Abstract
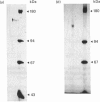
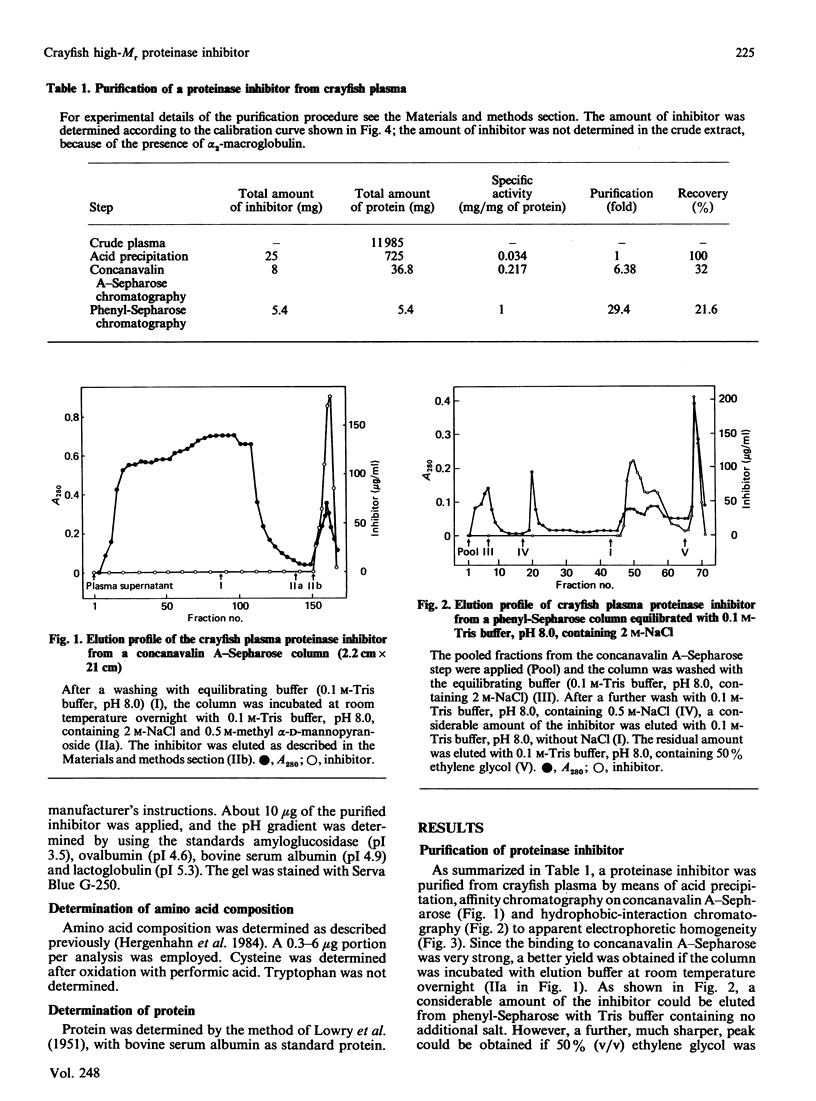
Crayfish plasma was found to contain a proteinase inhibitor, which was purified to apparent homogeneity by acid precipitation, affinity chromatography on concanavalin A-Sepharose and hydrophobic-interaction chromatography. The inhibitor is a monomeric protein with an Mr of about 155,000 and a pI in the range 4.6-4.8. It is heat-stable and tolerant to low pH. It inhibits the serine proteinases trypsin and chymotrypsin, but not thrombin or subtilisin. Furthermore, it is efficient in decreasing the activity of a proteinase from crayfish haemolymph that is involved in the activation cascade of pro-phenol oxidase and can also block pro-phenol oxidase activation by this serine proteinase. This cascade is believed to play a central role in the recognition mechanism of non-self material in crustaceans and insects. The data presented give some evidence that the new proteinase inhibitor is involved in the regulation of this system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong P. B., Levin J., Quigley J. P. Role of endogenous proteinase inhibitors in the regulation of the blood clotting system of the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Oct 31;52(2):117–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong P. B., Quigley J. P. Proteinase inhibitory activity released from the horseshoe crab blood cell during exocytosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 1;827(3):453–459. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong P. B., Rossner M. T., Quigley J. P. An alpha 2-macroglobulinlike activity in the blood of chelicerate and mandibulate arthropods. J Exp Zool. 1985 Oct;236(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402360102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hergenhahn H. G., Kegel G., Sedlmeier D. Ca2+-binding proteins in crayfish abdominal muscle. Evidence for a calmodulin lacking trimethyllysine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 14;787(2):196–203. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90080-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang S. H., Fuchs M. S. Purification and partial-characterization of a protease inhibitor from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 14;611(2):379–383. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley J. P., Armstrong P. B. A homologue of alpha 2-macroglobulin purified from the hemolymph of the horseshoe crab Limulus polyphemus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12715–12719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley J. P., Armstrong P. B. An endopeptidase inhibitor, similar to mammalian alpha 2-macroglobulin, detected in the hemolymph of an invertebrate, Limulus polyphemus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7903–7906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe N. A. Invertebrate immunity--a primer for the non-specialist. Immunol Lett. 1985;10(5):253–270. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T. Chymotrypsin inhibitors from hemolymph of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Biochem. 1978 Aug;84(2):267–276. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Kobayashi K. Isolation of two novel proteinase inhibitors from hemolymph of silkworm larva, Bombyx mori. Comparison with human serum proteinase inhibitors. J Biochem. 1984 Apr;95(4):1009–1017. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul S. J., Sugumaran M. Protease inhibitor controls prophenoloxidase activation in Manduca sexta. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbuch M. The inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:760–772. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugumaran M., Saul S. J., Ramesh N. Endogenous protease inhibitors prevent undesired activation of prophenolase in insect hemolymph. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):1124–1129. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91923-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Natori S. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor of the cysteine protease from the hemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina larvae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5115–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Howard J. B. Structural characterization of human alpha2-macroglobulin subunits. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4452–4456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderhäll K. Prophenoloxidase activating system and melanization - a recognition mechanism of arthropods? A review. Dev Comp Immunol. 1982 Fall;6(4):601–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]