Abstract
1. myo-[3H]Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate [Ins(1,4,5)P3], when added to lysed platelets, was rapidly converted into [3H]inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate [Ins(1,3,4,5)P4], which was in turn converted into [3H]inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate [Ins(1,3,4)P3]. This result demonstrates that platelets have the same metabolic pathways for interconversion of inositol polyphosphates that are found in other cells. 2. Labelling of platelets with [32P]Pi, followed by h.p.l.c., was used to measure thrombin-induced changes in the three inositol polyphosphates. Interfering compounds were removed by a combination of enzymic and non-enzymic techniques. 3. Ins(1,4,5)P3 was formed rapidly, and reached a maximum at about 4 s. It was also rapidly degraded, and was no longer detectable after 30-60 s. 4. Formation of Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 was almost as rapid as that of Ins(1,4,5)P3, and it remained detectable for a longer time. 5. Ins(1,3,4)P3 was formed after an initial lag, and this isomer reached its maximum, which was 10-fold higher than that of Ins(1,4,5)P3, at 30 s. 6. Comparison of the intracellular Ca2+ concentration as measured with fura-2 indicates that agents other than Ins(1,4,5)P3 are responsible for the sustained maintenance of a high concentration of intracellular Ca2+. It is proposed that either Ins(1,3,4)P3 or Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 may also be Ca2+-mobilizing agents.
Full text
PDF

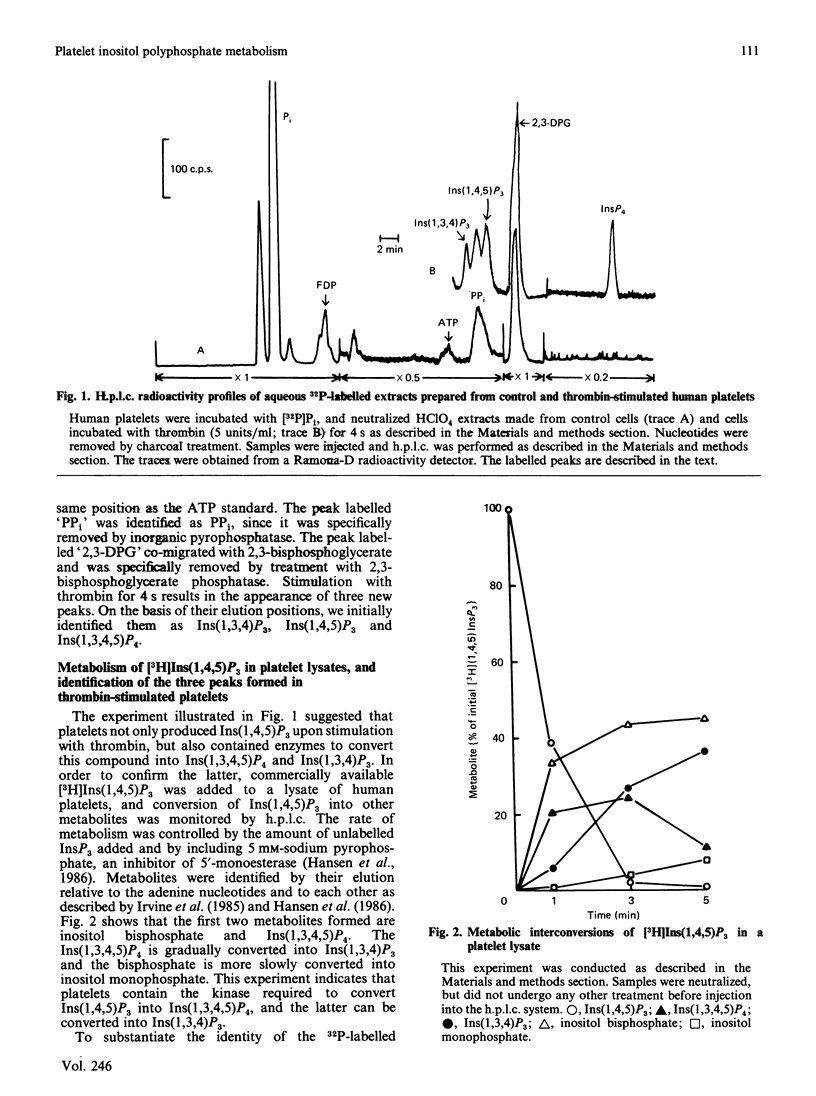


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTER R. H., JANDL J. H. PLATELET SEQUESTRATION IN MAN. I. METHODS. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:843–855. doi: 10.1172/JCI104970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
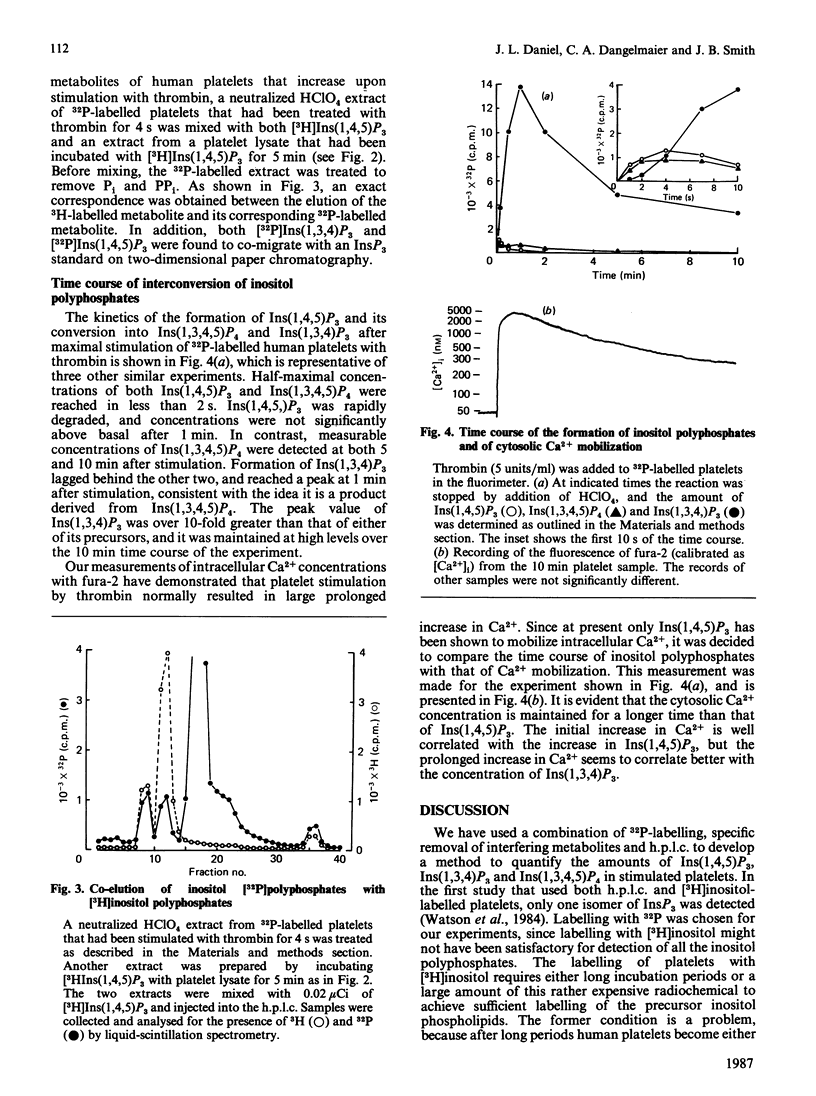
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Joseph S. K. A role for inositol triphosphate in intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and granule secretion in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15172–15179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., McKinney J. S., Irvine R. F., Putney J. W., Jr Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate formation in Ca2+-mobilizing-hormone-activated cells. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2320237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerdan S., Hansen C. A., Johanson R., Inubushi T., Williamson J. R. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic analysis of myo-inositol phosphates including inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14676–14680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dangelmaier C. A., Daniel J. L., Smith J. B. Determination of basal and stimulated levels of inositol triphosphate in [32P]orthophosphate-labeled platelets. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 1;154(2):414–419. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. L., Dangelmaier C. A., Selak M., Smith J. B. ADP stimulates IP3 formation in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81000-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Irvine R. F. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and not phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate is the probable precursor of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in agonist-stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):501–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2380501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Mah S., Williamson J. R. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8100–8103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Downes C. P. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands may both result indirectly from receptor-stimulated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2380507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Dangelmaier C. A., Akkerman J. W. Determination of levels of glycolytic intermediates and nucleotides in platelets by pulse-labeling with [32P]orthophosphate. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):266–272. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Anggård E. E., Letcher A. J., Downes C. P. Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2290505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Berridge M. J. Specificity of inositol phosphate-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization from Swiss-mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):301–304. doi: 10.1042/bj2400301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M. Micro-injection of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates sea urchin eggs by a mechanism dependent on external Ca2+. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):917–920. doi: 10.1042/bj2400917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii H., Connolly T. M., Bross T. E., Majerus P. W. Inositol cyclic triphosphate [inositol 1,2-(cyclic)-4,5-triphosphate] is formed upon thrombin stimulation of human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6397–6401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Thomas A. P., Williams R. J., Irvine R. F., Williamson J. R. myo-Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. A second messenger for the hormonal mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ in liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3077–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek J. L. Inositol bis-, tris-, and tetrakis(phosphate)s: analysis in tissues by HPLC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4162–4166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Kirk C. J., Jones L. M., Downes C. P., Creba J. A. The stimulation of inositol lipid metabolism that accompanies calcium mobilization in stimulated cells: defined characteristics and unanswered questions. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Dec 18;296(1080):123–138. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J., Irvine R. F. Liberation of [3H]arachidonic acid and changes in cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated by ionomycin and collagen. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):869–877. doi: 10.1042/bj2350869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E., Sasson J. P. Mass changes in myoinositol trisphosphate in human platelets stimulated by thrombin. Inhibitory effects of phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8657–8660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier M. F., Dentand I. A., Lew P. D., Capponi A. M., Vallotton M. B. Interconversion of inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate to inositol (1,3,4,5)-tetrakisphosphate and (1,3,4)-trisphosphate in permeabilized adrenal glomerulosa cells is calcium-sensitive and ATP-dependent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 29;139(1):259–265. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGINO Y., MIYOSHI Y. THE SPECIFIC PRECIPITATION OF ORTHOPHOSPHATE AND SOME BIOCHEMICAL APPLICATIONS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2360–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. J., Prpic V., Powers F. S., Bocckino S. B., Isaacks R. E., Exton J. H. Perturbation of the human T-cell antigen receptor-T3 complex leads to the production of inositol tetrakisphosphate: evidence for conversion from inositol trisphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6098–6102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. The rapid formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets by thrombin is inhibited by prostacyclin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13199–13203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Reep B., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. Collagen stimulates [3H]inositol trisphosphate formation in indomethacin-treated human platelets. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 15;226(3):831–837. doi: 10.1042/bj2260831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


