Abstract
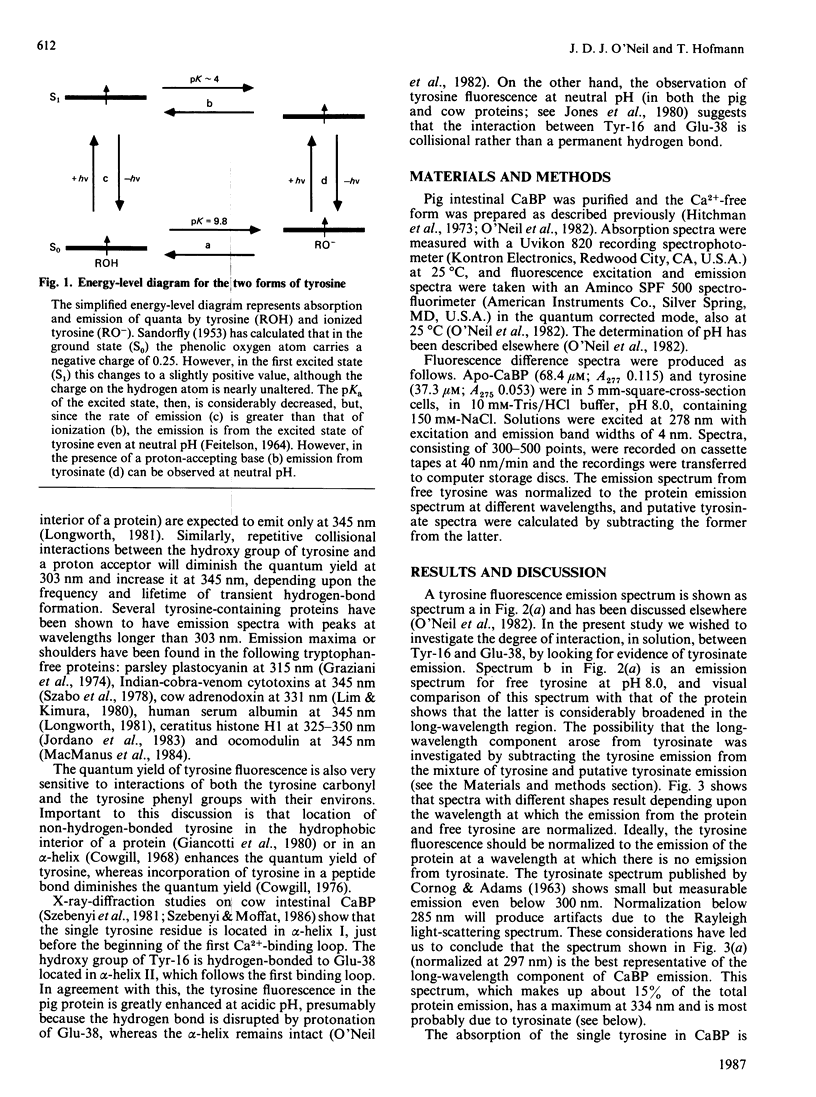
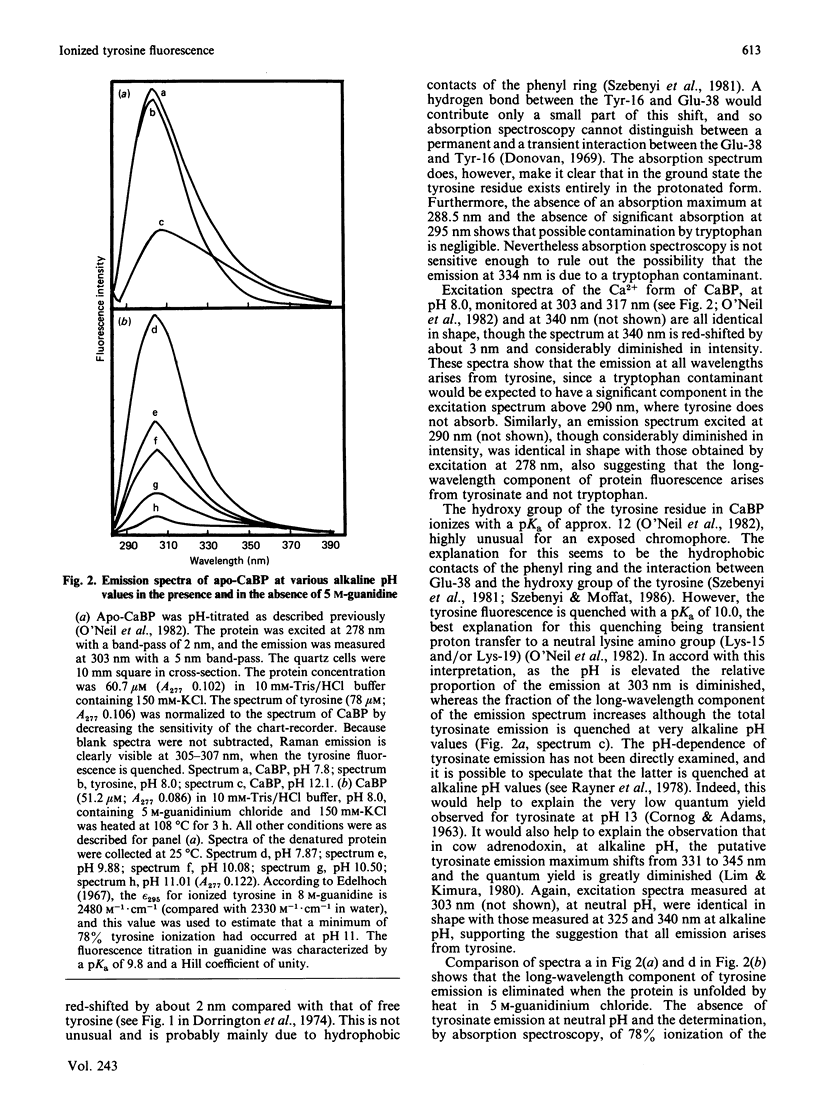
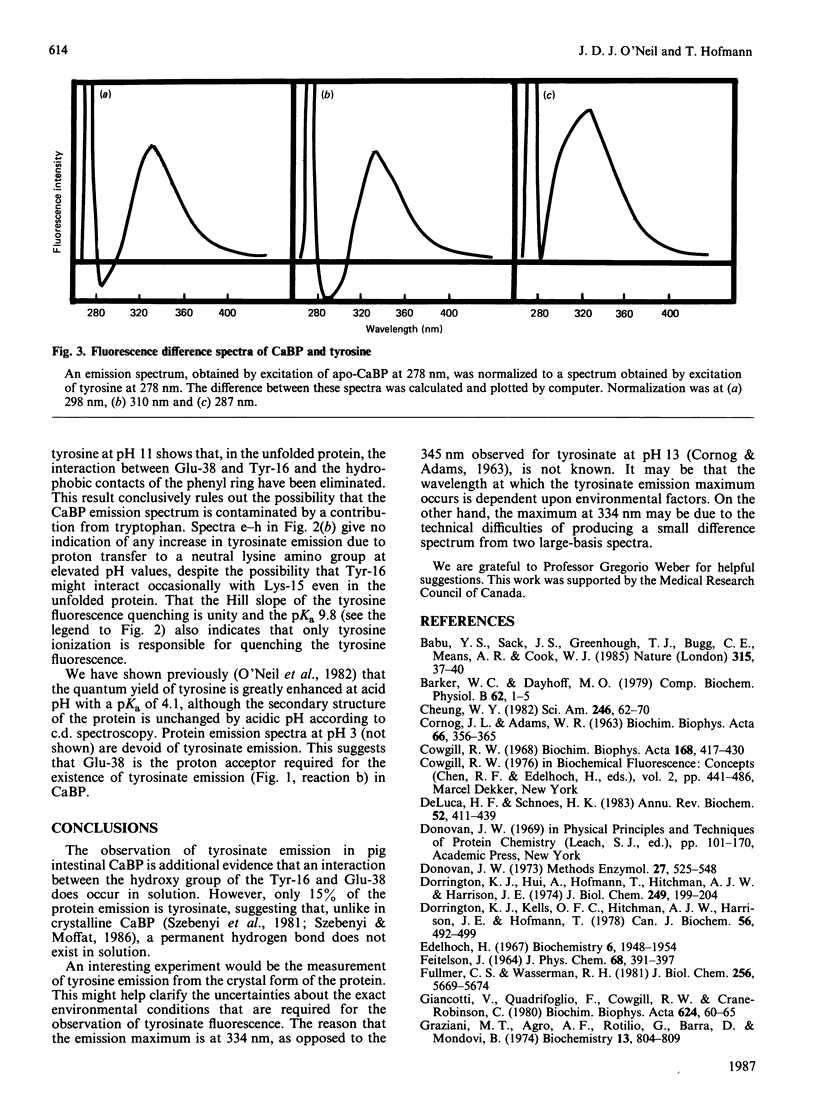
The single tyrosine residue in both pig and cow intestinal Ca2+-binding proteins fluoresces at 303 nm although the crystal structure of the cow protein shows a hydrogen bond between the hydroxy group of the tyrosine and glutamate-38 [Szebenyi & Moffat (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261, 8761-8777]. The latter interaction suggests that tyrosinate fluorescence should dominate the emission spectra of these proteins. A fluorescence difference spectrum, produced by subtracting the spectrum of free tyrosine from the spectrum of the protein, gives a peak at 334 nm due to ionized tyrosine. That this component of the emission spectrum is not due to a tryptophan-containing contaminant is shown by its elimination when the protein is denatured by guanidine and when glutamate-38 is protonated. We conclude that, in solution, the tyrosine residue in this protein interacts occasionally with glutamate-38 but that a permanent hydrogen bond is not formed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babu Y. S., Sack J. S., Greenhough T. J., Bugg C. E., Means A. R., Cook W. J. Three-dimensional structure of calmodulin. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):37–40. doi: 10.1038/315037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. C., Dayhoff M. O. Evolution of homologous physiological mechanisms based on protein sequence data. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1979;62(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(79)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORNOG J. L., Jr, ADAMS W. R. The fluorescence of tyrosine in alkaline solution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 21;66:356–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin. Sci Am. 1982 Jun;246(6):62–70. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0682-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowgill R. W. Fluorescence and protein structure. XIV. Tyrosine fluorescence in helical muscle proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 3;168(3):417–430. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F., Schnoes H. K. Vitamin D: recent advances. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:411–439. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. W. Spectrophotometric titration of the functional groups of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1973;27:525–548. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(73)27025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington K. J., Hui A., Hofmann T., Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E. Porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Molecular properties and the effect of binding calcium ions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington K. J., Kells D. I., Hitchman A. J., Hartison J. E., Hofmann T. Spectroscopic studies on the binding of divalent cations to porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jun;56(6):492–499. doi: 10.1139/o78-076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer C. S., Wasserman R. H. The amino acid sequence of bovine intestinal calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5669–5674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti V., Quadrifoglio F., Cowgill R. W., Crane-Robinson C. Fluorescence of buried tyrosine residues in proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 24;624(1):60–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani M. T., Agrò A. F., Rotilio G., Barra D., Mondovi B. Parsley plastocyanin. The possible presence of sulfhydryl and tyrosine in the copper environment. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):804–809. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., James M. N. Structure of the calcium regulatory muscle protein troponin-C at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):653–659. doi: 10.1038/313653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchman A. J., Kerr M. K., Harrison J. E. The purification of pig vitamin D-induced intestinal calcium binding protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):221–222. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann T., Kawakami M., Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E., Dorrington K. J. The amino acid sequence of porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):737–748. doi: 10.1139/o79-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordano J., Barbero J. L., Montero F., Franco L. Fluorescence of histones H1. A tyrosinate-like fluorescence emission in Ceratitis capitata H1 at neutral pH values. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):315–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. Gene triplication deduced from the tertiary structure of a muscle calcium binding protein. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 15;240(98):85–88. doi: 10.1038/newbio240085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. Structure and evolution of calcium-modulated proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;8(2):119–174. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim B. T., Kimura T. Conformation-associated anomalous tyrosine fluorescence of adrenodoxin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2440–2444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longworth J. W. A new component in protein fluorescence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;366:237–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb20757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacManus J. P., Szabo A. G., Williams R. E. Conformational changes induced by binding of bivalent cations to oncomodulin, a paravalbumin-like tumour protein. Biochem J. 1984 May 15;220(1):261–268. doi: 10.1042/bj2200261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mani R. S., Boyes B. E., Kay C. M. Physicochemical and optical studies on calcium- and potassium-induced conformational changes in bovine brain S-100b protein. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2607–2612. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moews P. C., Kretsinger R. H. Refinement of the structure of carp muscle calcium-binding parvalbumin by model building and difference Fourier analysis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 15;91(2):201–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil J. D., Dorrington K. J., Hofmann T. Luminescence and circular-dichroism analysis of terbium binding by pig intestinal calcium-binding protein (relative mass = 9000). Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;62(6):434–442. doi: 10.1139/o84-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil J. D., Dorrington K. J., Kells D. I., Hofmann T. Fluorescence and circular-dichroism properties of pig intestinal calcium-binding protein (Mr=9000), a protein with a single tyrosine residue. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):389–396. doi: 10.1042/bj2070389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelling J. G., Sykes B. D. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance study of the two calcium-binding sites of porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8342–8347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelling J. G., Sykes B. D., O'Neil J. D., Hofmann T. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of porcine intestinal calcium binding protein. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2649–2654. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaralingam M., Bergstrom R., Strasburg G., Rao S. T., Roychowdhury P., Greaser M., Wang B. C. Molecular structure of troponin C from chicken skeletal muscle at 3-angstrom resolution. Science. 1985 Feb 22;227(4689):945–948. doi: 10.1126/science.3969570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo A. G., Lynn K. R., Krajcarski D. T., Rayner D. M. Tyrosinate fluorescence maxima at 345 nm in proteins lacking tryptophan at pH 7. FEBS Lett. 1978 Oct 15;94(2):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80948-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szebenyi D. M., Moffat K. The refined structure of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine intestine. Molecular details, ion binding, and implications for the structure of other calcium-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8761–8777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szebenyi D. M., Obendorf S. K., Moffat K. Structure of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine intestine. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):327–332. doi: 10.1038/294327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H. J., Drakenberg T., Forsén S., O'Neil J. D., Hofmann T. Structural differences in the two calcium binding sites of the porcine intestinal calcium binding protein: a multinuclear NMR study. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):3870–3876. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G., ROSENHECK K. PROTON-TRANSFER EFFECTS IN THE QUENCHING OF FLUORESCENCE OF TYROSINE COPOLYMERS. Biopolym Symp. 1964;13:333–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


