Abstract
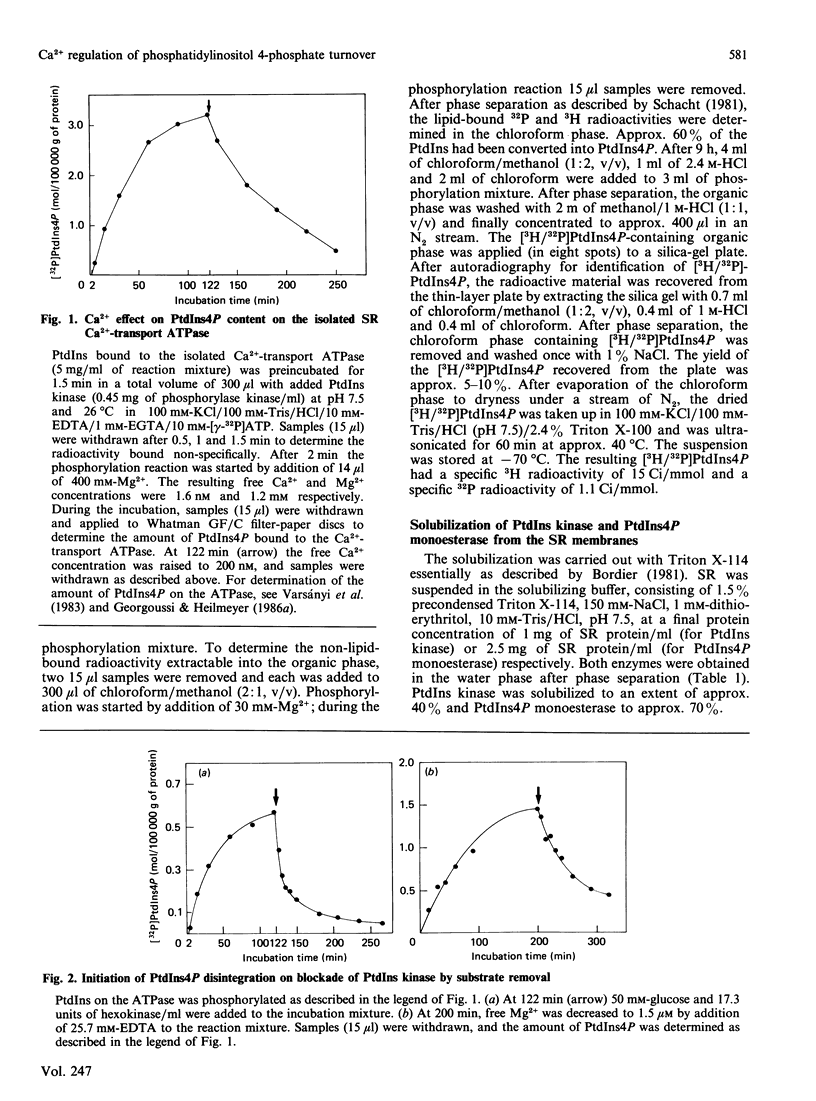
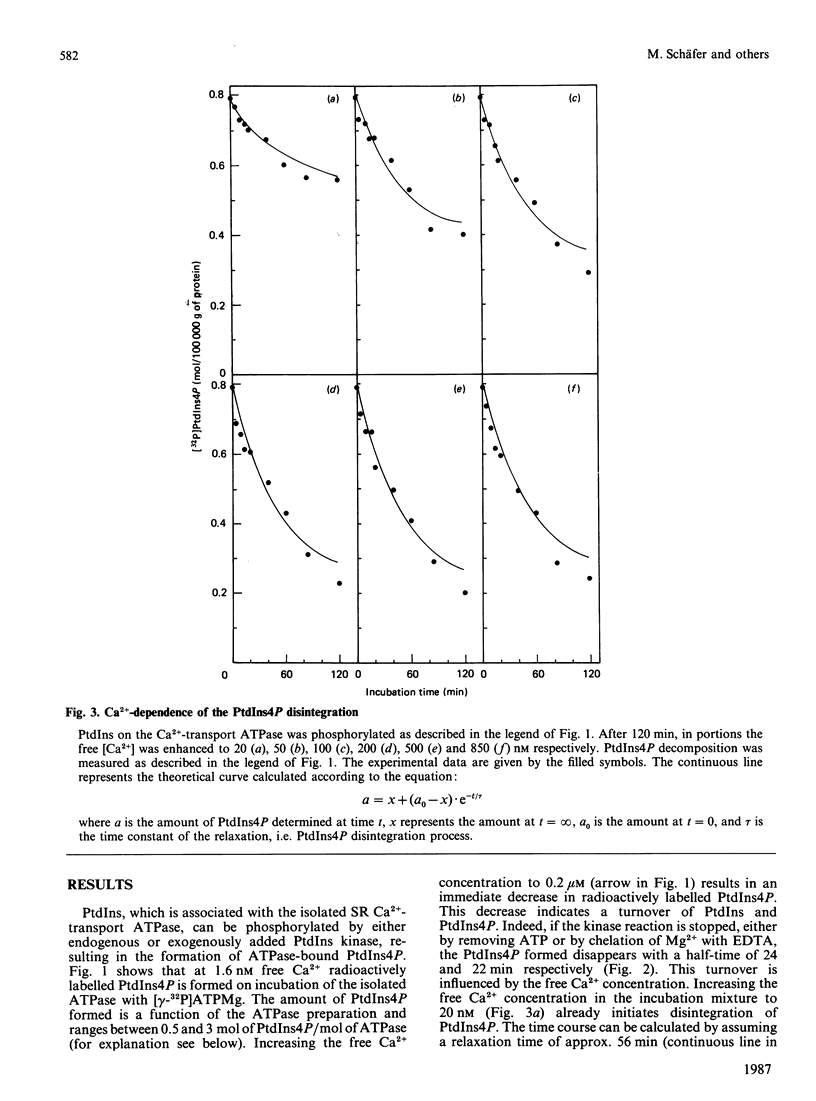
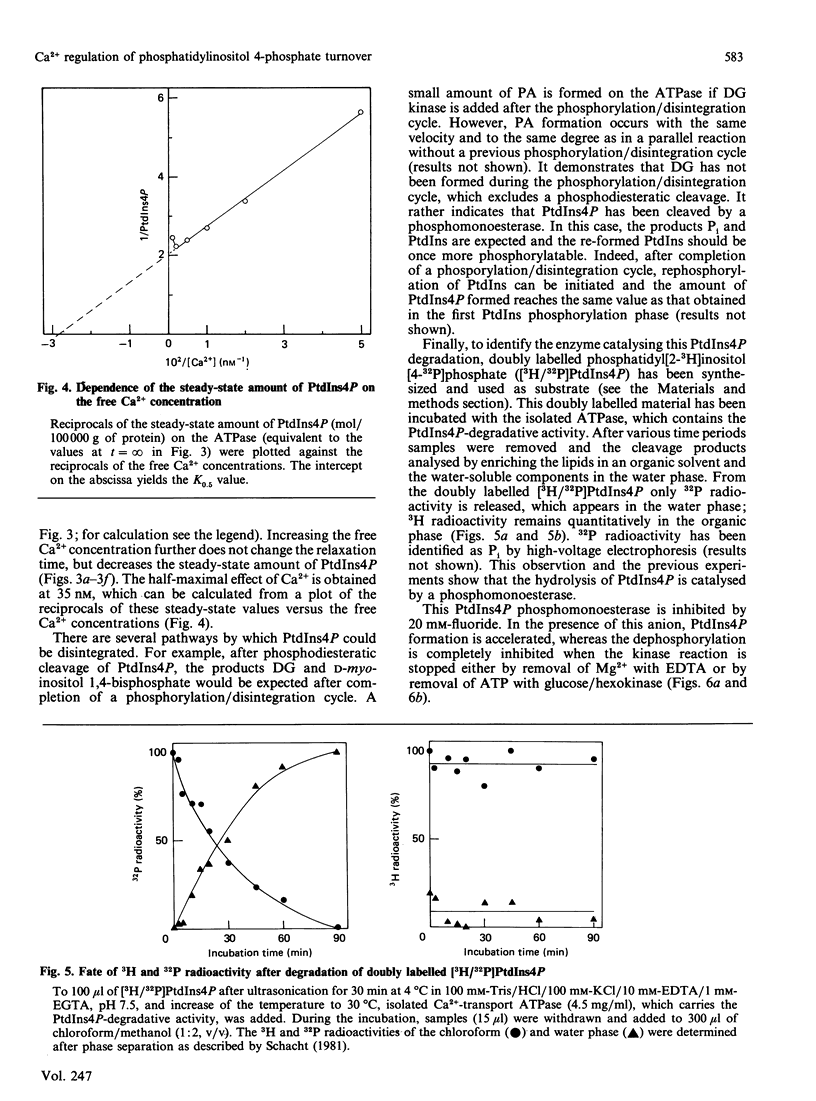
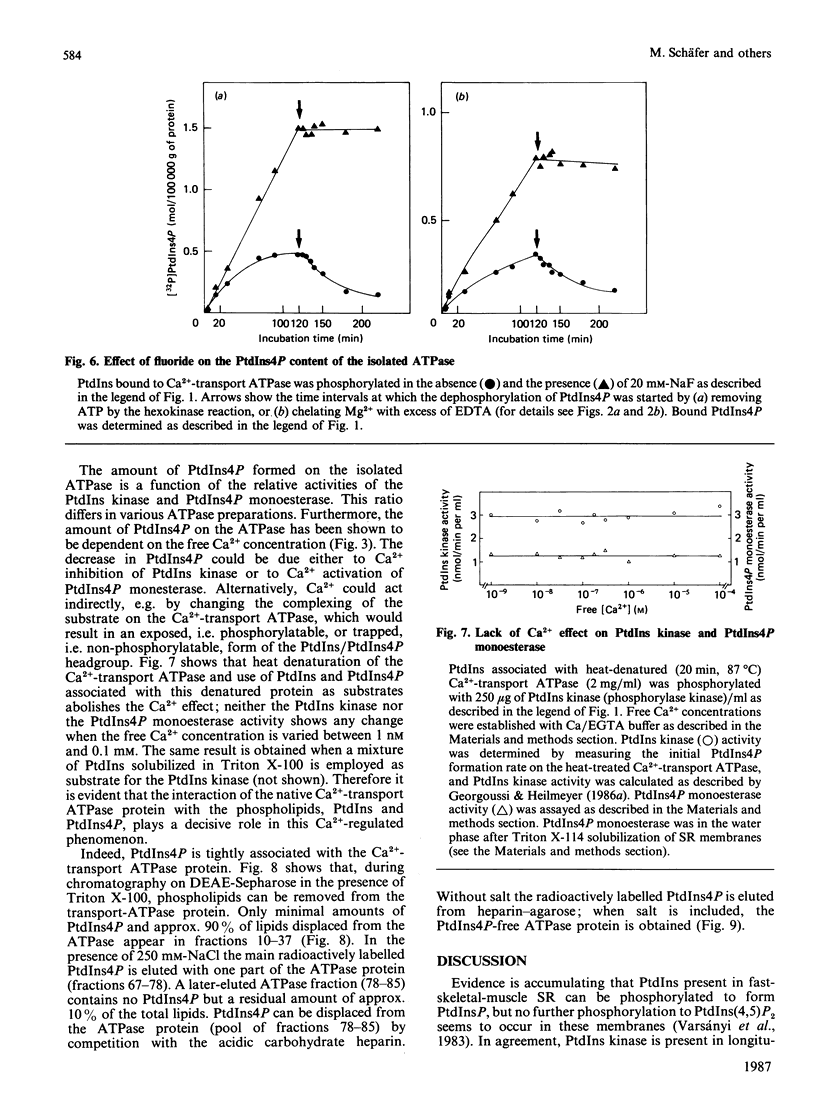
Lipid phosphorylation was shown to occur on the isolated sarcoplasmic-reticulum (SR) Ca2+-transport ATPase. More than 95% of the radioactivity incorporated on incubation of the SR ATPase with [gamma-32P]ATPMg can be extracted with acidic organic solvents and was identified as 1-(3-sn-phosphatidyl)-1D-myo-inositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P) [Varsányi, Toelle, Heilmeyer, Dawson & Irvine (1983) EMBO J. 2, 1543-1548]. This lipid phosphorylation is only observed at nanomolar concentrations of free Ca2+; in the presence of micromolar free Ca2+ PtdIns4P disintegrates rapidly. Also, upon blockade of the kinase reaction PtdIns4P decomposes, indicating a PtdIns/PtdIns4P turnover. The PtdIns4P concentration is dependent on the free Ca2+ concentration, being half-maximal at 35 nM-Ca2+. PtdIns4P hydrolysis is catalysed by a PtdIns4P phosphomonoesterase; accordingly no diacylglycerol is formed, which would be a product of a phosphodiesteratic cleavage. Fluoride inhibits this phosphomonoesterase. Ca2+ does not influence directly either the PtdIns kinase or the PtdIns4P phosphomonoesterase. PtdIns4P forms a tight complex with the transport ATPase, from which it can be removed only by chromatography on heparin-agarose in the presence of Triton X-100. It is concluded that Ca2+ regulates the PtdIns/PtdIns4P turnover by availability of substrate, depending on the Ca2+-transport-ATPase conformation, which traps or exposes the respective lipid head groups.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Ernst Klenk Lecture, November 1985. Intracellular signalling through inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Jun;367(6):447–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choquette D., Hakim G., Filoteo A. G., Plishker G. A., Bostwick J. R., Penniston J. T. Regulation of plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPases by lipids of the phosphatidylinositol cycle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 28;125(3):908–915. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The subunit structure of rabbit-skeletal-muscle phosphorylase kinase, and the molecular basis of its activation reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. A., Wells W. W. Identification of phosphatidylinositol kinase in rat liver lysosomal membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2130–2134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meis L., Hasselbach W. Acetyl phosphate as substrate for Ca 2+ uptake in skeletal muscle microsomes. Inhibition by alkali ions. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4759–4763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgoussi Z., Evangelopoulos A., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Labeling of sarcoplasmic reticulum peptides with 32P-phosphate and fluorescein 5'-isothiocyanate. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Dec 15;35(24):4571–4573. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90780-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgoussi Z., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Evidence that phosphorylase kinase exhibits phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3867–3874. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessová Z., Thieleczek R., Varsányi M., Falkenberg F. W., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Monoclonal antibodies to rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. Probes for studies of subunit function. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10111–10117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C., Carrasco M. A., Magendzo K., Jaimovich E. Phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol by transverse tubule vesicles and its possible role in excitation-contraction coupling. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jun 23;202(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80651-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennissen H. P., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr General aspects of hydrophobic chromatography. Adsorption and elution characteristics of some skeletal muscle enzymes. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 25;14(4):754–760. doi: 10.1021/bi00675a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jergil B., Sundler R. Phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol in rat liver Golgi. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7968–7973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPorte D. C., Koshland D. E., Jr Phosphorylation of isocitrate dehydrogenase as a demonstration of enhanced sensitivity in covalent regulation. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):286–290. doi: 10.1038/305286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. H., Fain J. N. Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase in rat hepatocyte plasma membranes: inhibition by vasopressin and purification of the enzyme. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;168:25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. H., Wallace M. A., Fain J. N. Regulation of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase activity in hepatocyte plasma membranes by vasopressin and phenylephrine. Endocrinology. 1983 Dec;113(6):2268–2275. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-6-2268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H. Purification and properties of an adenosine triphosphatase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4508–4518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J. Extraction and purification of polyphosphoinositides. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:626–631. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekar M. C., Hokin L. E. The role of phosphoinositides in signal transduction. J Membr Biol. 1986;89(3):193–210. doi: 10.1007/BF01870664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh N. A., Palmer F. B. Phosphoinositide kinases in chick brain and sciatic nerve, a developmental study. J Neurochem. 1977 Feb;28(2):395–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb07760.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Wells W. W. Phosphorylation of rat liver nuclear envelopes. II. Characterization of in vitro lipid phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9368–9373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varsanyi M., Tölle H. G., Heilmeyer M. G., Jr, Dawson R. M., Irvine R. F. Activation of sarcoplasmic reticular Ca2+ transport ATPase by phosphorylation of an associated phosphatidylinositol. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1543–1548. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01621.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varsányi M., Behle G., Schäfer M. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol phosphorylation in the sarcoplasmic reticular Ca2+-transport ATPase by vanadate. Z Naturforsch C. 1986 Mar;41(3):310–314. doi: 10.1515/znc-1986-0311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varsányi M., Messer M., Brandt N. R., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate formation in rabbit skeletal and heart muscle membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1395–1404. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80438-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walseth T. F., Johnson R. A. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-(32)P]nucleoside triphosphates, cyclic [32P] AMP, and cyclic [32P] GMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 28;562(1):11–31. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


