Abstract
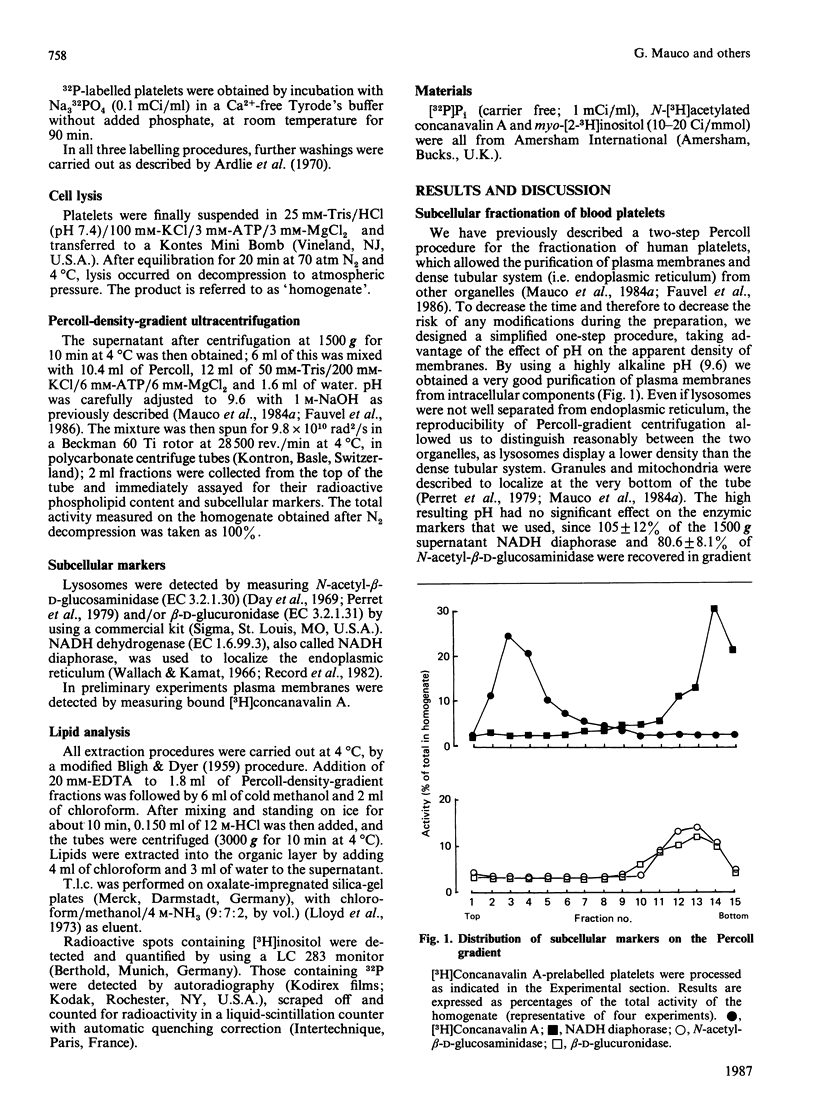
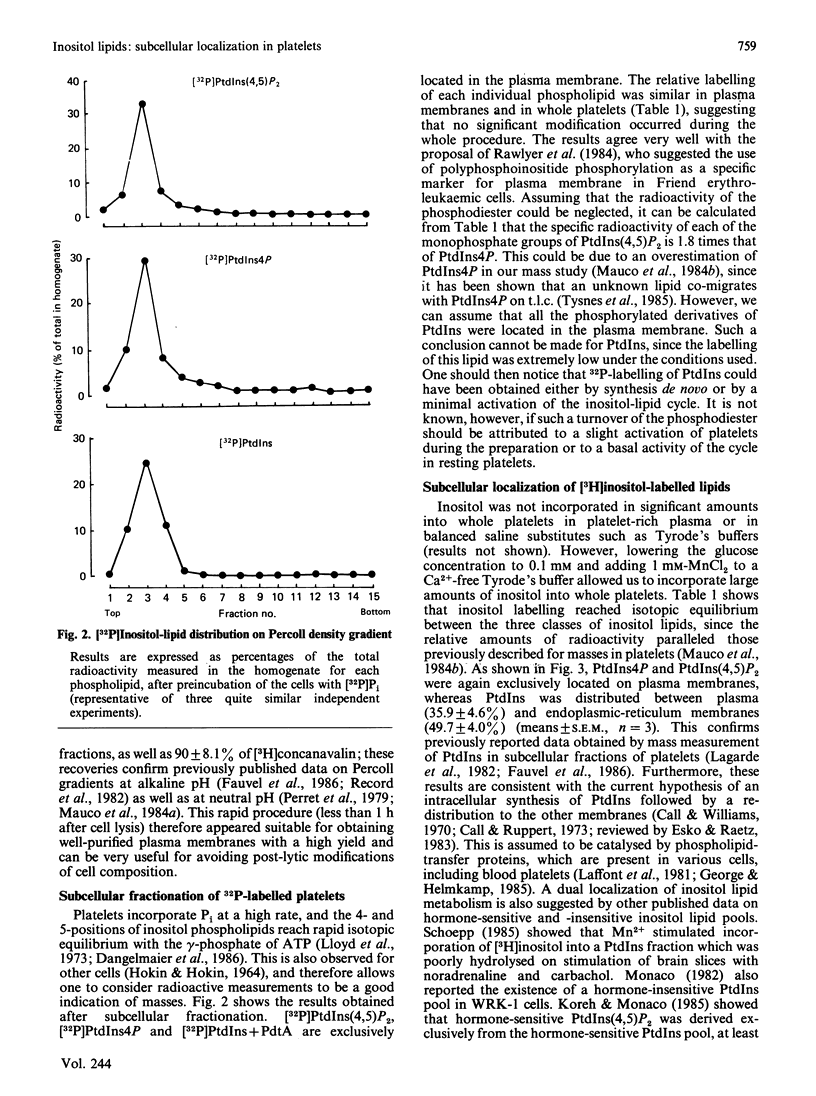
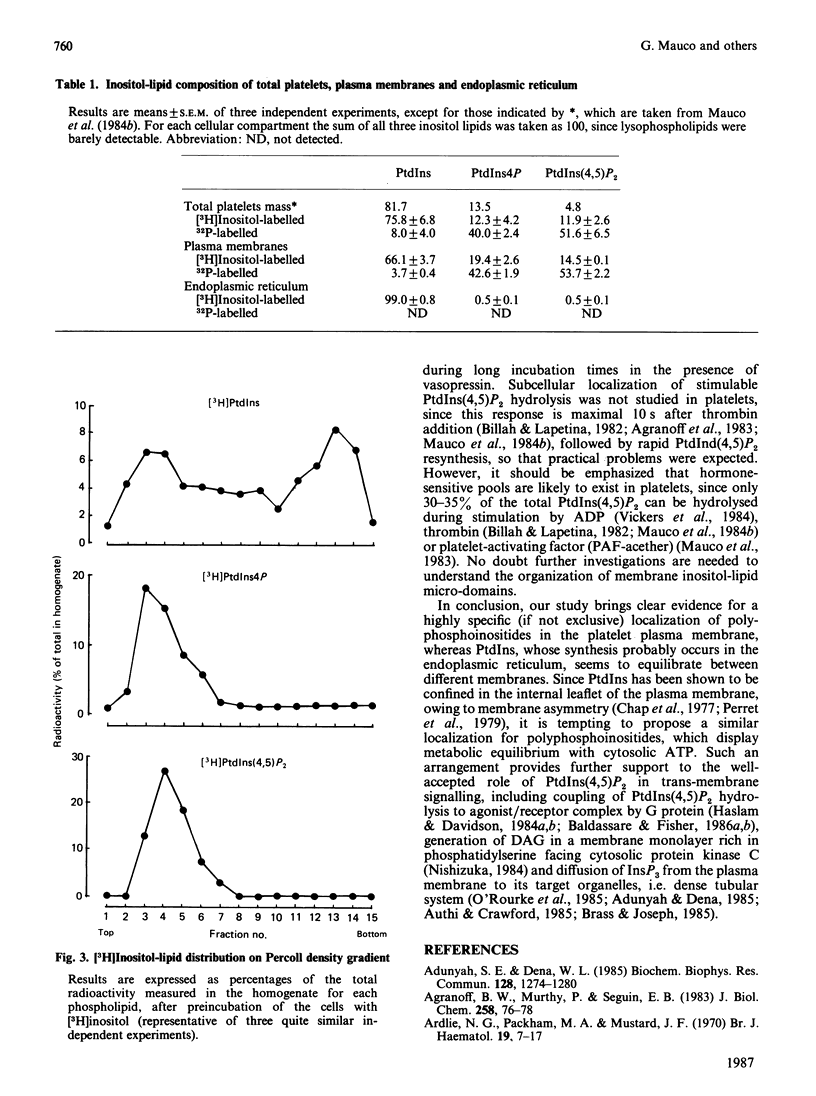
1. By rapid fractionation of blood platelet lysates on Percoll density gradients at alkaline pH (9.6), a very pure plasma-membrane fraction was obtained, as well as discrimination between endoplasmic reticulum and lysosomes. 2. Labelling of intact platelets with [32P]Pi followed by subcellular fractionation showed an exclusive localization of all inositol lipids in the plasma membrane. 3. Preincubation of whole platelets with myo-[3H]inositol in a buffer containing 1 mM-MnCl2 allowed incorporation of the label into PtdIns (phosphatidylinositol) of both plasma and endoplasmic-reticulum membrane, whereas [3H]PtdIns4P (phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate) and [3H]PtdIns(4,5)P2 (phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate) were exclusively found on the plasma membrane. 4. It is concluded that PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2 are exclusively localized in the plasma membrane, whereas PtdIns is present in both plasma and endoplasmic-reticulum membranes. This could provide an explanation for previously reported data on hormone-sensitive and -insensitive inositol lipid pools.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adunyah S. E., Dean W. L. Inositol triphosphate-induced Ca2+ release from human platelet membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1274–1280. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation in suspensions of washed rabbit platelets. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jul;19(1):7–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Authi K. S., Crawford N. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced release of sequestered Ca2+ from highly purified human platelet intracellular membranes. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):247–253. doi: 10.1042/bj2300247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldassare J. J., Fisher G. J. GTP and cytosol stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis in isolated platelet membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):801–805. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldassare J. J., Fisher G. J. Regulation of membrane-associated and cytosolic phospholipase C activities in human platelets by guanosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11942–11944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Rapid decrease of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12705–12708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Joseph S. K. A role for inositol triphosphate in intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and granule secretion in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15172–15179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call F. L., 2nd, Rubert M. Diglyceride kinase in human platelets. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jul;14(4):466–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell C. R., Fishman J. B., Fine R. E. Coated vesicles contain a phosphatidylinositol kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):10948–10951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter J. R., Kennedy E. P. Enzymatic synthesis of cytidine diphosphate diglyceride. J Lipid Res. 1966 Sep;7(5):678–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chap H. J., Zwaal R. F., van Deenen L. L. Action of highly purified phospholipases on blood platelets. Evidence for an asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in the surface membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 2;467(2):146–164. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90192-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dangelmaier C. A., Daniel J. L., Smith J. B. Determination of basal and stimulated levels of inositol triphosphate in [32P]orthophosphate-labeled platelets. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 1;154(2):414–419. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day H. J., Holmsen H., Hovig T. Subcellular particles of human platelets. A biochemical and electron microscopic study with particular reference to the influence of fractionation techniques. Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1969;7:3–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel J., Chap H., Roques V., Levy-Toledano S., Douste-Blazy L. Biochemical characterization of plasma membranes and intracellular membranes isolated from human platelets using Percoll gradients. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 27;856(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George P. Y., Helmkamp G. M., Jr Purification and characterization of a phosphatidylinositol transfer protein from human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 11;836(2):176–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., HOKIN M. R. THE INCORPORATION OF 32P FROM TRIPHOSPHATE INTO POLYPHOSPHOINOSITIDES (GAMMA-32P)ADENOSINE AND PHOSPHATIDIC ACID IN ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 2;84:563–575. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN M. R., HOKIN L. E. Enzyme secretion and the incorporation of P32 into phospholipides of pancreas slices. J Biol Chem. 1953 Aug;203(2):967–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Guanine nucleotides decrease the free [Ca2+] required for secretion of serotonin from permeabilized blood platelets. Evidence of a role for a GTP-binding protein in platelet activation. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 20;174(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Potentiation by thrombin of the secretion of serotonin from permeabilized platelets equilibrated with Ca2+ buffers. Relationship to protein phosphorylation and diacylglycerol formation. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):351–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2220351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Receptors and phosphoinositide-generated second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:205–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koréh K., Monaco M. E. The relationship of hormone-sensitive and hormone-insensitive phosphatidylinositol to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in the WRK-1 cell. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):88–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laffont F., Chap H., Soula G., Douste-Blazy L. Phospholipid exchange proteins from platelet cytosol possibly involved in phospholipid effect. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Oct 30;102(4):1366–1371. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagarde M., Guichardant M., Menashi S., Crawford N. The phospholipid and fatty acid composition of human platelet surface and intracellular membranes isolated by high voltage free flow electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3100–3104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Stimulation of phosphatidic acid production in platelets precedes the formation of arachidonate and parallels the release of serotonin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 25;573(2):394–402. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. V., Nishizawa E. E., Joist J. H., Mustard J. F. Effect of ADP-induced aggregation on 32 PO 4 incorporation into phosphatidic acid and the phosphoinositides of rabbit platelets. Br J Haematol. 1973 May;24(5):589–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. T., Call F. L., 2nd, Williams W. J. The biosynthesis of phosphatidylinositol in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1949–1955. doi: 10.1172/JCI106414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg G. A., Jergil B., Sundler R. Subcellular localization and enzymatic properties of rat liver phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 30;846(3):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre D. E., Pollock W. K. Platelet-activating factor stimulates phosphatidylinositol turnover in human platelets. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):433–437. doi: 10.1042/bj2120433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Platelet activating factor (PAF-acether) promotes an early degradation of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate in rabbit platelets. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 21;153(2):361–365. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80643-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Chap H., Simon M. F., Douste-Blazy L. Phosphatidic and lysophosphatidic acid production in phospholipase C-and thrombin-treated platelets. Possible involvement of a platelet lipase. Biochimie. 1978 Sep 29;60(6-7):653–661. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80784-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Dangelmaier C. A., Smith J. B. Inositol lipids, phosphatidate and diacylglycerol share stearoylarachidonoylglycerol as a common backbone in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):933–940. doi: 10.1042/bj2240933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Fauvel J., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Studies on enzymes related to diacylglycerol production in activated platelets. II. Subcellular distribution, enzymatic properties and positional specificity of diacylglycerol- and monoacylglycerol-lipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 14;796(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco M. E. The phosphatidylinositol cycle in WRK-1 cells. Evidence for a separate, hormone-sensitive phosphatidylinositol pool. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2137–2139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke F. A., Halenda S. P., Zavoico G. B., Feinstein M. B. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate releases Ca2+ from a Ca2+-transporting membrane vesicle fraction derived from human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):956–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret B., Chap H. J., Douste-Blazy L. Asymmetric distribution of arachidonic acid in the plasma membrane of human platelets. A determination using purified phospholipases and a rapid method for membrane isolation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 5;556(3):434–446. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rana R. S., Kowluru A., MacDonald M. J. Secretagogue-responsive and -unresponsive pools of phosphatidylinositol in pancreatic islets. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Mar;245(2):411–416. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawyler A. J., Roelofsen B., Wirtz K. W., Op den Kamp J. A. (poly) Phosphoinositide phosphorylation is a marker for plasma membrane in Friend erythroleukaemic cells. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 1;148(1):140–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E. Human platelets contain phospholipase C that hydrolyzes polyphosphoinositides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5417–5420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp D. D. Manganese stimulates the incorporation of [3H]inositol into a pool of phosphatidylinositol in brain that is not coupled to agonist-induced hydrolysis. J Neurochem. 1985 Nov;45(5):1481–1486. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfred M. A., Wells W. W. Subcellular incorporation of 32P into phosphoinositides and other phospholipids in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7659–7665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfred M. A., Wells W. W. Subcellular site and mechanism of vasopressin-stimulated hydrolysis of phosphoinositides in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7666–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Wells W. W. Phosphorylation of rat liver nuclear envelopes. I. Characterization of in vitro protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9360–9367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenawa T., Egawa K. CDP-diglyceride:inositol transferase from rat liver. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5419–5423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W., MacDonald G. Synthesis of molecular classes of cytidine diphosphate diglyceride by rat liver in vivo and in vitro. Can J Biochem. 1977 Nov;55(11):1153–1158. doi: 10.1139/o77-172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooke N. E., Hales C. N., Hutton J. C. Ca2+-sensitive phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate metabolism in a rat beta-cell tumour. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 15;219(2):471–480. doi: 10.1042/bj2190471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tysnes O. B., Aarbakke G. M., Verhoeven A. J., Holmsen H. Thin-layer chromatography of polyphosphoinositides from platelet extracts: interference by an unknown phospholipid. Thromb Res. 1985 Nov 1;40(3):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers J. D., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Mustard J. F. Accumulation of the inositol phosphates in thrombin-stimulated, washed rabbit platelets in the presence of lithium. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):399–405. doi: 10.1042/bj2240399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


