Abstract
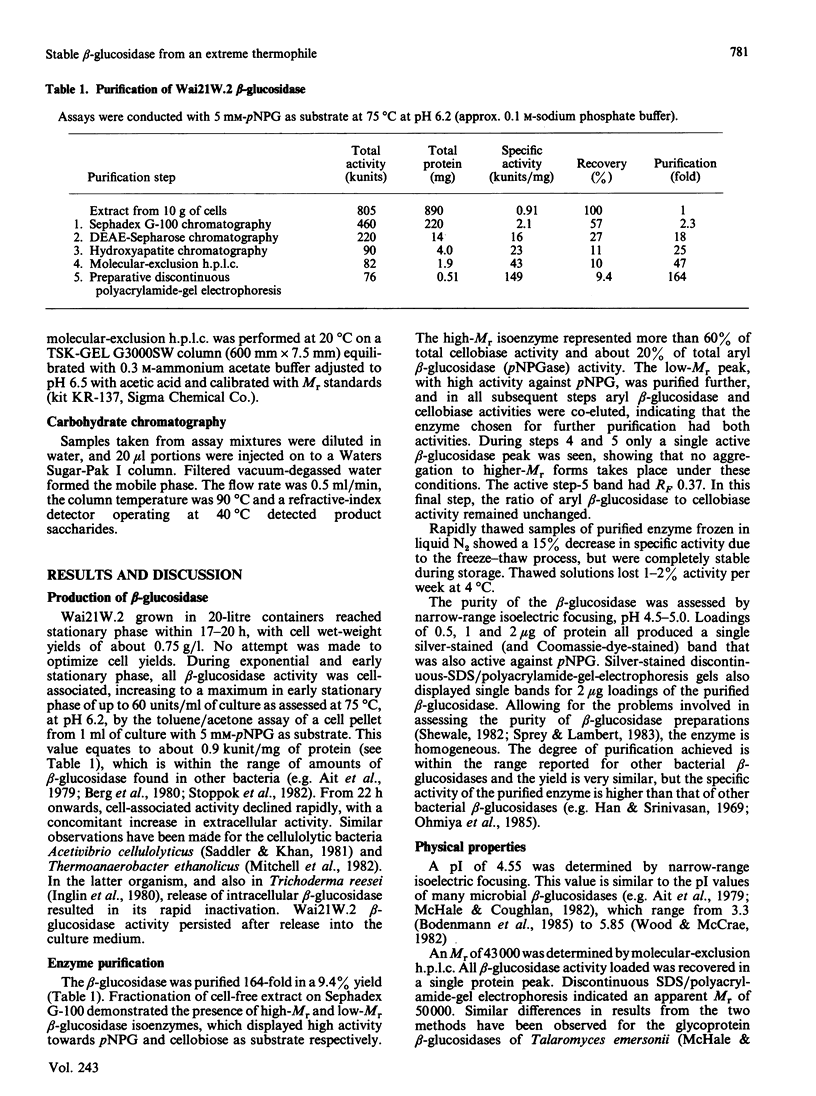
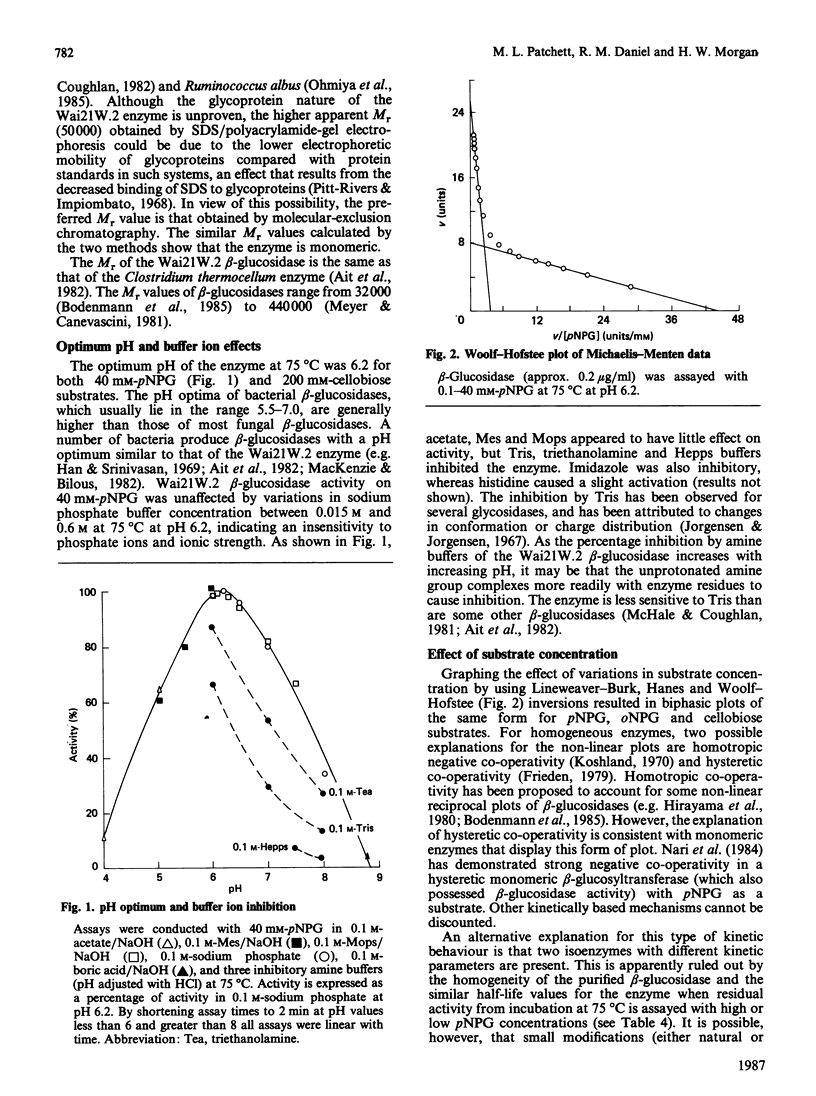
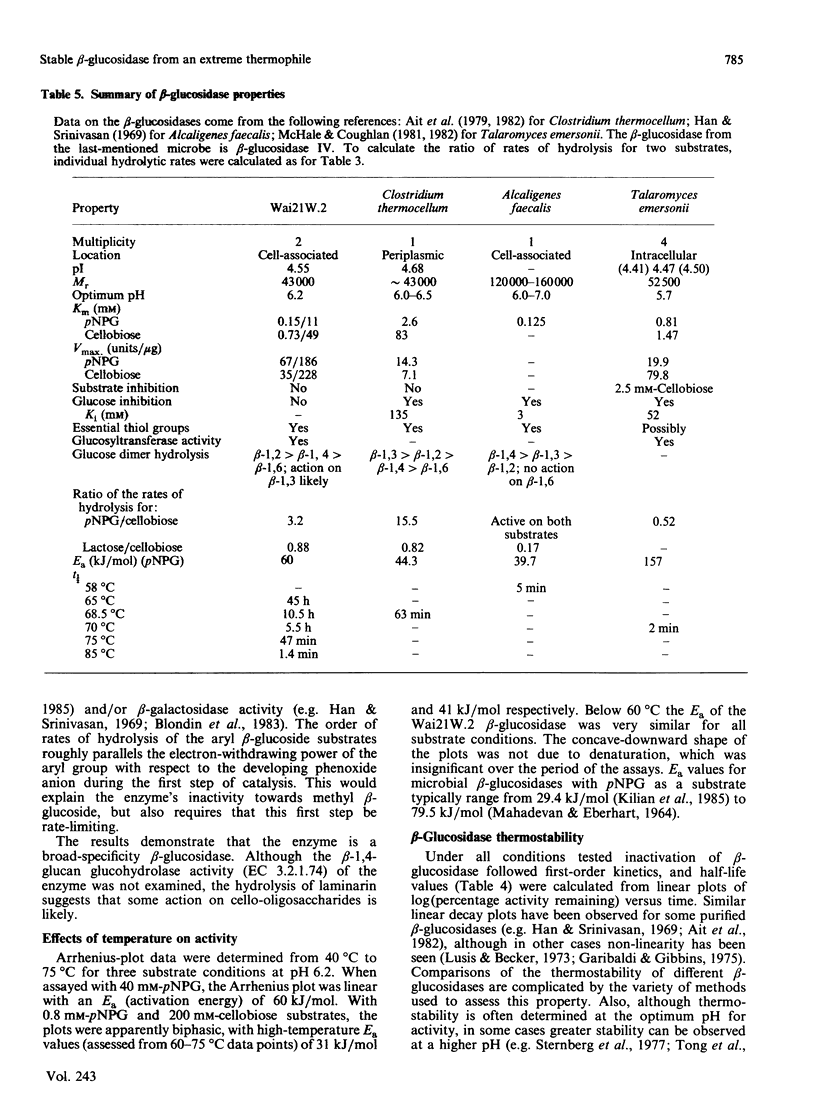
A beta-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.21) was purified to homogeneity from cell-free extracts of an extremely thermophilic anaerobic bacterium. The enzyme has an Mr of 43,000 as determined by molecular-exclusion chromatography, has a pI of 4.55 and shows optimum activity at pH 6.2. The enzyme is active against a wide range of aryl beta-glycosides and beta-linked disaccharides, with beta-galactosidase activity only slightly less than beta-glucosidase activity, and significant beta-xylosidase activity. Lineweaver-Burk plots for p-nitrophenyl beta-glucoside, o-nitrophenyl beta-glucoside and cellobiose substrates are biphasic concave-downwards. Inhibition of the beta-glucosidase by substrates and glucose is negligible. Thermal inactivation follows first-order kinetics, with t1/2 (65 degrees C) 45 h, t1/2 (75 degrees C) 47 min and t1/2 (85 degrees C) 1.4 min and a deactivation energy of 380 kJ/mol at pH 6.2. At pH 7.0, which is the optimum pH for thermostability, t1/2 (75 degrees C) is 130 min. At 75 degrees C, at pH 6.2, the thermostability is enhanced about 8-fold by 10% (w/v) glycerol, about 6-fold by 0.2 M-cellobiose and about 3-fold by 5 mM-dithiothreitol and 5 mM-2-mercaptoethanol.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aït N., Creuzet N., Cattanéo J. Characterization and purification of thermostable beta-glucosidase from Clostridium thermocellum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 27;90(2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91269-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beldman G., Searle-Van Leeuwen M. F., Rombouts F. M., Voragen F. G. The cellulase of Trichoderma viride. Purification, characterization and comparison of all detectable endoglucanases, exoglucanases and beta-glucosidases. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):301–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett F., Sternberg D. Immobilization of Aspergillus beta-glucosidase on chitosan. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Apr;35(4):750–755. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.4.750-755.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucht B., Eriksson K. E. Extracellular enzyme system utilized by the rot fungus Stereum sanguinolentum for the breakdown of cellulose. IV. Separation of cellobiase and aryl beta-glucosidase activities. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Feb;129(2):416–420. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Groleau D. Stability of the endo-beta-1,4-glucanase and beta-1,4-glucosidase from Bacteroides succinogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Jan;28(1):144–148. doi: 10.1139/m82-017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C. Slow transitions and hysteretic behavior in enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:471–489. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garibaldi A., Gibbins L. N. Partial purification and properties of a beta-glucosidase from Erwinia herbicola Y46. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Apr;21(4):513–520. doi: 10.1139/m75-073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gekko K., Timasheff S. N. Thermodynamic and kinetic examination of protein stabilization by glycerol. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4677–4686. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groleau D., Forsberg C. W. Cellulolytic activity of the rumen bacterium Bacteroides succinogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):517–530. doi: 10.1139/m81-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Y. W., Srinivasan V. R. Purification and characterization of beta-glucosidase of Alcaligenes faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1355–1363. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1355-1363.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama T., Nagayama H., Matsuda K. Studies on cellulases of a phytopathogenic fungus, Pyricularia oryzae Cavara. IV. Kinetic studies on beta-glucosidases. J Biochem. 1980 Apr;87(4):1203–1208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglin M., Feinberg B. A., Loewenberg J. R. Partial purification and characterization of a new intracellular beta-glucosidase of Trichoderma reesei. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 1;185(2):515–519. doi: 10.1042/bj1850515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jermyn M. A. Fungal cellulases. XV. Acceptor specificity of the aryl beta-glucosidase of Stachybotrys atra. Aust J Biol Sci. 1966 Oct;19(5):903–917. doi: 10.1071/bi9660903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen B. B., Jorgensen O. B. Inhibition of barley malt alpha-glucosidase by Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane and erythritol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 12;146(1):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., Becker R. R. The beta-glucosidase system of the thermophilic fungus Chaetomium thermophile var. coprophile n. var. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 2;329(1):5–16. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHADEVAN P. R., EBERHART B. THE BETA-GLUCOSIDASE SYSTEM OF NEUROSPORA CRASSA. II. PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF ARYL BETA-GLUCOSIDASE. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Oct;108:22–29. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macris B. J. Production and Characterization of Cellulase and beta-Glucosidase from a Mutant of Alternaria alternata. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):560–565. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.560-565.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H. P., Canevascini G. Separation and Some Properties of Two Intracellular beta-Glucosidases of Sporotrichum (Chrysosporium) thermophile. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):924–931. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.924-931.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldoveanu N., Kluepfel D. Comparison of beta-Glucosidase Activities in Different Streptomyces Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):17–21. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.17-21.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nari J., Noat G., Ricard J. pH-induced co-operative effects in hysteretic enzymes. 2. pH-induced co-operative effects in a cell-wall beta-glucosyltransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 3;145(2):319–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmiya K., Shirai M., Kurachi Y., Shimizu S. Isolation and properties of beta-glucosidase from Ruminococcus albus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):432–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.432-434.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt-Rivers R., Impiombato F. S. The binding of sodium dodecyl sulphate to various proteins. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):825–830. doi: 10.1042/bj1090825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese E. T., Mandels M. Stability of the cellulase of Trichoderma reesei under use conditions. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1980 Feb;22(2):323–335. doi: 10.1002/bit.260220207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodionova N. A., Rumiantseva G. N., Tiunova N. A., Martinovich L. I., Bakhtadze L. N. beta-Gliukozidazy iz griba Geotrichum candidum. Biokhimiia. 1977 Jan;42(1):43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saddler J. N., Khan A. W. Cellulolytic enzyme system of Acetivibrio cellulolyticus. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Mar;27(3):288–294. doi: 10.1139/m81-045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Amemura A., Harada T. Purification and properties of a beta-1,6-clucosidase from Flavobacterium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 19;377(2):410–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliemann W. Beta-D-Glucosidasen (EC 3.2.1.21) der Mikroorganismen. Eine tabellarische Ubersicht. Pharmazie. 1983 May;38(5):287–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd M. G., Tong C. C., Cole A. L. Substrate specificity and mode of action of the cellulases from the thermophilic fungus Thermoascus aurantiacus. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):67–74. doi: 10.1042/bj1930067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewale J. G. Beta-Glucosidase: its role in cellulase synthesis and hydrolysis of cellulose. Int J Biochem. 1982;14(6):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(82)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spears G., Sneyd J. G., Loten E. G. A method for deriving kinetic constants for two enzymes acting on the same substrate. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1149–1151. doi: 10.1042/bj1251149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg D., Vijayakumar P., Reese E. T. beta-Glucosidase: microbial production and effect on enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Feb;23(2):139–147. doi: 10.1139/m77-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppok W., Rapp P., Wagner F. Formation, Location, and Regulation of Endo-1,4-beta-Glucanases and beta-Glucosidases from Cellulomonas uda. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):44–53. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.44-53.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong C. C., Cole A. L., Shepherd M. G. Purification and properties of the cellulases from the thermophilic fungus Thermoascus aurantiacus. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):83–94. doi: 10.1042/bj1910083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezurike G. M. The beta-glucosidase from Botryodiplodia theobromae Pat. Kinetics of enzyme-catalysed hydrolysis of o-nitrophenyl beta-D-glucopyranoside in dioxan/water. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):455–459. doi: 10.1042/bj1750455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezurike G. M. The beta-glucosidase from Botryodiplodia theobromae. Mechanism of enzyme action. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 1;199(1):203–209. doi: 10.1042/bj1990203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. M. The cellulase of Fusarium solani. Purification and specificity of the -(1-4)-glucanase and the -D-glucosidase components. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):353–362. doi: 10.1042/bj1210353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


