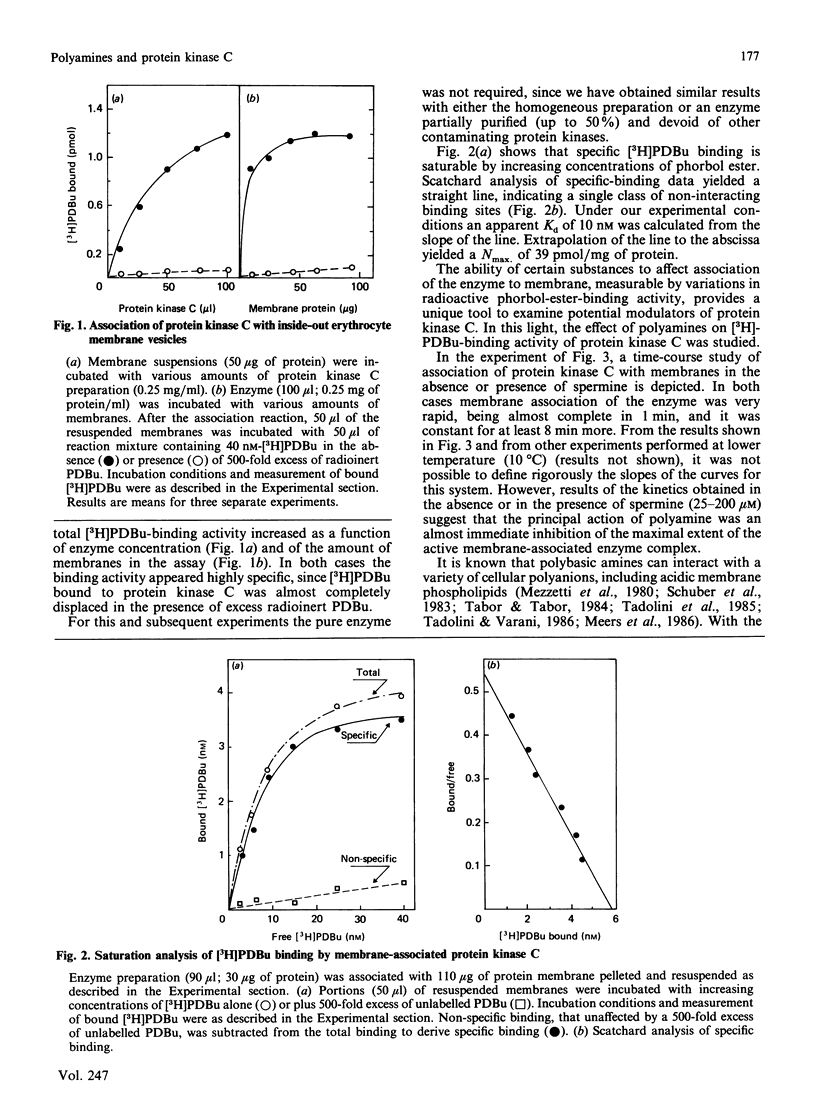
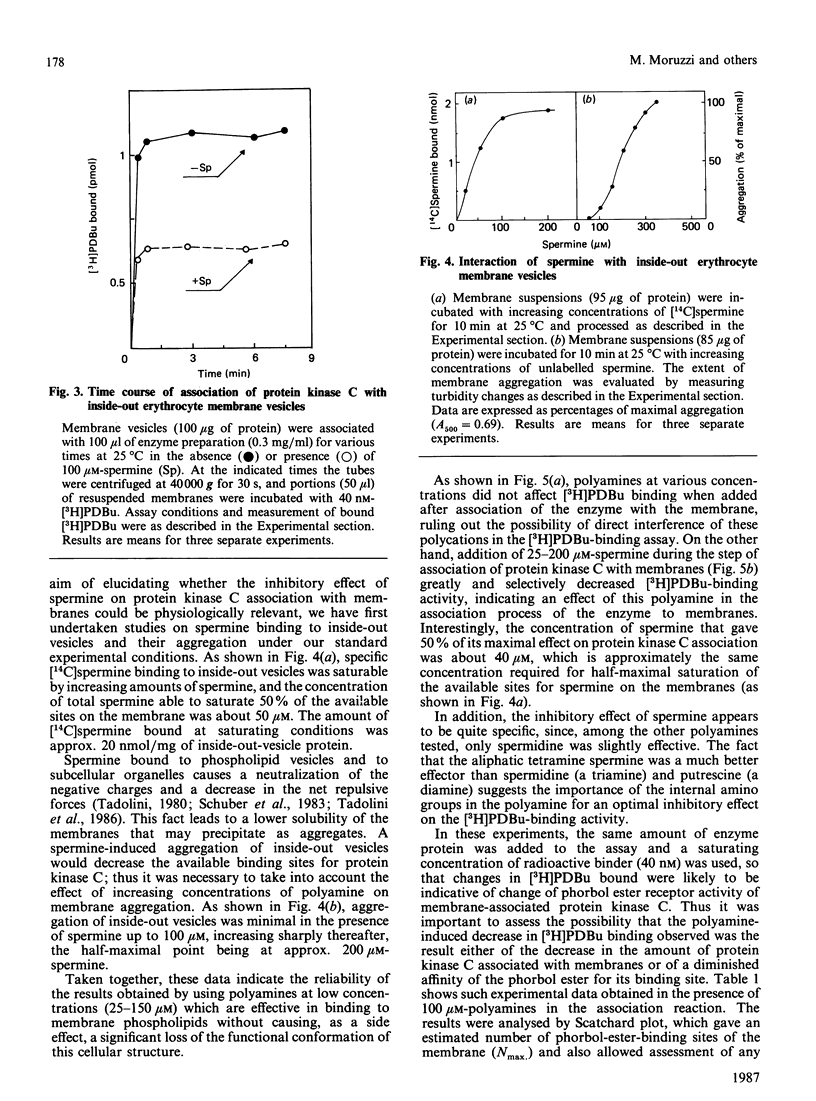
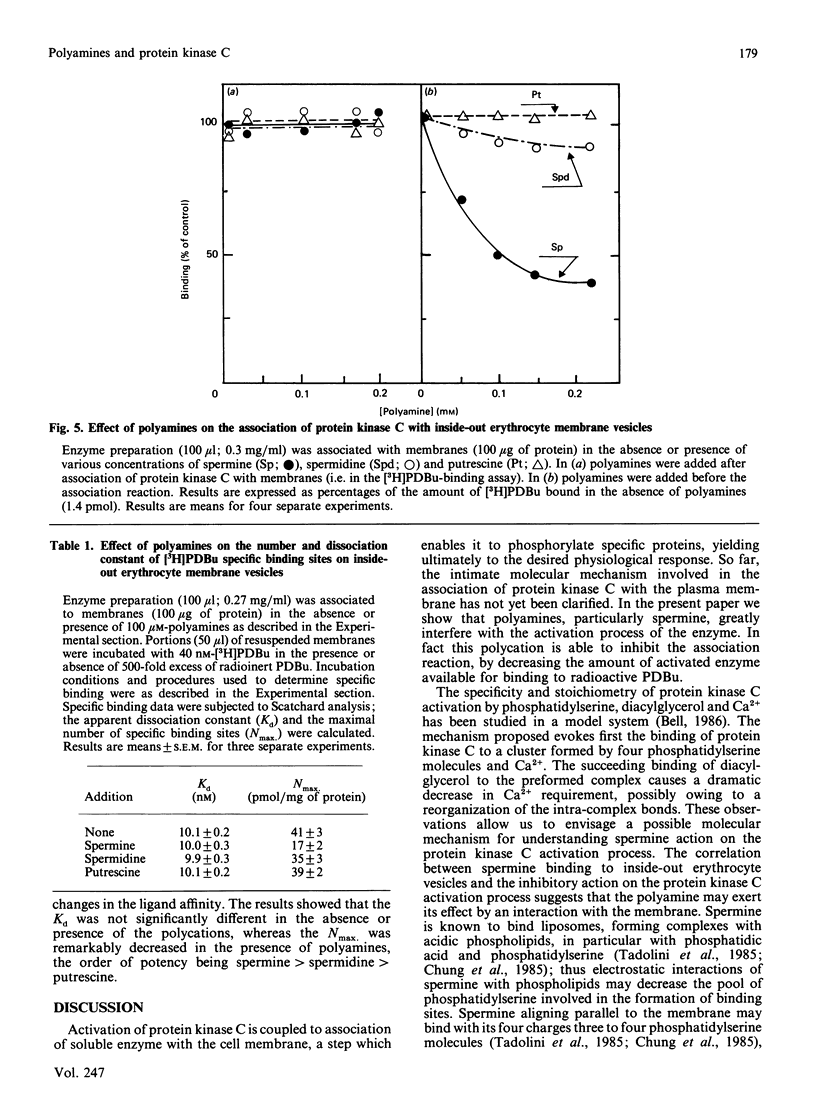
Abstract
Physiological activation of protein kinase C requires the interaction of this enzyme with cellular membranes [Nishizuka (1986) Science 233, 305-312]. In the present work a reconstituted system of protein kinase C and human inside-out erythrocyte vesicles was utilized to study the effect in vitro of naturally occurring polyamines on the activation process of protein kinase C. The active membrane-associated complex was conveniently determined by its ability to bind radioactive phorbol ester with an exact 1:1 stoichiometry. The association reaction of the enzyme to membrane was rapid, being complete within 1 min at 25 degrees C. The addition of polyamines, particularly spermine, greatly decreased in a dose-dependent manner the amount of protein kinase C bound to membranes (i.e. in the activated form). The effect observed was quite specific, since it was dependent on the chemical structure of the polyamine and it was manifest at micromolar concentrations of the polycation; the order of potency was spermine greater than spermidine greater than putrescine. A characterization of this effect is presented and possible physiological implications are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashendel C. L. The phorbol ester receptor: a phospholipid-regulated protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 9;822(2):219–242. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M. Protein kinase C activation by diacylglycerol second messengers. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):631–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90774-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Jaken S., König B., Sharkey N. A., Leach K. L., Jeng A. Y., Yeh E. Mechanism of action of the phorbol ester tumor promoters: specific receptors for lipophilic ligands. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 15;33(6):933–940. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung L., Kaloyanides G., McDaniel R., McLaughlin A., McLaughlin S. Interaction of gentamicin and spermine with bilayer membranes containing negatively charged phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):442–452. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Chambaz E. M. Polyamine-mediated protein phosphorylations: a possible target for intracellular polyamine action. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1983 Jun;30(3):247–266. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(83)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Souvignet C., Keramidas M., Chambaz E. M. Altered catalytic properties of protein kinase C in phorbol ester treated cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard P. R., Mazzei G. J., Wood J. G., Kuo J. F. Polyclonal antibodies to phospholipid/Ca2+-dependent protein kinase and immunocytochemical localization of the enzyme in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3030–3034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Bell R. M. Protein kinase C activation in mixed micelles. Mechanistic implications of phospholipid, diacylglycerol, and calcium interdependencies. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7184–7190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Takahashi K., Yamamoto M., Kisaki H., Endo H. Polyamines alter the phosphorylation pattern of chromatin proteins by endogenous protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 14;106(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Traugh J. A. Interaction of polyamines and magnesium with casein kinase II. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Aug 15;233(1):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90609-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota K., Hirota T., Aguilera G., Catt K. J. Hormone-induced redistribution of calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in pituitary gonadotrophs. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3243–3246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopewell R., Martin-Sanz P., Martin A., Saxton J., Brindley D. N. Regulation of the translocation of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase between the cytosol and the endoplasmic reticulum of rat liver. Effects of unsaturated fatty acids, spermine, nucleotides, albumin and chlorpromazine. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 1;232(2):485–491. doi: 10.1042/bj2320485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Tanaka Y., Miyake R., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C as a possible receptor protein of tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11442–11445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G. The phosphorylation of proteins: a major mechanism for biological regulation. Fourteenth Sir Frederick Gowland Hopkins memorial lecture. Biochem Soc Trans. 1985 Oct;13(5):813–820. doi: 10.1042/bst0130813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa M., Yokoyama K., Ishibashi S. Polyamines stimulate the binding of hexokinase type II to mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 23;759(1-2):92–98. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach K. L., James M. L., Blumberg P. M. Characterization of a specific phorbol ester aporeceptor in mouse brain cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4208–4212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezzetti G., Moruzzi M. S., Capone G., Barbiroli B. Polyamine binding by a cytoplasmic factor in the duodenal mucosa of new-born chick. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 17;97(1):222–229. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezzetti G., Moruzzi M., Monti M. G., Piccinini G., Barbiroli B. Polyamine-sensitive protein kinase from chick intestinal mucosa. Mol Cell Biochem. 1985 Mar;66(2):175–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00220785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezzetti G., Moruzzi M., Piccinini G., Monti M. G., Barbiroli B. Modulation of cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinase from chick intestine by naturally occurring polyamines and mucopolysaccharides. Mol Cell Biochem. 1986 May;70(2):141–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00229429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moruzzi G., Barbiroli B., Caldarera C. M. Polyamines and nucleic acid metabolism in chick embryo. Incorporation of labelled precursors into nucleic acids of subcellular fractions and polyribosomal patterns. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(5):609–613. doi: 10.1042/bj1070609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey H. C., Waseem A. Protein kinase C in the human erythrocyte. Translocation to the plasma membrane and phosphorylation of bands 4.1 and 4.9 and other membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):16021–16029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi D. F., Schatzman R. C., Mazzei G. J., Turner R. S., Raynor R. L., Liao S., Kuo J. F. Polyamines inhibit phospholipid-sensitive and calmodulin-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinases. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 1;213(2):281–288. doi: 10.1042/bj2130281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B., Szász I., Gárdos G. Characteristics and regulation of active calcium transport in inside-out red cell membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 23;598(2):326–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuber F., Hong K., Düzgünes N., Papahadjopoulos D. Polyamines as modulators of membrane fusion: aggregation and fusion of liposomes. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 20;22(26):6134–6140. doi: 10.1021/bi00295a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwantke N., Le Bouffant F., Dorée M., Le Peuch C. J. Protein kinase C: properties and possible role in cellular division and differentiation. Biochimie. 1985 Oct-Nov;67(10-11):1103–1110. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadolini B. Polyamines effect on subcellular fractionation of rat liver homogenate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):598–605. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90375-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadolini B., Varani E., Cabrini L. The influence of poly(ethylene glycol) 6000 on spermine-induced aggregation of liposomes. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 15;236(3):651–655. doi: 10.1042/bj2360651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadolini B., Varani E. Interaction of spermine with polyphosphoinositides containing liposomes and myo-inositol 1,4,5 triphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):58–64. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90942-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thams P., Capito K., Hedeskov C. J. An inhibitory role for polyamines in protein kinase C activation and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):131–138. doi: 10.1042/bj2370131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Valentine K. A., Ngai P. K., Carruthers C. A., Hollenberg M. D. Ca2+-dependent hydrophobic-interaction chromatography. Isolation of a novel Ca2+-binding protein and protein kinase C from bovine brain. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):117–127. doi: 10.1042/bj2240117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. Interaction of protein kinase C with membranes is regulated by Ca2+, phorbol esters, and ATP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15718–15722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., LeVine H., 3rd, May W. S., Jr, Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. A model for intracellular translocation of protein kinase C involving synergism between Ca2+ and phorbol esters. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):546–549. doi: 10.1038/317546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


