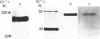Abstract
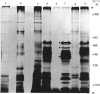
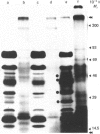
The location of cell proteins with covalently attached lipid was examined in two human squamous-carcinoma cell lines. Cells were labelled with either palmitic acid or myristic acid and disrupted by sonication, followed by differential centrifugation of the cell lysates. SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of the resulting cell fractions indicated that most of the palmitate-labelled proteins were found in cell membranes, whereas most of the myristate-labelled proteins were found in the cytosol, although some were located in cell membranes. Experiments with lipid-labelled proteins extracted with the phase-separable detergent Triton X-114 showed that palmitate-labelled proteins behaved as hydrophobic proteins, partitioning into the lower phase of the detergent, whereas most of the myristate-labelled proteins remained in the upper phase. Although one of these cell lines expressed large amounts of epidermal-growth-factor receptor, this could not be labelled by either myristic acid or palmitic acid, whereas transferrin receptor was labelled by palmitic acid. The lipids normally attached to cell proteins in these two human squamous-carcinoma cell lines were characterized by labelling the cells with [3H]acetate. The labelled cell proteins were exhaustively extracted with organic solvents, and subjected to sequential alkaline and acid hydrolyses to release the attached lipids, which were then analysed by h.p.l.c. Most of the lipid released by the alkaline treatment chromatographed as palmitic acid or stearic acid, whereas the subsequent acid treatment released myristic acid as well as some palmitic acid and stearic acid. No other fatty acids apart from these were found attached to cell proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Cohen P., Santikarn S., Williams D. H., Calder A. G., Smith A., Klee C. B. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of calcineurin B as myristic acid. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S. A., Biemann K., Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Titani K. n-Tetradecanoyl is the NH2-terminal blocking group of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley G. P., Smith J. A., Gusterson B. A. Increased EGF receptors on human squamous carcinoma cell lines. Br J Cancer. 1986 Feb;53(2):223–229. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easty D. M., Easty G. C., Carter R. L., Monaghan P., Butler L. J. Ten human carcinoma cell lines derived from squamous carcinomas of the head and neck. Br J Cancer. 1981 Jun;43(6):772–785. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1981.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Only membrane-associated RSV src proteins have amino-terminally bound lipid. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):161–163. doi: 10.1038/302161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusterson B., Cowley G., McIlhinney J., Ozanne B., Fisher C., Reeves B. Evidence for increased epidermal growth factor receptors in human sarcomas. Int J Cancer. 1985 Dec 15;36(6):689–693. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Krutzsch H. C., Oroszlan S. Myristyl amino-terminal acylation of murine retrovirus proteins: an unusual post-translational proteins modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning R., Lange-Mutschler J. Tightly associated lipids may anchor SV40 large T antigen in plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):736–738. doi: 10.1038/305736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeg J. M., Meng M. S., Ronan R., Fairwell T., Brewer H. B., Jr Human apolipoprotein A-I. Post-translational modification by fatty acid acylation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):3911–3914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Krangel M. S., Strominger J. L. Cysteines in the transmembrane region of major histocompatibility complex antigens are fatty acylated via thioester bonds. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7230–7238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockmann U., Deppert W. Acylated simian virus 40-specific proteins in the plasma membrane of HeLa cells infected with adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid virus Ad2+ND2. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):717–720. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Courtneidge S. A. Two classes of fatty acid acylated proteins exist in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1137–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Koyama A. H., Malfer C., Wen D., Schlesinger M. J. Release of fatty acids from virus glycoproteins by hydroxylamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 10;798(2):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlhinney R. A., Pelly S. J., Chadwick J. K., Cowley G. P. Studies on the attachment of myristic and palmitic acid to cell proteins in human squamous carcinoma cell lines: evidence for two pathways. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1145–1152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien P. J., Zatz M. Acylation of bovine rhodopsin by [3H]palmitic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5054–5057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Glaser L., Merlie J. P. Alpha and beta subunits of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor contain covalently bound lipid. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5364–5367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Towler D. A., Glaser L. Specificity of fatty acid acylation of cellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3784–3790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omary M. B., Trowbridge I. S. Covalent binding of fatty acid to the transferrin receptor in cultured human cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4715–4718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozols J., Carr S. A., Strittmatter P. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase as myristic acid and the complete amino acid sequence of the membrane-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13349–13354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. An N-terminal peptide from p60src can direct myristylation and plasma membrane localization when fused to heterologous proteins. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):374–377. doi: 10.1038/314374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Bracha M., Schlesinger M. J. Evidence for covalent attachment of fatty acids to Sindbis virus glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1687–1691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid binding to vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein: a new type of post-translational modification of the viral glycoprotein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Relation of fatty acid attachment to the translation and maturation of vesicular stomatitis and Sindbis virus membrane glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3334–3339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staufenbiel M., Lazarides E. Ankyrin is fatty acid acylated in erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D., Glaser L. Acylation of cellular proteins with endogenously synthesized fatty acids. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 25;25(4):878–884. doi: 10.1021/bi00352a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S., Omary M. B. Human cell surface glycoprotein related to cell proliferation is the receptor for transferrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3039–3043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Christensen A., Hubbert N. L., Papageorge A. G., Lowy D. R. The p21 ras C-terminus is required for transformation and membrane association. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):583–586. doi: 10.1038/310583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]