Abstract
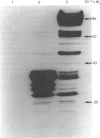
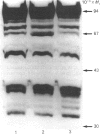
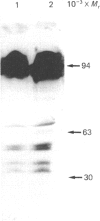
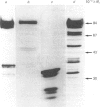
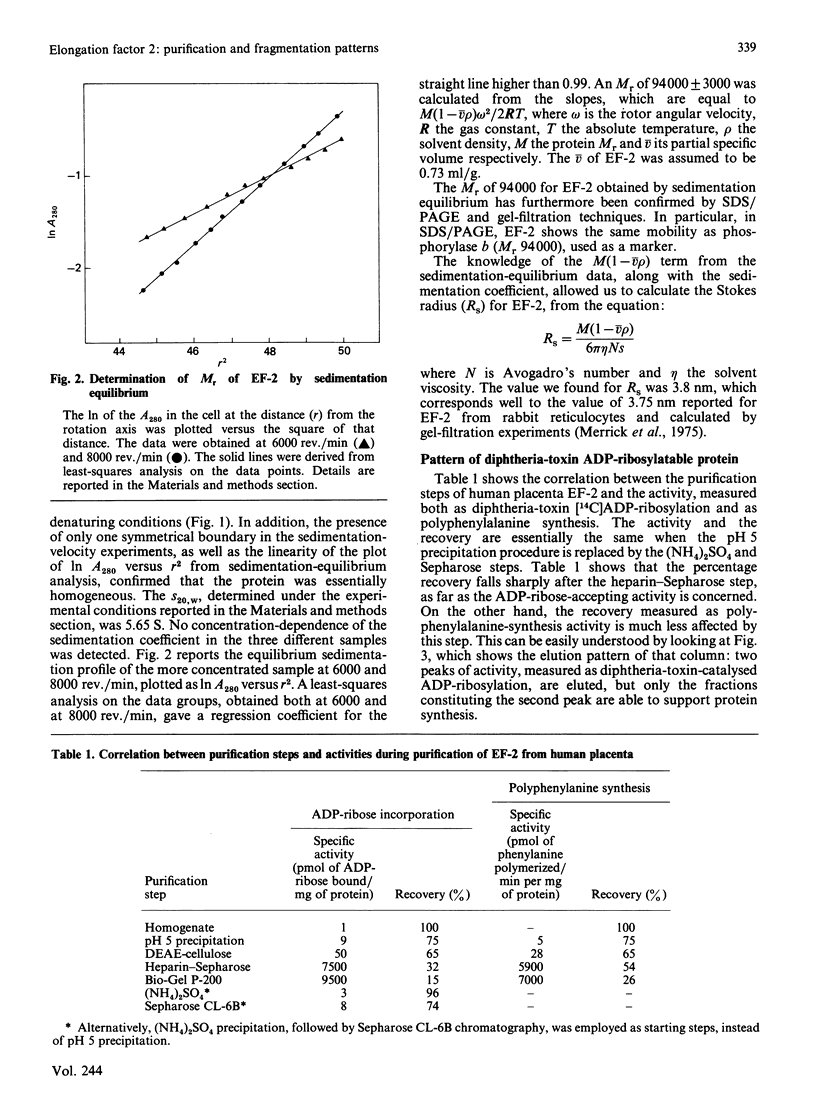
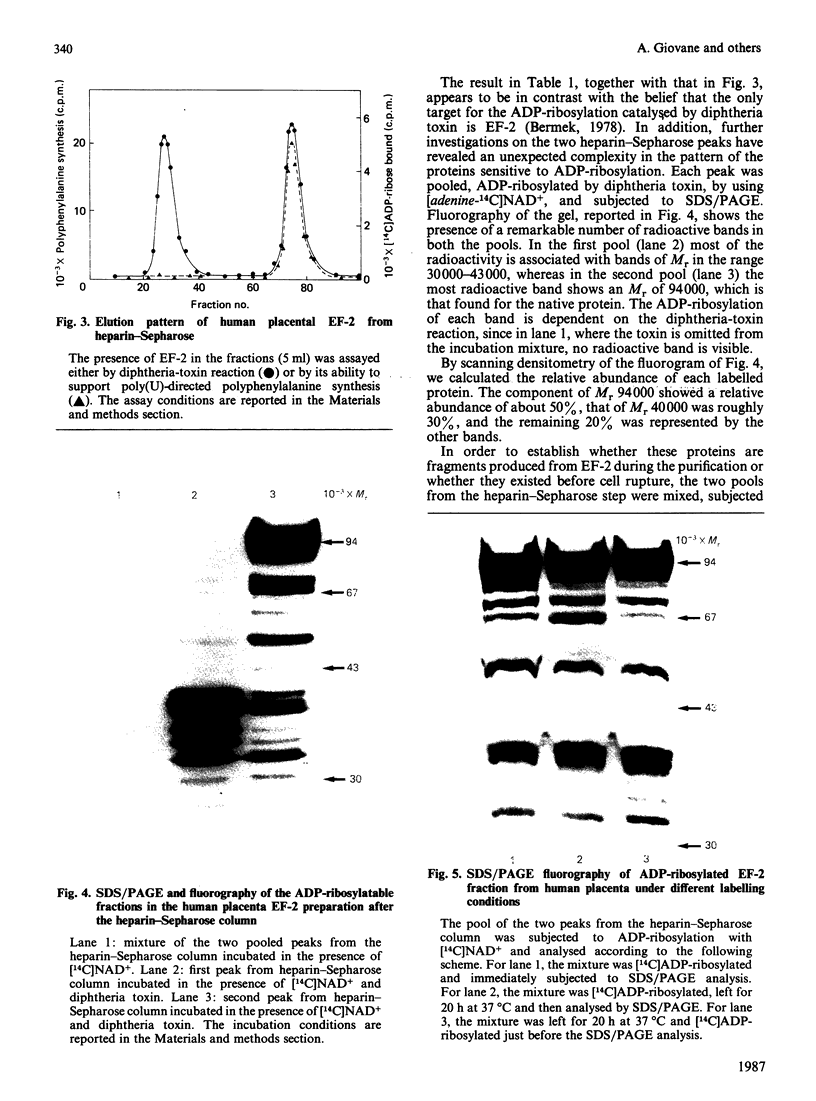
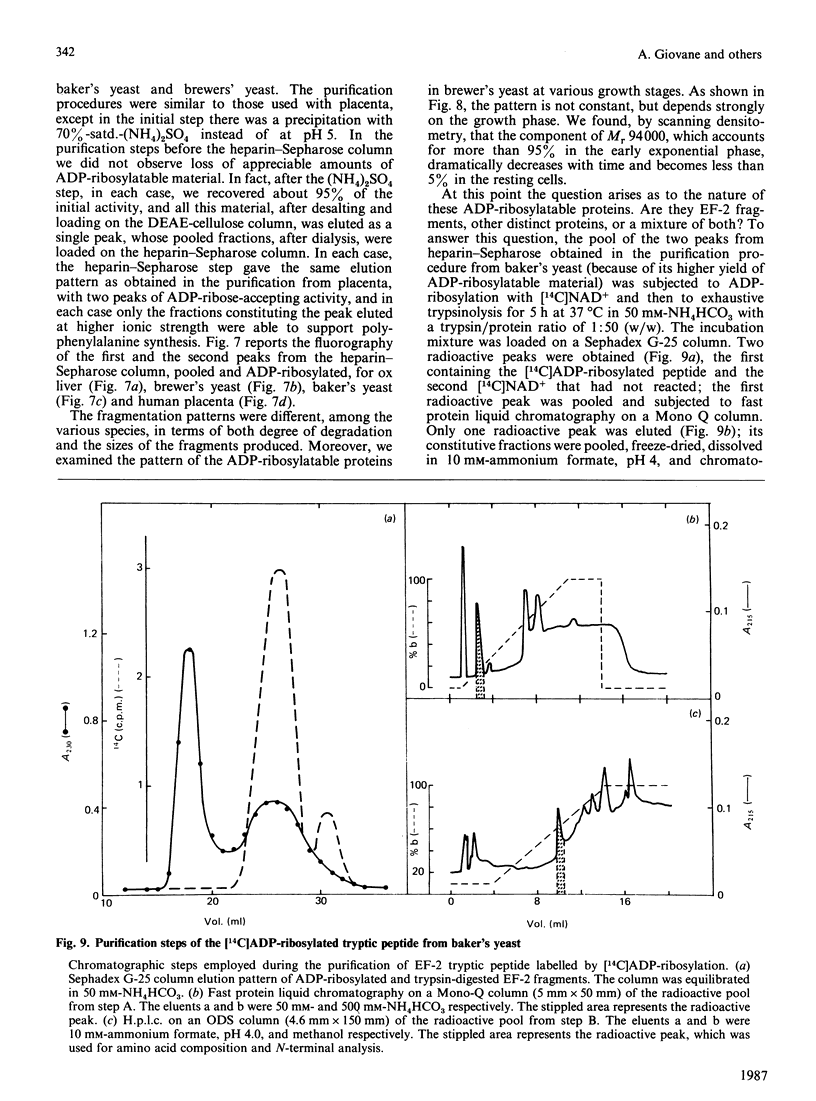
While preparing human placenta elongation factor 2 (EF-2), whose purification and some molecular properties are reported, we noticed the presence of numerous protein fractions which did not have EF-2 activity, but were ADP-ribosylated by diphtheria toxin in the presence of NAD+. All these proteins, like EF-2, were selectively retained by a heparin-Sepharose column, which we used as an affinity-chromatography step. This was also observed when EF-2 was prepared, by this purification step, from other sources, i.e. ox liver and two species of yeasts. In order to assess whether these proteins were a degradation product of EF-2, independent proteins or a mixture of both, they were analysed by subjecting them, after [14C]ADP-ribosylation, to exhaustive trypsinolysis. Only one radioactive peptide was found, thus suggesting that those proteins originate from EF-2 by some proteolytic process. Our findings indicate that this proteolysis does not occur after cell disruption, but is more or less active in the intact cell, depending on the system considered.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bermek E. Formation of a complex involving ADP-ribosylated human translocation factor, guanosine nucleotide and ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermek E. Mechanisms in polypeptide chain elongation on ribosomes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1978;21:63–100. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Bodley J. W. Primary structure at the site in beef and wheat elongation factor 2 of ADP-ribosylation by diphtheria toxin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):253–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang D. M., Weissbach H. Studies on elongation factor II from calf brain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Sep;152(1):114–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Effect of diphtheria toxin on protein synthesis: inactivation of one of the transfer factors. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):83–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. F., Raeburn S., Maxwell E. S. Aminoacyltransferase II from rat liver. II. Some physical and chemical properties of the purified enzyme and its adenosine diphosphate ribose derivative. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1049–1054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera F., Martinez J. A., Moreno N., Sadnik I., McLaughlin C. S., Feinberg B., Moldave K. Identification of an altered elongation factor in temperature-sensitive mutant ts 7'-14 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14347–14349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3553–3555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski W. J., Lee H., Muller P. ADP-ribosyltransferase from beef liver which ADP-ribosylates elongation factor-2. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jul 23;173(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski W. J., Lee H. Purification and properties of an altered form of elongation factor 2 from mutant cells resistant to intoxication by diphtheria toxin. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 1;134(2):237–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel J., Collier R. J., Chung D. W. Interaction of fragment A from diphtheria toxin with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2088–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., Iglewski W. J. Cellular ADP-ribosyltransferase with the same mechanism of action as diphtheria toxin and Pseudomonas toxin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2703–2707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C. Assays for eukaryotic protein synthesis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:108–123. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C., Kemper W. M., Kantor J. A., Anderson W. F. Purification and properties of rabbit reticulocyte protein synthesis elongation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2620–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizumoto K., Iwasaki K., Tanaka M., Kaziro Y. Studies on polypeptide elongation factor 2 from pig liver. I. Purification and properties. J Biochem. 1974 May;75(5):1047–1056. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitikov A. S., Davydova E. K., Ovchinnikov L. P. Endogenous ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 in polyribosome fraction of rabbit reticulocytes. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 15;176(1):261–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80953-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Howard J. B., Bodley J. W. ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 by diphtheria toxin. NMR spectra and proposed structures of ribosyl-diphthamide and its hydrolysis products. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10710–10716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]