Abstract
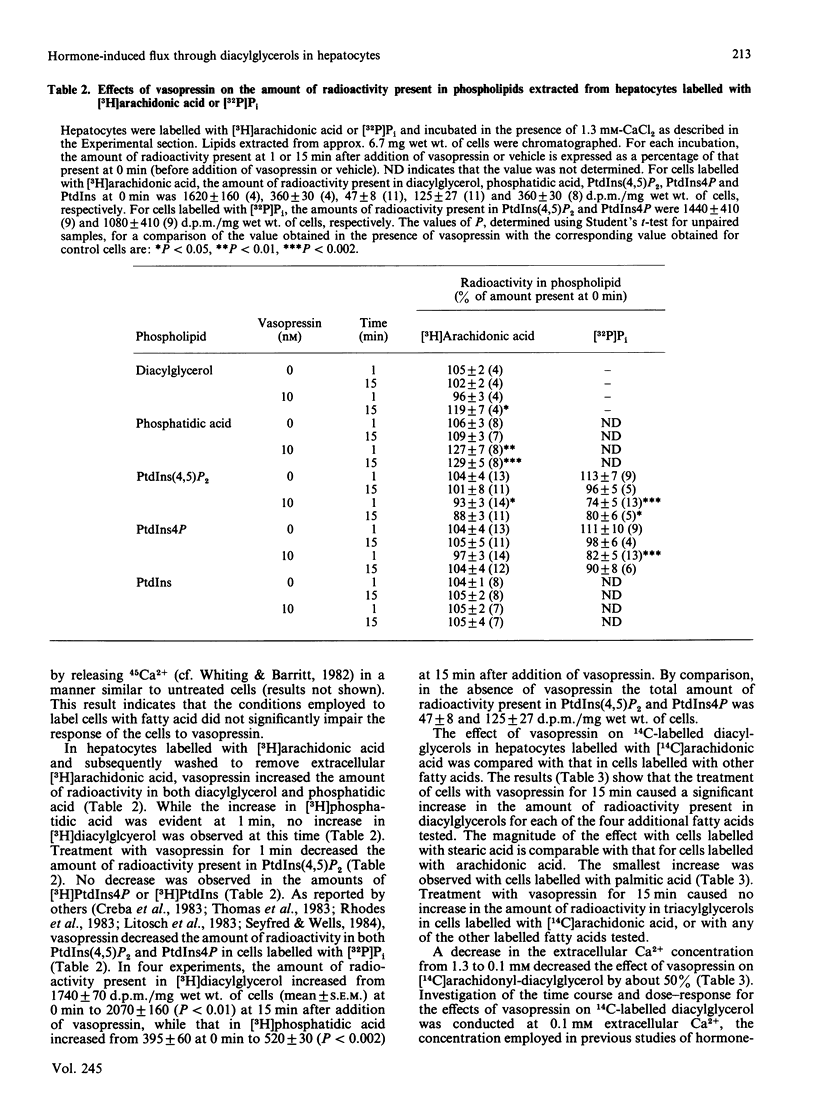
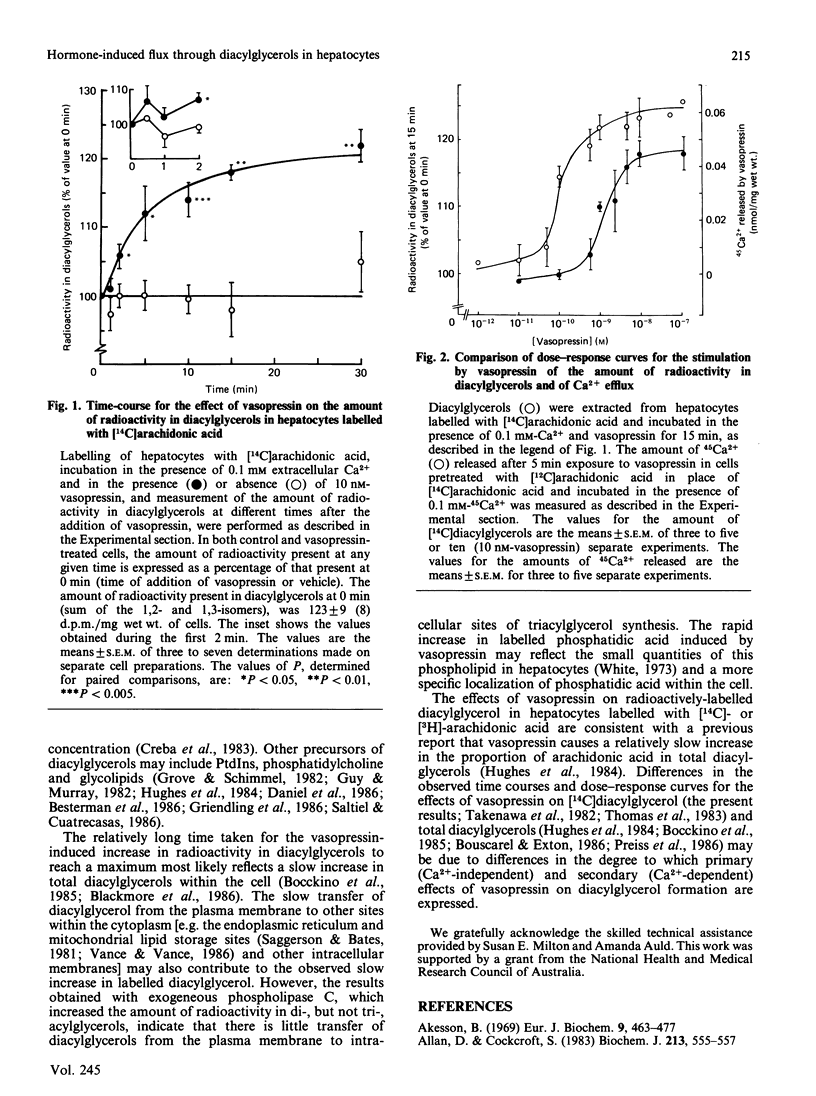
1. In isolated hepatocytes prelabelled with [14C]-arachidonic, -stearic, -linoleic, -oleic or -palmitic acids, vasopressin increased the amount of radioactivity present in diacylglycerols. The largest increase was observed in cells labelled with arachidonic or stearic acids. 2. In cells prelabelled with [14C]- or [3H]-arachidonic acid, the onset of the increase in radioactivity in diacylglycerols induced by vasopressin was slow, the increase was partly dependent on the presence of extracellular Ca2+, and was associated with an increase in radioactivity present in phosphatidic acid which was more rapid in onset. Vasopressin decreased the amount of [3H]arachidonyl-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, but the magnitude of this decrease was less than 10% of the observed increase in radioactivity in [3H]arachidonyl-diacylglycerol. 3. The concentration of vasopressin which gave half-maximal increase in [14C]arachidonyl-diacylglycerol at low extracellular Ca2+ was 10-fold higher than that which gave half-maximal stimulation of 45Ca2+ efflux. Phenylephrine, but not glucagon, also increased the amount of [14C]arachidonyl-diacylglycerol. 4. It is concluded that an early action of vasopressin on the liver cell is to increase the flux of carbon from phospholipids, including the phosphoinositides, to diacylglycerols.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akesson B. Composition of rat liver triacylglycerols and diacylglycerols. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jul;9(4):463–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Cockcroft S. The fatty acid composition of 1,2-diacylglycerol and polyphosphoinositides from human erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 1;213(2):555–557. doi: 10.1042/bj2130555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Duronio V., Cuatrecasas P. Rapid formation of diacylglycerol from phosphatidylcholine: a pathway for generation of a second messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C activities of platelets. Differential substrate specificity, Ca2+ requirement, pH dependence, and cellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10227–10231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol metabolism in rat hepatocytes stimulated by glycogenolytic hormones. Effects of angiotensin, vasopressin, adrenaline, ionophore A23187 and calcium-ion deprivation. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):661–668. doi: 10.1042/bj1820661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Strickland W. G., Bocckino S. B., Exton J. H. Mechanism of hepatic glycogen synthase inactivation induced by Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Studies using phospholipase C and phorbol myristate acetate. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):235–242. doi: 10.1042/bj2370235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Stimulation of 1,2-diacylglycerol accumulation in hepatocytes by vasopressin, epinephrine, and angiotensin II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14201–14207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouscarel B., Exton J. H. Regulation of hepatic glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen synthase by calcium and diacylglycerol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 29;888(1):126–134. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bréant B., Keppens S., De Wulf H. Heterologous desensitization of the cyclic AMP-independent glycogenolytic response in rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 15;200(3):509–514. doi: 10.1042/bj2000509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Godfrey P. P., McKinney J. S., Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F., Putney J. W., Jr The second messenger linking receptor activation to internal Ca release in liver. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):63–66. doi: 10.1038/309063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Prpić V., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Stimulation of inositol trisphosphate formation in hepatocytes by vasopressin, adrenaline and angiotensin II and its relationship to changes in cytosolic free Ca2+. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 1;227(1):79–90. doi: 10.1042/bj2270079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel L. W., Waite M., Wykle R. L. A novel mechanism of diglyceride formation. 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate stimulates the cyclic breakdown and resynthesis of phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9128–9132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K., Rittenhouse S. E., Brock T. A., Ekstein L. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Sustained diacylglycerol formation from inositol phospholipids in angiotensin II-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5901–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove R. I., Schimmel S. D. Effects of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate on glycerolipid metabolism in cultured myoblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 13;711(2):272–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy G. R., Murray A. W. Effects of a tumor promoter on phospholipid metabolism in HeLa cells. Cancer Res. 1983 Nov;43(11):5564–5569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy G. R., Murray A. W. Tumor promoter stimulation of phosphatidylcholine turnover in HeLa cells. Cancer Res. 1982 May;42(5):1980–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halenda S. P., Rubin R. P. Phospholipid turnover in isolated rat pancreatic acini. Consideration of the relative roles of phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):713–721. doi: 10.1042/bj2080713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holub B. J., Kuksis A. Differential distribution of orthophosphate- 32 P and glycerol- 14 C among molecular species of phosphatidylinositols of rat liver in vivo. J Lipid Res. 1971 Nov;12(6):699–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holub B. J., Kuksis A. Metabolism of molecular species of diacylglycerophospholipids. Adv Lipid Res. 1978;16:1–125. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024916-9.50007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holub B. J., Kuksis A., Thompson W. Molecular species of mono-, di-, and triphosphoinositides of bovine brain. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):558–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes B. P., Rye K. A., Pickford L. B., Barritt G. J., Chalmers A. H. A transient increase in diacylglycerols is associated with the action of vasopressin on hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):535–540. doi: 10.1042/bj2220535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Michell R. H. Hormone-stimulated metabolism of inositol lipids and its relationship to hepatic receptor function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Oct;9(5):377–379. doi: 10.1042/bst0090377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Michell R. H., Hems D. A. Phosphatidylinositol metabolism in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):155–165. doi: 10.1042/bj1940155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Lin S. H., Fain J. N. Rapid changes in hepatocyte phosphoinositides induced by vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13727–13732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Kirk C. J., Jones L. M., Downes C. P., Creba J. A. The stimulation of inositol lipid metabolism that accompanies calcium mobilization in stimulated cells: defined characteristics and unanswered questions. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Dec 18;296(1080):123–138. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M. J., Gershengorn M. C. Thyroliberin stimulates rapid hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate by a phosphodiesterase in rat mammotropic pituitary cells. Evidence for an early Ca2+-independent action. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):287–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2160287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Prpić V., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in hepatocytes by vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2770–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin stimulates the generation from hepatic plasma membranes of modulators derived from an inositol glycolipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfred M. A., Wells W. W. Subcellular site and mechanism of vasopressin-stimulated hydrolysis of phosphoinositides in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7666–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenawa T., Homma Y., Nagai Y. Increased formation of phosphatidic acid induced with vasopressin or Ca2+ ionophore A23187 in rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Aug 15;31(16):2663–2667. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90715-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Alexander J., Williamson J. R. Relationship between inositol polyphosphate production and the increase of cytosolic free Ca2+ induced by vasopressin in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5574–5584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Marks J. S., Coll K. E., Williamson J. R. Quantitation and early kinetics of inositol lipid changes induced by vasopressin in isolated and cultured hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5716–5725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing R. J., Prpic V., Jiang H., Exton J. H. Hormone-stimulated polyphosphoinositide breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance J. E., Vance D. E. Specific pools of phospholipids are used for lipoprotein secretion by cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4486–4491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting J. A., Barritt G. J. On the mechanism by which hormones induce the release of Ca2+ from mitochondria in the liver cell. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):121–129. doi: 10.1042/bj2060121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


