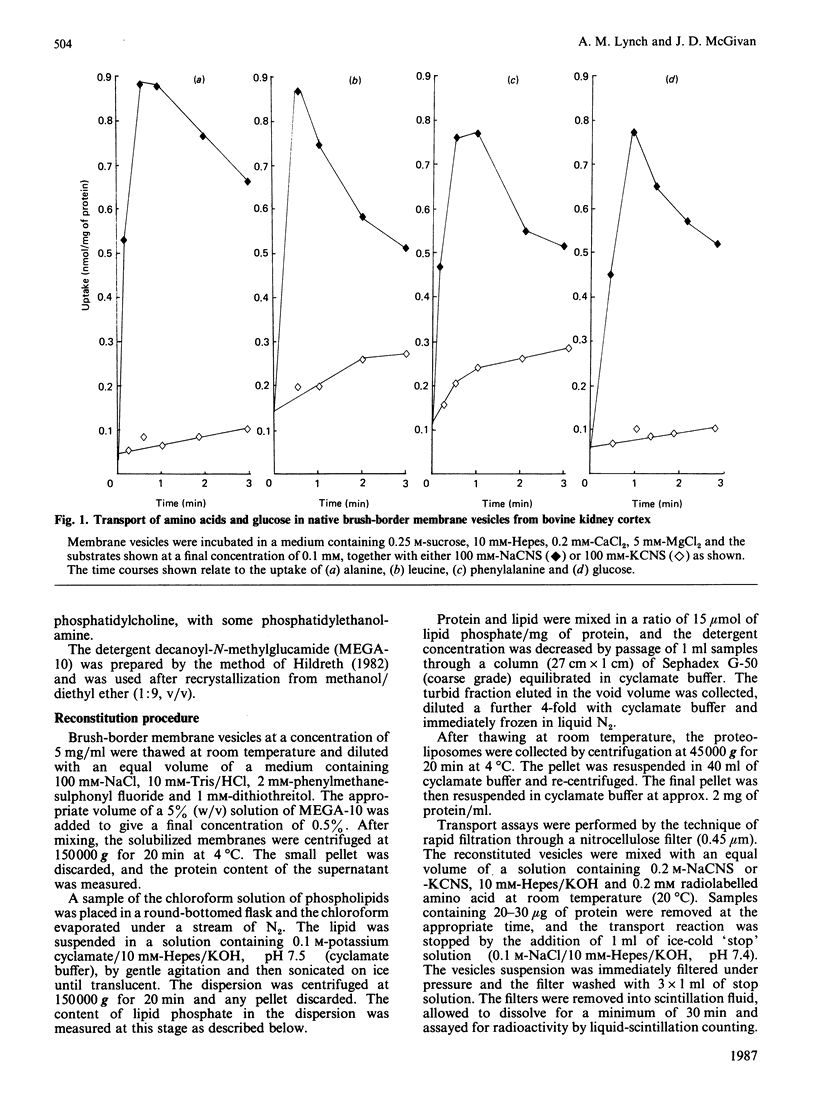
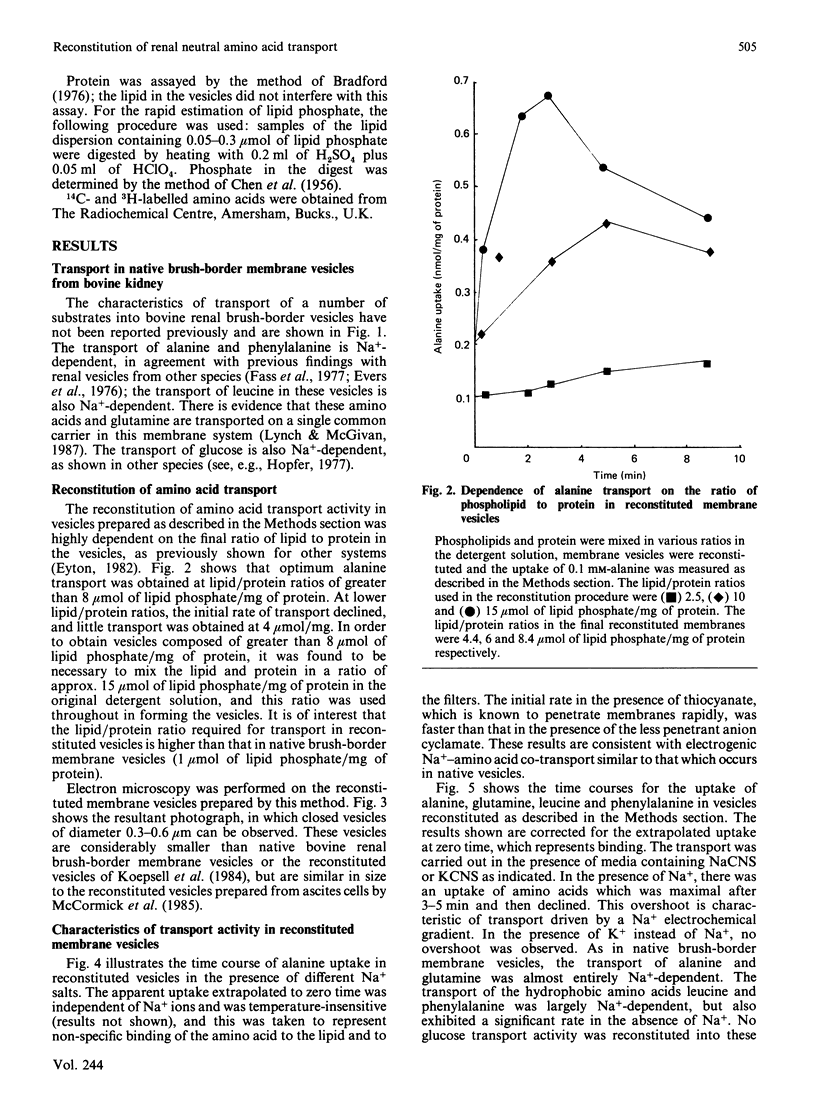
Abstract
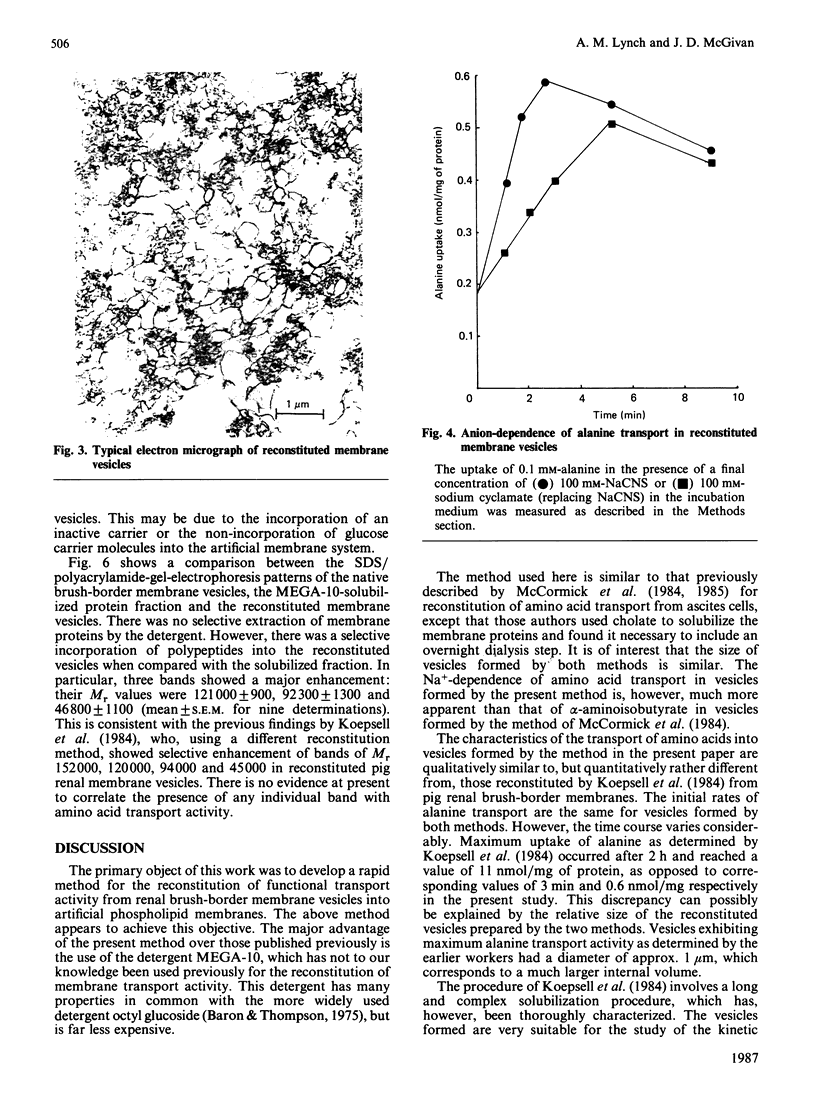
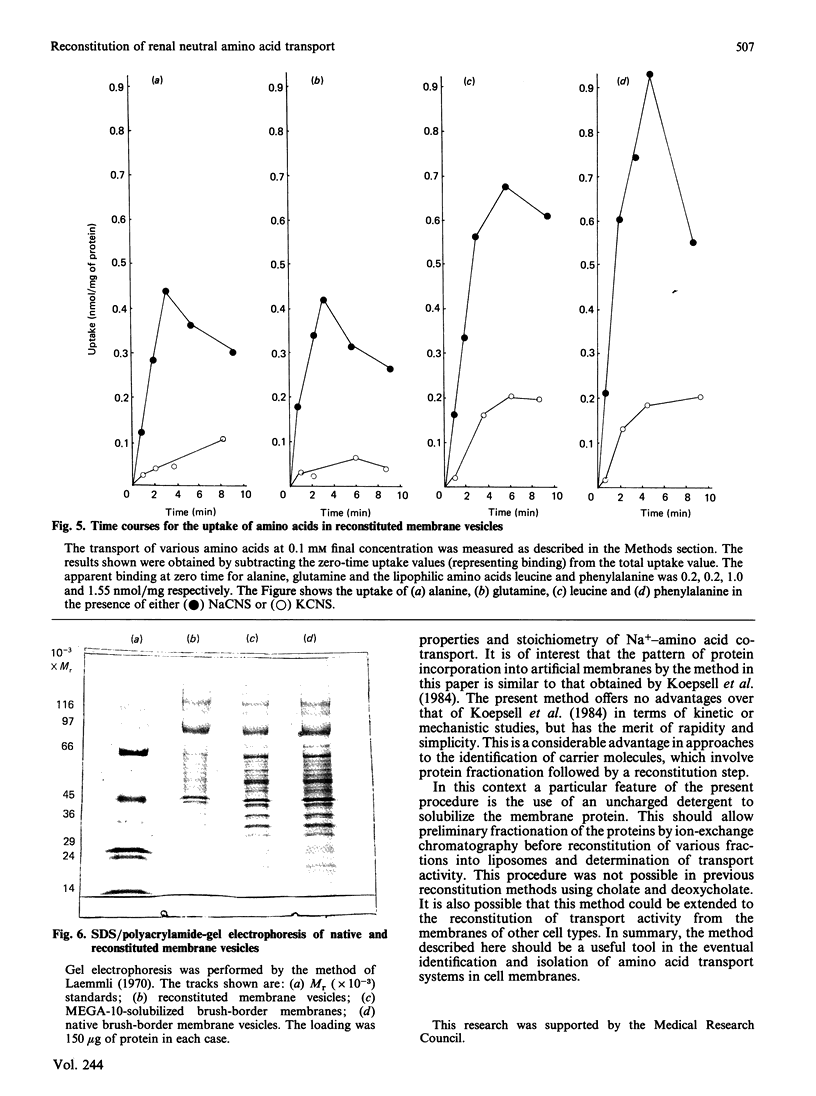
1. A simple and rapid method for the reconstitution of Na+-dependent neutral amino acid transport activity from bovine renal brush border membranes is described. 2. The neutral detergent decanoyl-N-methylglucamide ('MEGA-10') was employed to solubilize the membrane protein. This obviated the necessity for a prolonged dialysis step. 3. The properties of amino acid transport in these vesicles were similar to those observed in native membranes. 4. This should be a useful procedure in the eventual identification and isolation of amino acid transport proteins.
Full text
PDF

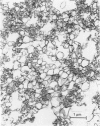
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alleyne G. A., Anderson N. M., Scott B. Glutamine uptake by cortical slices and luminal brush border vesicles of rat kidney. Int J Biochem. 1980;12(1-2):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C., Thompson T. E. Solubilization of bacterial membrane proteins using alkyl glucosides and dioctanoyl phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;382(3):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biber J., Stange G., Stieger B., Murer H. Transport of L-cystine by rat renal brush border membrane vesicles. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Mar;396(4):335–341. doi: 10.1007/BF01063939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biber J., Stieger B., Haase W., Murer H. A high yield preparation for rat kidney brush border membranes. Different behaviour of lysosomal markers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 2;647(2):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchini G., Payne G. S., Oxender D. L. Reconstitution of neutral amino acid transport systems from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Membr Biochem. 1978;1(3-4):269–278. doi: 10.3109/09687687809063851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. ON THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF PHOSPHOLIPASE A. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:414–423. doi: 10.1042/bj0880414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers J., Murer H., Kinne R. Phenylalanine uptake in isolated renal brush border vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 5;426(4):598–615. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eytan G. D. Use of liposomes for reconstitution of biological functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 20;694(2):185–202. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass S. J., Hammerman M. R., Sacktor B. Transport of amino acids in renal brush border membrane vesicles. Uptake of the neutral amino acid L-alanine. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):583–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmann D. R., Roth K. S., Langfitt T. W., Jr, Segal S. L-proline transport by newborn rat kidney brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):253–256. doi: 10.1042/bj1780253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerman M. R., Sacktor B. Na+-dependent transport of glycine in renal brush border membrane vesicles. Evidence for a single specific transport system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 7;686(2):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90112-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerman M. R., Sacktor B. Transport of amino acids in renal brush border membrane vesicles. Uptake of L-proline. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):591–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildreth J. E. N-D-Gluco-N-methylalkanamide compounds, a new class of non-ionic detergents for membrane biochemistry. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 1;207(2):363–366. doi: 10.1042/bj2070363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer U. Kinetics of Na+-dependent D-glucose transport. J Supramol Struct. 1977;7(1):1–13. doi: 10.1002/jss.400070102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne R., Faust R. G. Incorporation of D-glucose-, L-alanine- and phosphate-transport systems from rat renal brush-border membranes into liposomes. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):311–314. doi: 10.1042/bj1680311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsell H., Korn K., Ferguson D., Menuhr H., Ollig D., Haase W. Reconstitution and partial purification of several Na+ cotransport systems from renal brush-border membranes. Properties of the L-glutamate transporter in proteoliposomes. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6548–6558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. I., Silvius J. R., Johnstone R. M. Effect of alkali cations on freeze-thaw-dependent reconstitution of amino acid transport from Ehrlich ascites cell plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5706–5714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. I., Tsang D., Johnstone R. M. A simple and efficient method for reconstitution of amino acid and glucose transport systems from Ehrlich ascites cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jun;231(2):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90398-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane-Anderson N., Alleyne G. A. Transport of glutamine by rat kidney brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):295–300. doi: 10.1042/bj1820295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara P. D., Pepe L. M., Segal S. Cystine uptake by rat renal brush-border vesicles. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 15;194(2):443–449. doi: 10.1042/bj1940443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara P. D., Pepe L. M., Segal S. Sodium gradient dependence of proline and glycine uptake in rat renal brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 4;556(1):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90427-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medow M. S., Roth K. S., Ginkinger K., Segal S. Renal brush-border-membrane vesicles prepared from newborn rats by free-flow electrophoresis and their proline uptake. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):209–214. doi: 10.1042/bj2140209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mircheff A. K., Kippen I., Hirayama B., Wright E. M. Delineation of sodium-stimulated amino acid transport pathways in rabbit kidney brush border vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1982;64(1-2):113–122. doi: 10.1007/BF01870773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger B., Stange G., Biber J., Murer H. Transport of L-cysteine by rat renal brush border membrane vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1983;73(1):25–37. doi: 10.1007/BF01870338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]