Abstract
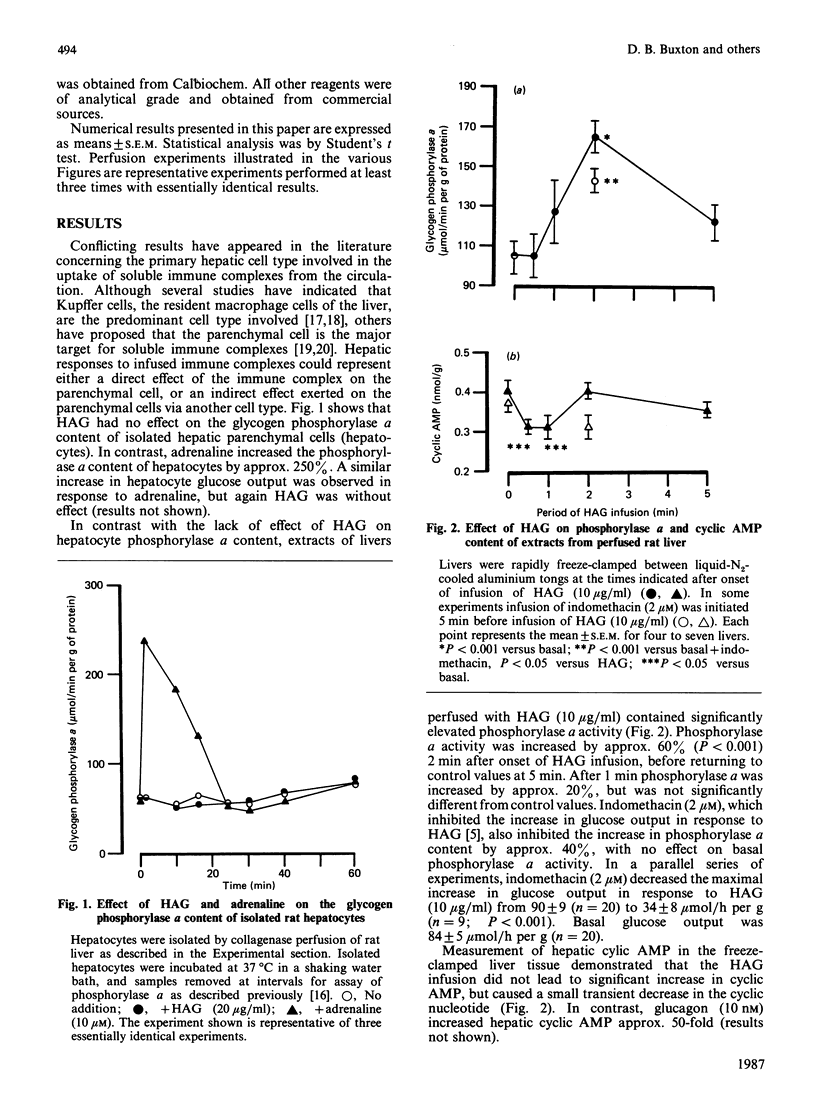
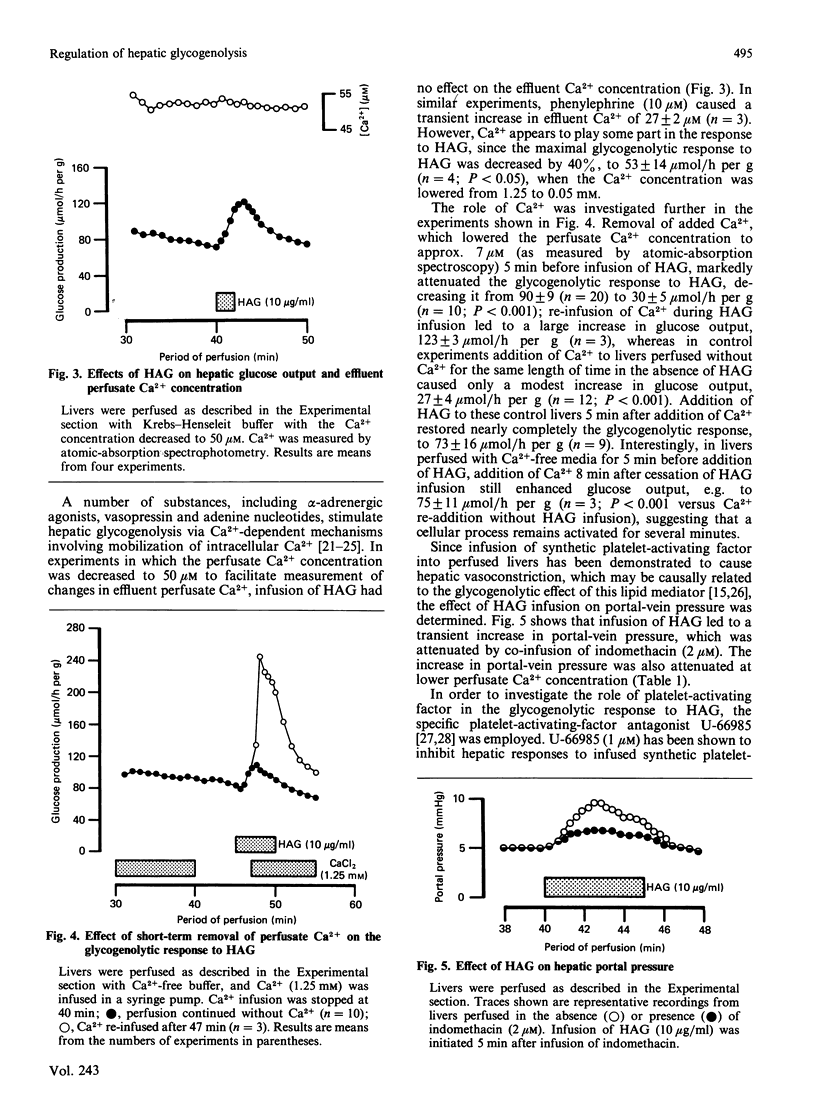
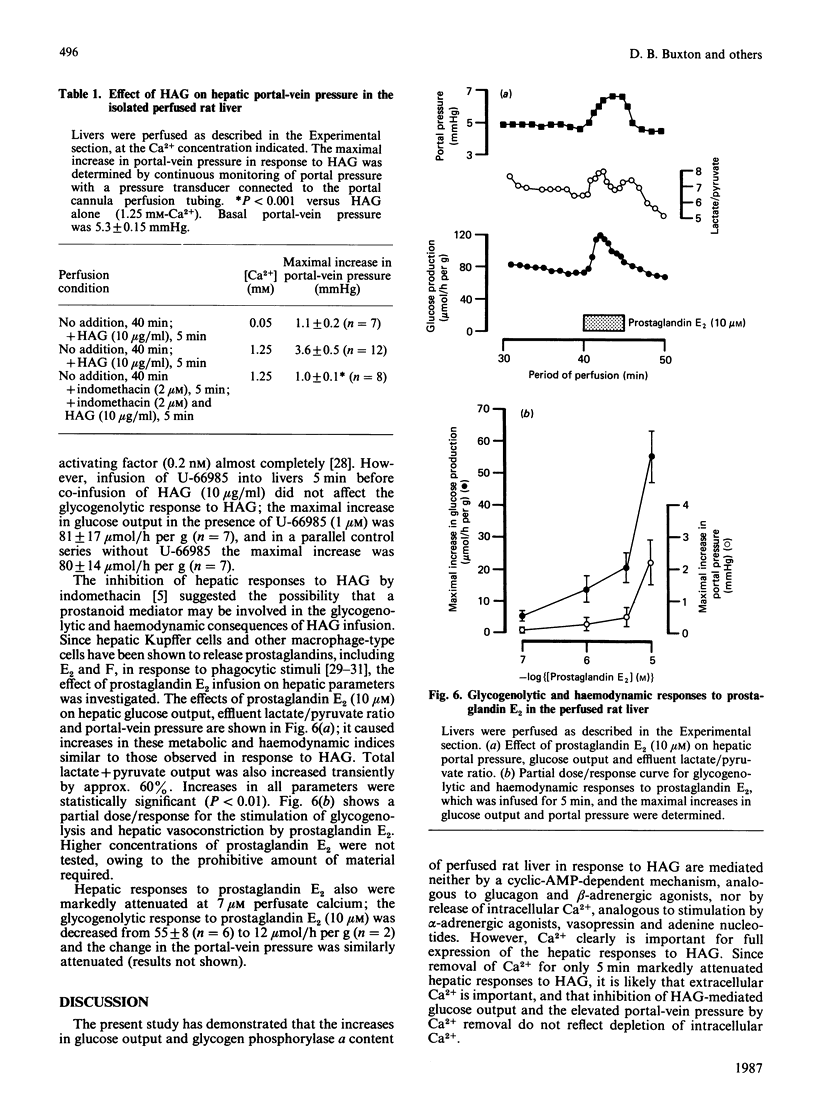
Infusion of heat-aggregated immunoglobulin G (HAG) into perfused livers from fed rats caused transient increases in hepatic glycogenolysis and portal-vein pressure, accompanied by a transient increase in hepatic glycogen phosphorylase alpha content. The hepatic responses to HAG were inhibited by indomethacin (2 microM). In contrast, HAG was without effect on phosphorylase alpha content and glucose output in isolated hepatocytes. HAG infusion caused a transient decrease in hepatic cyclic AMP. Lowering the extracellular Ca2+ concentration to 6 or 50 microM attenuated markedly the glycogenolytic and haemodynamic responses to HAG; efflux of Ca2+ from the liver was not observed in response to HAG. Co-infusion of the specific platelet-activating-factor antagonist U-66985 (1-O-octadecyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoric acid 6'-trimethylammoniumhexyl ester) did not attenuate the glycogenolytic response to HAG. Infusion of prostaglandin E2 caused increases in glucose output, portal-vein pressure and the reduction state of the cytosolic NAD(H) redox couple similar to those seen with HAG. The present study suggests that the glycogenolytic activation after HAG infusion may be an indirect consequence of the haemodynamic response of the hepatic vasculature to stimulation of the reticuloendothelial cells of the liver.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Mannik M. Studies on antigen-antibody complexes. II. Quantification of tissue uptake of soluble complexes in normal and complement-depleted rabbits. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):63–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Mannik M. The macrophage receptor for IgG: number and affinity of binding sites. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1455–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., SEBESTYEN M., COOPER N. S. The clearance of antigen antibody complexes from the blood by the reticuloendothelial system. J Immunol. 1959 Feb;82(2):131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermelin M., Decker K. Ca2+ flux as an initial event in phagocytosis by rat Kupffer cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 5;131(3):539–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmelin M., Decker K. Synthesis of prostanoids and cyclic nucleotides by phagocytosing rat Kupffer cells. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 16;142(2):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Brumley F. T., Marks J. L., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. Relationship between alpha-adrenergic stimulation of calcium efflux and activation of phosphorylase in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4851–4858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonney R. J., Naruns P., Davies P., Humes J. L. Antigen-antibody complexes stimulate the synthesis and release of prostaglandins by mouse peritoneal macrophages. Prostaglandins. 1979 Oct;18(4):605–616. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(79)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass E. P., Garrity M. J., Robertson R. P. Inhibition of glucagon-stimulated hepatic glycogenolysis by E-series prostaglandins. FEBS Lett. 1984 Apr 24;169(2):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80336-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Fisher R. A., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Platelet-activating factor-mediated vasoconstriction and glycogenolysis in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):644–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Specific antagonists of platelet activating factor-mediated vasoconstriction and glycogenolysis in the perfused rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Mar 15;35(6):893–897. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Stimulation of glycogenolysis and platelet-activating factor production by heat-aggregated immunoglobulin G in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13758–13761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Robertson S. M., Olson M. S. Stimulation of glycogenolysis by adenine nucleotides in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):773–780. doi: 10.1042/bj2370773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Shukla S. D., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Stimulation of hepatic glycogenolysis by acetylglyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1468–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Characterization of responses of isolated rat hepatocytes to ATP and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15789–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Babcock D. F., Lardy H. A. Norepinephrine, vasopressin, glucagon, and A23187 induce efflux of calcium from an exchangeable pool in isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng A., Fitzgerald T. J., Carlson G. M. Adenosine 5'-diphosphate as an allosteric effector of phosphorylase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2535–2542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson W., Jessup S. J., McDonald-Gibson W., Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E. Prostaglandin uptake and metabolism by the perfused rat liver. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;39(3):585–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Robison G. A., Sutherland E. W., Park C. R. Studies on the role of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the hepatic actions of glucagon and catecholamines. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6166–6177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. A., Kumar R., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Effects of beta-adrenergic stimulation on 1-O-hexadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine-mediated vasoconstriction and glycogenolysis in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8817–8823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. A., Shukla S. D., Debuysere M. S., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. The effect of acetylglyceryl ether phosphorylcholine on glycogenolysis and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate metabolism in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8685–8688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway C. V. Mechanisms and quantitative assessment of drug effects on cardiac output with a new model of the circulation. Pharmacol Rev. 1981 Dec;33(4):213–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems D. A., Whitton P. D. Control of hepatic glycogenolysis. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jan;60(1):1–50. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf U., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Dierich M. P. Demonstration of binding sites for IgG Fc and the third complement component (C3) on isolated hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):639–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., De Wulf H. P2-purinergic control of liver glycogenolysis. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):797–799. doi: 10.1042/bj2310797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson D. W., Kijlstra A., Van Es L. A. Association and dissociation of aggregated IgG from rat peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1368–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemberg A., Wikinski R., Izurieta E. M., Halperin H., Paglione A. M., De Neuman P., Jauregui H. Effects of prostaglandin E 1 and norepinephrine on glucose and lipid metabolism in isolated perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 5;248(2):198–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. A. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on hepatic cyclic AMP activity, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Prostaglandins. 1974 Jun 25;6(6):509–521. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luyckx A. S., Lefebvre P. J. Possible role of endogenous prostaglandins in glucagon secretion by isolated guinea-pig islets. Diabetologia. 1978 Nov;15(5):411–416. doi: 10.1007/BF01219651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCuskey R. S. A dynamic and static study of hepatic arterioles and hepatic sphincters. Am J Anat. 1966 Nov;119(3):455–477. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001190307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Ganguli S., Sperling M. A. Prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors impair hepatic glucose production in response to glucagon and epinephrine stimulation. Diabetes. 1983 May;32(5):439–444. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.5.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pek S., Tai T. Y., Elster A., Fajans Stimulation by prostaglandin E2 of glucagon and insulin release from isolated rat pancreas. Prostaglandins. 1975 Sep;10(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport A. M. The microcirculatory hepatic unit. Microvasc Res. 1973 Sep;6(2):212–228. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(73)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly F. D., McCuskey R. S., Cilento E. V. Hepatic microvascular regulatory mechanisms. I. Adrenergic mechanisms. Microvasc Res. 1981 Jan;21(1):103–116. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(81)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Chen M. A role for prostaglandin E in defective insulin secretion and carbohydrate intolerance in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):747–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI108827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Scott W. A., Kempe J., Cohn Z. A. Prostaglandin synthesis by macrophages requires a specific receptor-ligand interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4279–4282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacca L., Perez G., Rengo F., Condorelli M. Effects of different prostaglandins on glucose kinetics in the rat. Diabetes. 1974 Jun;23(6):532–535. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.6.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., González E., Escanero J. F., Egido J. Binding kinetics of monomeric and aggregated IgG to Kupffer cells and hepatocytes of mice. Immunology. 1984 Oct;53(2):283–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz R., Hansen W., Thurman R. G. Interaction of mixed-function oxidation with biosynthetic processes. 1. Inhibition of gluconeogenesis by aminopyrine in perfused rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 21;38(1):64–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D., Buxton D. B., Olson M. S., Hanahan D. J. Acetylglyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. A potent activator of hepatic phosphoinositide metabolism and glycogenolysis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10212–10214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogh T., Blomhoff R., Eskild W., Berg T. Hepatic uptake of circulating IgG immune complexes. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):585–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweat F. W., Yamashita L., Jubiz W. Dissociation of E prostaglandin effects on liver glycogenolysis and cyclic AMP levels. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1983 Oct;32(2-3):131–142. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(83)90077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumura A., Homma H., Hanahan D. J. Structural analogs of alkylacetylglycerophosphocholine inhibitory behavior on platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12710–12714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi V., Poli A., Ferretti E., Barnabei O. Hormone and prostaglandin E1 control of potassium and cyclic AMP levels in isolated rat liver cells. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1975;13:189–200. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(75)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISER R. S., LAXSON C. The fate of fluorescein-labeled soluble antigen-antibody complex in the mouse. J Infect Dis. 1962 Jul-Aug;111:55–58. doi: 10.1093/infdis/111.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler G. E., Epand R. M. Prostaglandin E1: anomalous effects on glucose production in rat liver. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 May;11(3):335–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Lund P., Krebs H. A. The redox state of free nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):514–527. doi: 10.1042/bj1030514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


