Abstract
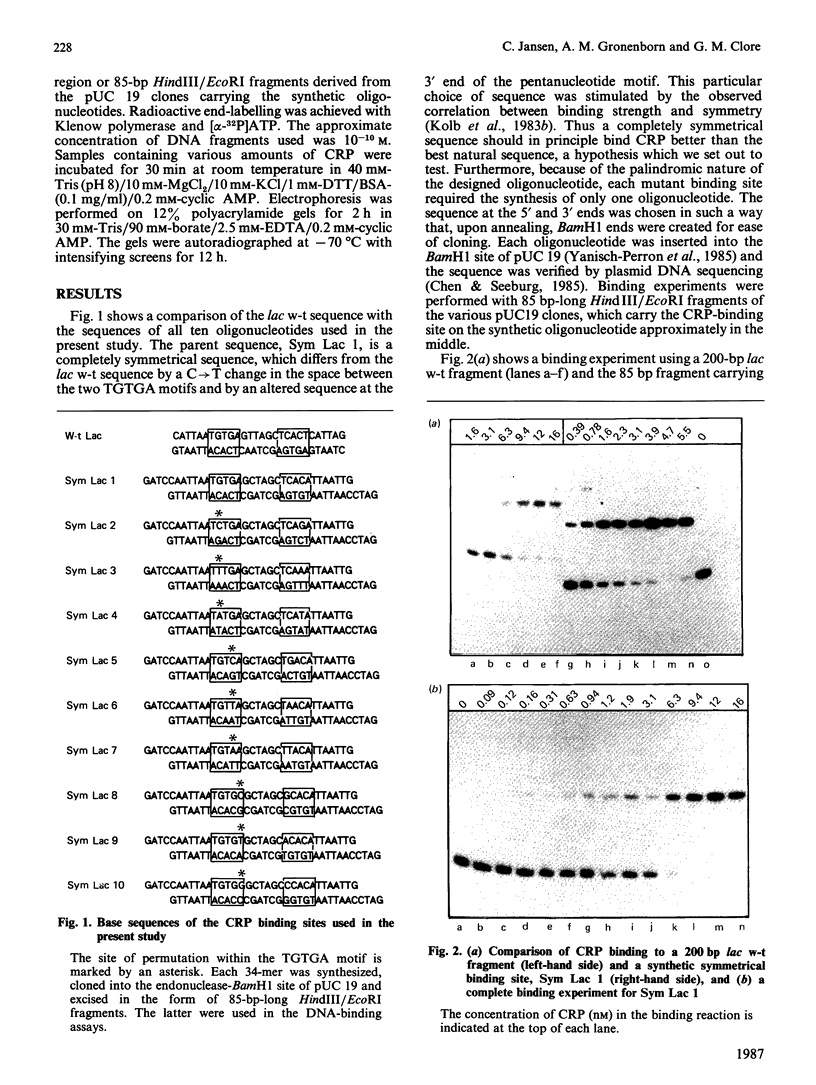
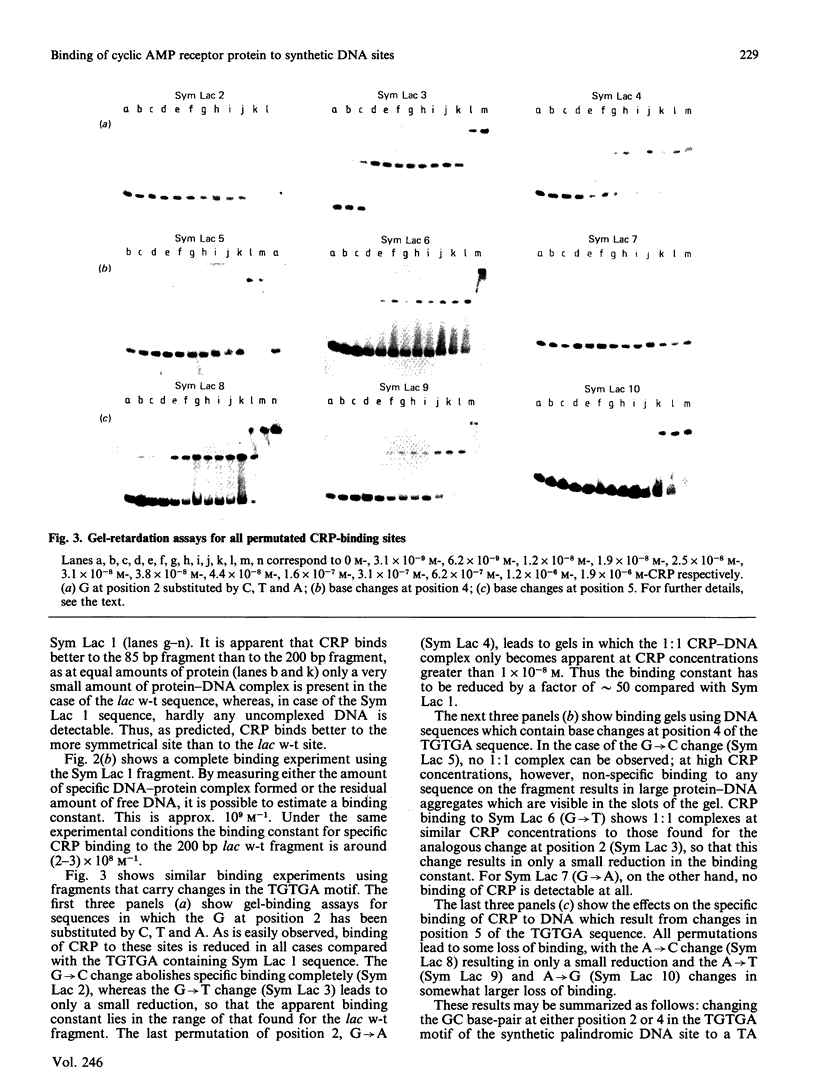
The binding of the cyclic AMP receptor protein (CRP) to symmetrical synthetic DNA-binding sites was investigated with a gel-retardation assay. A set of ten different sequences was employed, comprising all base permutations at positions 2, 4, and 5 of the consensus sequence 5'(TGTGA)3'. We show that: (i) CRP has a higher affinity for the completely symmetrical site than towards the lac wild-type site; (ii) base substitutions at position 2 lead to either a complete loss of specific CRP binding (G----C), a reduction in specific CRP binding (G----A) or only marginal effects on specific CRP binding (G----T); (iii) changes at position 4 abolish (G----C; G----A) or reduce (G----T) specific CRP binding; and (iv) base permutations at position 5 reduce specific CRP binding, but never completely abolish it. Thus position 4, and to a lesser extent position 2, in the DNA consensus sequence are the most crucial ones for specific binding by CRP.
Full text
PDF
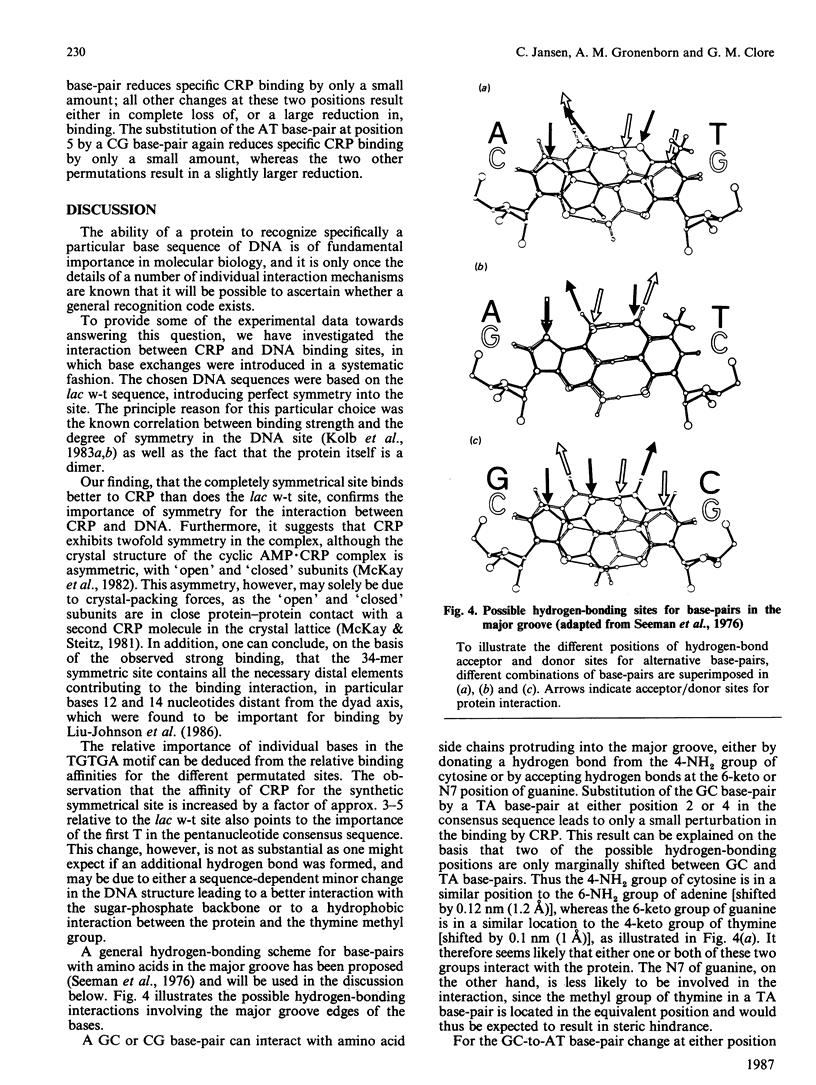
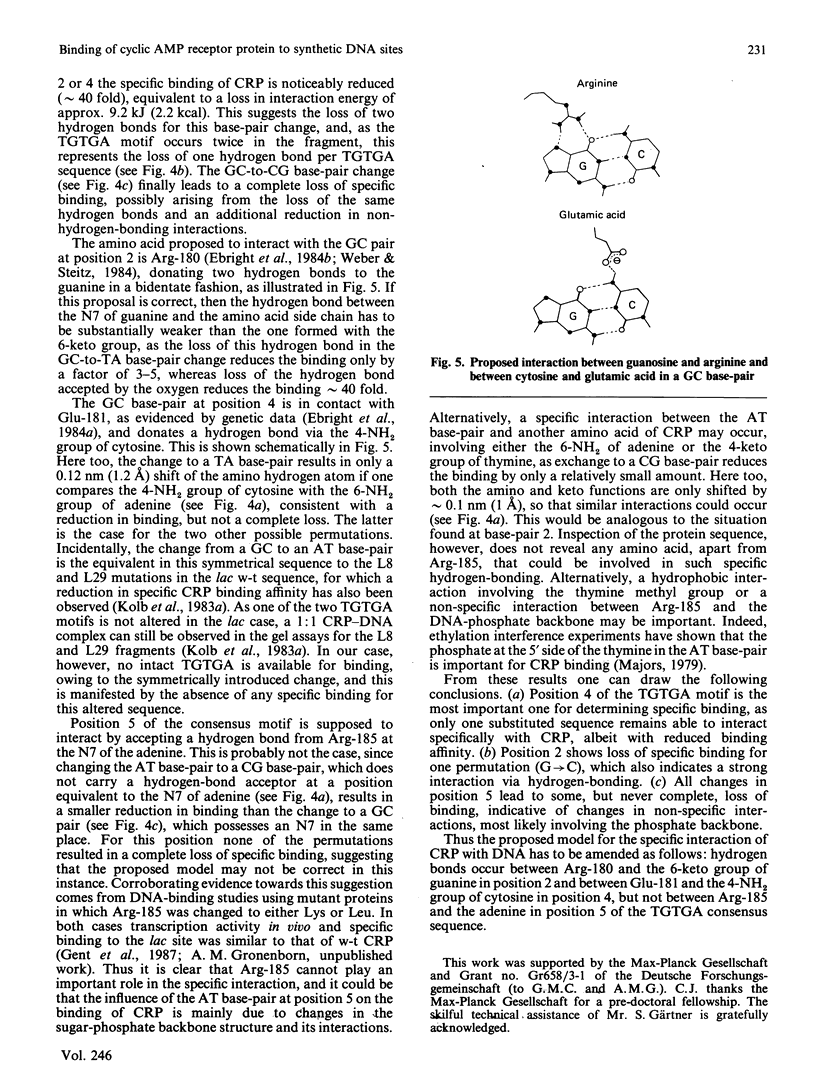

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busby S., Dreyfus M. Segment-specific mutagenesis of the regulatory region in the Escherichia coli galactose operon: isolation of mutations reducing the initiation of transcription and translation. Gene. 1983 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Cossart P., Gicquel-Sanzey B., Beckwith J. Molecular basis of DNA sequence recognition by the catabolite gene activator protein: detailed inferences from three mutations that alter DNA sequence specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7274–7278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Cossart P., Gicquel-Sanzey B., Beckwith J. Mutations that alter the DNA sequence specificity of the catabolite gene activator protein of E. coli. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):232–235. doi: 10.1038/311232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gent M. E., Gronenborn A. M., Davies R. W., Clore G. M. Probing the sequence-specific interaction of the cyclic AMP receptor protein with DNA by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):645–653. doi: 10.1042/bj2420645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Overproduction of the cyclic AMP receptor protein of Escherichia coli and expression of the engineered C-terminal DNA-binding domain. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 15;236(3):643–649. doi: 10.1042/bj2360643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Busby S., Herbert M., Kotlarz D., Buc H. Comparison of the binding sites for the Escherichia coli cAMP receptor protein at the lactose and galactose promoters. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):217–222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Spassky A., Chapon C., Blazy B., Buc H. On the different binding affinities of CRP at the lac, gal and malT promoter regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7833–7852. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9 A resolution suggests binding to left-handed B-DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):744–749. doi: 10.1038/290744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9-A resolution. Incorporation of amino acid sequence and interactions with cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9518–9524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Model of specific complex between catabolite gene activator protein and B-DNA suggested by electrostatic complementarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]