphates that accumulated consisted of 10% [3H]inositol monophosphate, 88% [3H]inositol bisphosphate ([3H]IP2) and 2% [3H]inositol trisphosphate ([3H]IP3). Omission of ATP and MgCl2 led to depletion of membrane [3H]polyphosphoinositides and marked decreases in the formation of [3H]inositol phosphates. Thrombin (2 units/ml) or GTP (4-100 microM) alone weakly stimulated [3H]IP2 formation, but together they acted synergistically to exert an effect comparable with that of 10 microM-GTP[S]. The action of thrombin was also potentiated by 0.1 microM-GTP[S]. Guanosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate not only inhibited the effects of GTP[S], GTP and GTP with thrombin, but also blocked the action of thrombin alone, suggesting that this depended on residual GTP. Incubation with either GTP[S] or thrombin and GTP decreased membrane [3H]phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate ([H]PIP) and prevented an increase in [3H]phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate ([3H]PIP2) observed in controls. Addition of unlabelled IP3 to trap [3H]IP3 before it was degraded to [3H]IP2 showed that only about 20% of the additional [3H]inositol phosphates that accumulated with GTP[S] or thrombin and GTP were derived from the action of phospholipase C on [3H]PIP2. The results provide further evidence that guanine-nucleotide-binding protein mediates signal transduction between the thrombin receptor and phospholipase C, and suggest that PIP may be a major substrate of this enzyme in the platelet.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agranoff B. W., Murthy P., Seguin E. B. Thrombin-induced phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2076–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation in suspensions of washed rabbit platelets. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jul;19(1):7–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldassare J. J., Fisher G. J. GTP and cytosol stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis in isolated platelet membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):801–805. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1790–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Formation of lysophosphatidylinositol in platelets stimulated with thrombin or ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5196–5200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Rapid decrease of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12705–12708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Codina J., Mattera R., Cerione R. A., Hildebrandt J. D., Sunyer T., Rojas F. J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Iyengar R. Regulation of hormone receptors and adenylyl cyclases by guanine nucleotide binding N proteins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1985;41:41–99. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571141-8.50006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate may represent the site of release of plasma membrane-bound calcium upon stimulation of human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 16;120(1):226–231. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91437-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Baldwin J. M., Allan D. The Ca2+-activated polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of human and rabbit neutrophil membranes. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):477–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2210477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Michell R. H. The polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1980133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Mussat M. C., Michell R. H. The inositol trisphosphate phosphomonoesterase of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):169–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2030169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Wusteman M. M. Breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and not phosphatidylinositol accounts for muscarinic agonist-stimulated inositol phospholipid metabolism in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):633–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2160633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Brown M. L., Fraser E. D., Northup J. K. Purification of the major GTP-binding proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):7052–7059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales R. A., Crews F. T. Guanine nucleotides stimulate production of inositol trisphosphate in rat cortical membranes. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):799–804. doi: 10.1042/bj2320799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff G., Nahas N., Nikolopoulou M., Natarajan V., Schmid H. H. Possible regulation of phospholipase C activity in human platelets by phosphatidylinositol 4',5'-bisphosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jan;228(1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandt R., Aktories K., Jakobs K. H. Evidence for two GTPases activated by thrombin in membranes of human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj2370669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Guanine nucleotides decrease the free [Ca2+] required for secretion of serotonin from permeabilized blood platelets. Evidence of a role for a GTP-binding protein in platelet activation. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 20;174(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Receptor-induced diacylglycerol formation in permeabilized platelets; possible role for a GTP-binding protein. J Recept Res. 1984;4(1-6):605–629. doi: 10.3109/10799898409042576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Dangelmaier C. A., Rongved S. Tight coupling of thrombin-induced acid hydrolase secretion and phosphatidate synthesis to receptor occupancy in human platelets. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):157–167. doi: 10.1042/bj2220157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Bojanic D., Gawler D., O'Hagan S., Wilson A. Thrombin, unlike vasopressin, appears to stimulate two distinct guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins in human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):109–113. doi: 10.1042/bj2380109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. M., Detwiler T. C. The effects of lithium on platelet phosphoinositide metabolism. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 15;236(3):895–901. doi: 10.1042/bj2360895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Anggård E. E., Letcher A. J., Downes C. P. Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2290505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Fain J. N. Regulation of phosphoinositide breakdown by guanine nucleotides. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 21;39(3):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90529-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Wallis C., Fain J. N. 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulates inositol phosphate production in a cell-free system from blowfly salivary glands. Evidence for a role of GTP in coupling receptor activation to phosphoinositide breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5464–5471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Carroll R. C., Cox A. C. Characterization of multiple forms of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C purified from human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):139–145. doi: 10.1042/bj2370139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A., Martin T. F. Direct stimulation by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) of polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in GH3 cell membranes by a guanine nucleotide-modulated mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):721–728. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLNAR J., LORAND L. Studies on apyrases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:353–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90278-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Bajjalieh S. M., Lucas D. O., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulation of polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in GH3 cell membranes is GTP dependent but insensitive to cholera or pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10141–10149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone activates a Ca2+-dependent polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in permeable GH3 cells. GTP gamma S potentiation by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2918–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Taylor C. W., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr Evidence suggesting that a novel guanine nucleotide regulatory protein couples receptors to phospholipase C in exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):337–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2360337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Kirk C. J., Jones L. M., Downes C. P., Creba J. A. The stimulation of inositol lipid metabolism that accompanies calcium mobilization in stimulated cells: defined characteristics and unanswered questions. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Dec 18;296(1080):123–138. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret B. P., Plantavid M., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Are polyphosphoinositides involved in platelet activation? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):660–667. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E. Activation of human platelet phospholipase C by ionophore A23187 is totally dependent upon cyclo-oxygenase products and ADP. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):103–110. doi: 10.1042/bj2220103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E. Human platelets contain phospholipase C that hydrolyzes polyphosphoinositides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5417–5420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfred M. A., Wells W. W. Subcellular site and mechanism of vasopressin-stimulated hydrolysis of phosphoinositides in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7666–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D. Platelet activating factor-stimulated formation of inositol triphosphate in platelets and its regulation by various agents including Ca2+, indomethacin, CV-3988, and forskolin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Aug 1;240(2):674–681. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W. Evidence for the formation of inositol 4-monophosphate in stimulated human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80760-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Properties and distribution of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C in human and horse platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 12;752(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Cox C. C., Snyderman R. Receptor-coupled activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C by an N protein. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):97–100. doi: 10.1126/science.3006254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Lane B. C., Kusaka I., Verghese M. W., Snyderman R. Chemoattractant receptor-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes. Requirement for a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5875–5878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., Gershengorn M. C. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone and GTP activate inositol trisphosphate formation in membranes isolated from rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2712–2717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing R. J., Prpic V., Jiang H., Exton J. H. Hormone-stimulated polyphosphoinositide breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers J. D., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Mustard J. F. Accumulation of the inositol phosphates in thrombin-stimulated, washed rabbit platelets in the presence of lithium. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):399–405. doi: 10.1042/bj2240399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers J. D., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Mustard J. F. Changes in the platelet phosphoinositides during the first minute after stimulation of washed rabbit platelets with thrombin. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 1;219(1):25–31. doi: 10.1042/bj2190025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers J. D., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Mustard J. F. The decrease in phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in ADP-stimulated washed rabbit platelets is not primarily due to phospholipase C activation. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 15;237(2):327–332. doi: 10.1042/bj2370327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers J. D., Mustard J. F. The phosphoinositides exist in multiple metabolic pools in rabbit platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):411–417. doi: 10.1042/bj2380411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. A., Fain J. N. Guanosine 5'-O-thiotriphosphate stimulates phospholipase C activity in plasma membranes of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9527–9530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. The rapid formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets by thrombin is inhibited by prostacyclin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13199–13203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Neufeld E. J., Majerus P. W. Phosphoinositide interconversion in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1046–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


