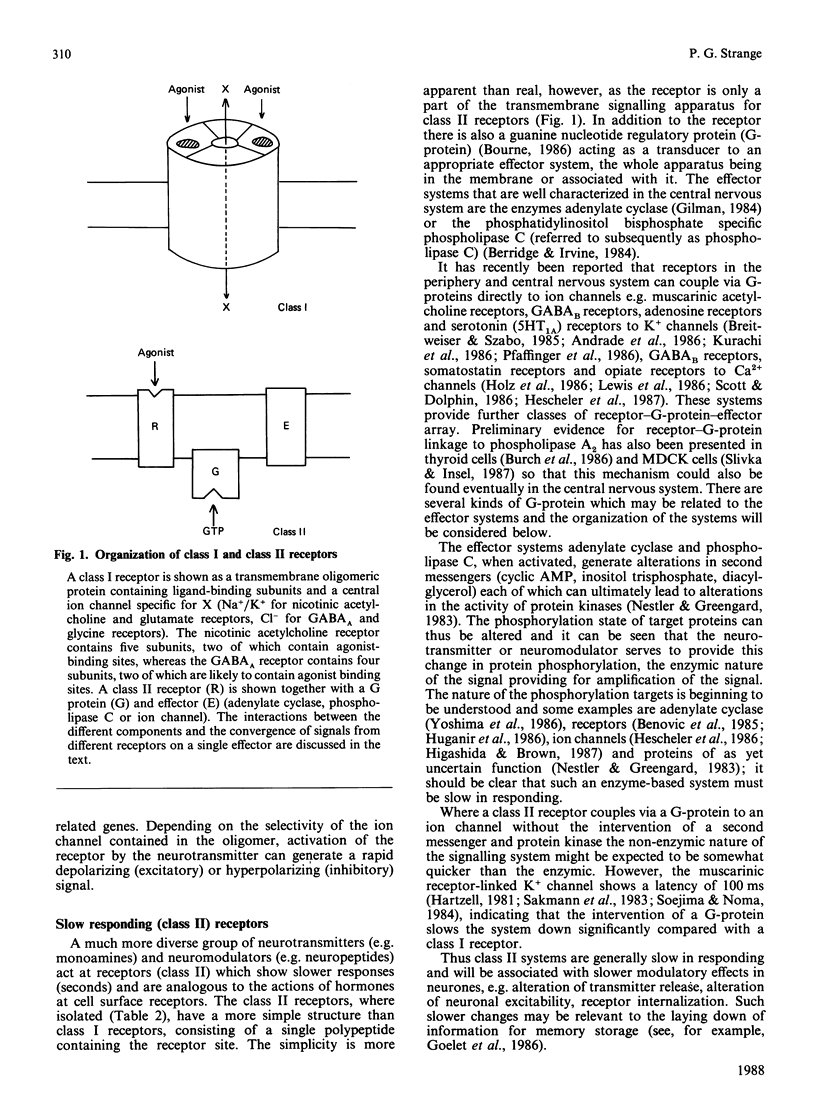
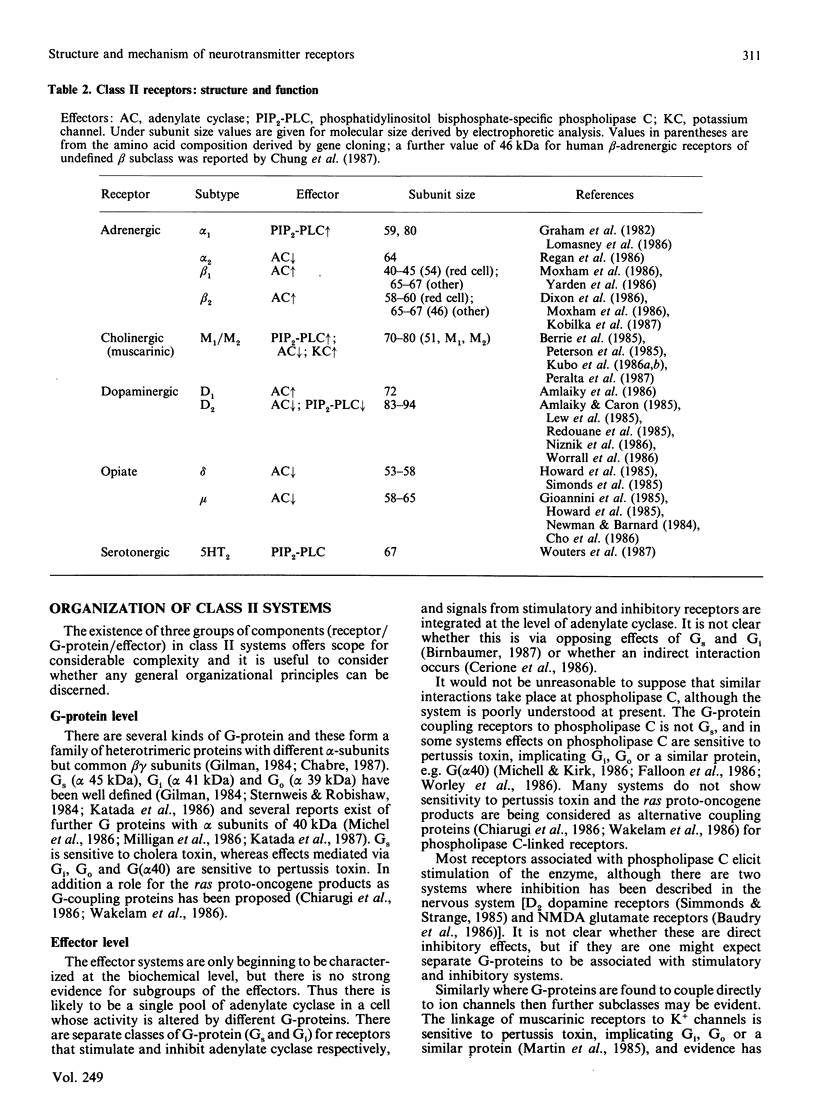
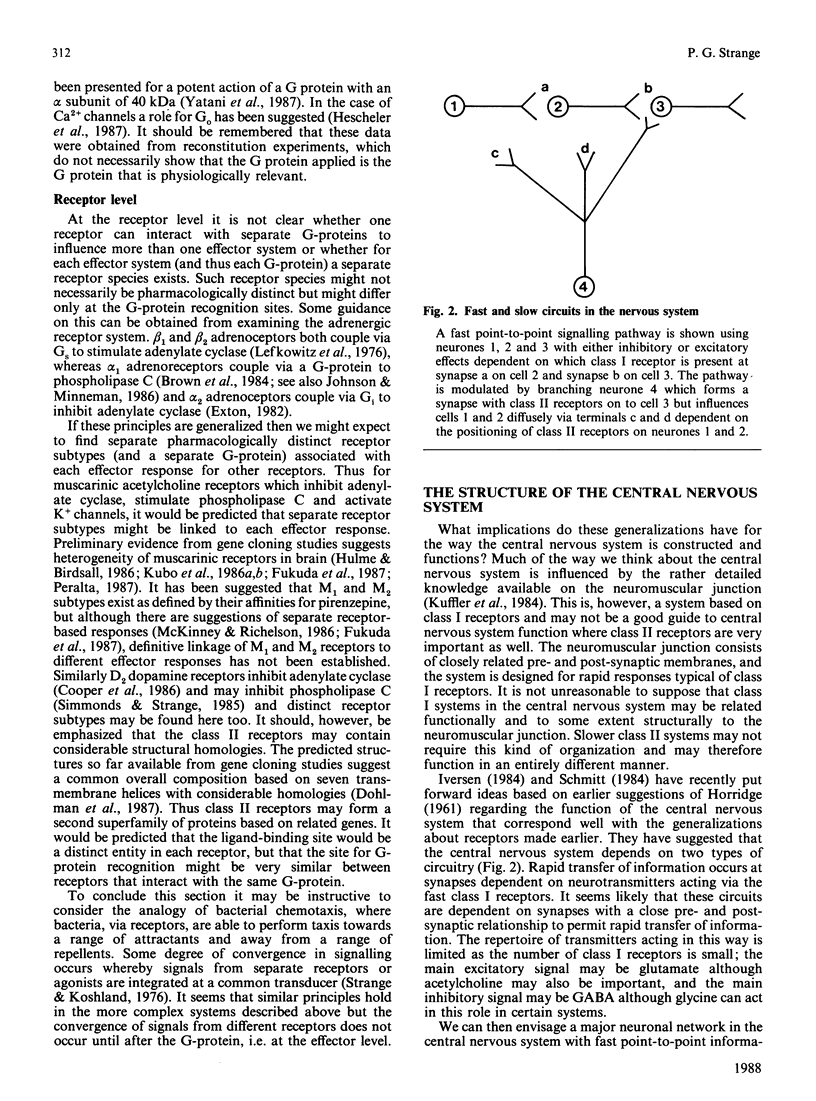
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amlaiky N., Caron M. G. Photoaffinity labeling of the D2-dopamine receptor using a novel high affinity radioiodinated probe. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):1983–1986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade R., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptors to the same channels in hippocampus. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1261–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.2430334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Ui M., Ogasawara N. Prevention of the agonist binding to gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptors by guanine nucleotides and islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in bovine cerebral cortex. Possible coupling of the toxin-sensitive GTP-binding proteins to receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12653–12658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardsley M. E., Roberts P. J. Molecular size of the high-affinity glutamate-binding site on synaptic membranes from rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90595-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., McBurney R. N. Phenobarbitone modulation of postsynaptic GABA receptor function on cultured mammalian neurons. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Dec 31;206(1164):319–327. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry M., Evans J., Lynch G. Excitatory amino acids inhibit stimulation of phosphatidylinositol metabolism by aminergic agonists in hippocampus. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):329–331. doi: 10.1038/319329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaudet A., Descarries L. The monoamine innervation of rat cerebral cortex: synaptic and nonsynaptic axon terminals. Neuroscience. 1978;3(10):851–860. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Pike L. J., Cerione R. A., Staniszewski C., Yoshimasa T., Codina J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation of the mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Regulation of the rate of receptor phosphorylation and dephosphorylation by agonist occupancy and effects on coupling of the receptor to the stimulatory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7094–7101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrie C. P., Birdsall N. J., Dadi H. K., Hulme E. C., Morris R. J., Stockton J. M., Wheatley M. Purification of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor from rat forebrain. Biochem Soc Trans. 1985 Dec;13(6):1101–1103. doi: 10.1042/bst0131101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E. The endorphins: a growing family of pharmacologically pertinent peptides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:151–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. GTP-binding proteins. One molecular machine can transduce diverse signals. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):814–816. doi: 10.1038/321814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen D. M., Davison A. N. Biochemical studies of nerve cells and energy metabolism in Alzheimer's disease. Br Med Bull. 1986 Jan;42(1):75–80. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and beta-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):538–540. doi: 10.1038/317538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. Neuropharmacology. Acetylcholine and brain cells. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):358–359. doi: 10.1038/319358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E., Kendall D. A., Nahorski S. R. Inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortical slices: I. Receptor characterisation. J Neurochem. 1984 May;42(5):1379–1387. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R., Arbuthnott G. W. The electrophysiology of dopamine (D2) receptors: a study of the actions of dopamine on corticostriatal transmission. Neuroscience. 1983 Oct;10(2):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Luini A., Axelrod J. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C are activated by distinct GTP-binding proteins in response to alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation in FRTL5 thyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7201–7205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne D. B., Langston J. W., Martin W. R., Stoessl A. J., Ruth T. J., Adam M. J., Pate B. D., Schulzer M. Positron emission tomography after MPTP: observations relating to the cause of Parkinson's disease. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):246–248. doi: 10.1038/317246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Staniszewski C., Gierschik P., Codina J., Somers R. L., Birnbaumer L., Spiegel A. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Mechanism of guanine nucleotide regulatory protein-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Studies with isolated subunits of transducin in a reconstituted system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9514–9520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesselet M. F. Presynaptic regulation of neurotransmitter release in the brain: facts and hypothesis. Neuroscience. 1984 Jun;12(2):347–375. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarugi V. P., Pasquali F., Vannucchi S., Ruggiero M. Point-mutated p21ras couples a muscarinic receptor to calcium channels and polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):591–599. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho T. M., Hasegawa J., Ge B. L., Loh H. H. Purification to apparent homogeneity of a mu-type opioid receptor from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4138–4142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung F. Z., Lentes K. U., Gocayne J., Fitzgerald M., Robinson D., Kerlavage A. R., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. Cloning and sequence analysis of the human brain beta-adrenergic receptor. Evolutionary relationship to rodent and avian beta-receptors and porcine muscarinic receptors. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):200–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor: correlation of molecular structure with functional properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:491–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. M., Bier-Laning C. M., Halford M. K., Ahlijanian M. K., Zahniser N. R. Dopamine, acting through D-2 receptors, inhibits rat striatal adenylate cyclase by a GTP-dependent process. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;29(2):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Price D. L., DeLong M. R. Alzheimer's disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1184–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.6338589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello A. C. Nonclassical neuronal communications. Fed Proc. 1983 Sep;42(12):2912–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descarries L., Beaudet A., Watkins K. C. Serotonin nerve terminals in adult rat neocortex. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 26;100(3):563–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Kobilka B. K., Strader D. J., Benovic J. L., Dohlman H. G., Frielle T., Bolanowski M. A., Bennett C. D., Rands E., Diehl R. E. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. A family of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2657–2664. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet G., Descarries L., Garcia S. Quantification of the dopamine innervation in adult rat neostriatum. Neuroscience. 1986 Oct;19(2):427–445. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W. Electrophysiology of opioid peptides and sensory systems. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):65–70. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Foster A. C. Amino acid neurotransmitters and their pathways in the mammalian central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1983 Aug;9(4):701–719. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falloon J., Malech H., Milligan G., Unson C., Kahn R., Goldsmith P., Spiegel A. Detection of the major pertussis toxin substrate of human leukocytes with antisera raised against synthetic peptides. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):352–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda K., Kubo T., Akiba I., Maeda A., Mishina M., Numa S. Molecular distinction between muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):623–625. doi: 10.1038/327623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. Guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):1–4. doi: 10.1172/JCI111179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioannini T. L., Howard A. D., Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. Purification of an active opioid-binding protein from bovine striatum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15117–15121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelet P., Castellucci V. F., Schacher S., Kandel E. R. The long and the short of long-term memory--a molecular framework. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):419–422. doi: 10.1038/322419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. M., Hess H. J., Homcy C. J. Biophysical characterization of the purified alpha 1-adrenergic receptor and identification of the hormone binding subunit. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15174–15181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Rienitz A., Schmitt B., Methfessel C., Zensen M., Beyreuther K., Gundelfinger E. D., Betz H. The strychnine-binding subunit of the glycine receptor shows homology with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):215–220. doi: 10.1038/328215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel E., Beaudet A. Electron microscopic autoradiographic localization of opioid receptors in rat neostriatum. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):155–157. doi: 10.1038/312155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C. Mechanisms of slow postsynaptic potentials. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):539–544. doi: 10.1038/291539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Kameyama M., Trautwein W. On the mechanism of muscarinic inhibition of the cardiac Ca current. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):182–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00580674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashida H., Brown D. A. Two polyphosphatidylinositide metabolites control two K+ currents in a neuronal cell. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):333–335. doi: 10.1038/323333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G., Hudson A. L. Inhibition of GABAB receptor binding by guanyl nucleotides. J Neurochem. 1984 Mar;42(3):652–657. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Drejer J., Nielsen M., Watkins J. C., Olverman H. J. Molecular target size of NMDA antagonist binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 7;136(1):137–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90793-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houser C. R., Crawford G. D., Salvaterra P. M., Vaughn J. E. Immunocytochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase in rat cerebral cortex: a study of cholinergic neurons and synapses. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Apr 1;234(1):17–34. doi: 10.1002/cne.902340103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard A. D., de La Baume S., Gioannini T. L., Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. Covalent labeling of opioid receptors with radioiodinated human beta-endorphin. Identification of binding site subunit. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10833–10839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Delcour A. H., Greengard P., Hess G. P. Phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor regulates its rate of desensitization. Nature. 1986 Jun 19;321(6072):774–776. doi: 10.1038/321774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulme E., Birdsall N. Distinctions in acetylcholine receptor activity. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):396–397. doi: 10.1038/323396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Bloom F. E. Studies of the uptake of 3 H-gaba and ( 3 H)glycine in slices and homogenates of rat brain and spinal cord by electron microscopic autoradiography. Brain Res. 1972 Jun 8;41(1):131–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90621-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L. Nonopioid neuropeptides in mammalian CNS. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:1–27. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L. The Ferrier Lecture, 1983. Amino acids and peptides: fast and slow chemical signals in the nervous system? Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 May 22;221(1224):245–260. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. D., Minneman K. P. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenoceptors which increase cyclic AMP accumulation in rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 7;129(3):293–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90439-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Kusakabe K., Ui M. A new GTP-binding protein in brain tissues serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 23;213(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81521-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Ui M. Two guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in rat brain serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. Interaction of the alpha-subunits with beta gamma-subunits in development of their biological activities. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8182–8191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. S. Electrophysiology of peptides in the central nervous system. Br Med Bull. 1982 Sep;38(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Dixon R. A., Frielle T., Dohlman H. G., Bolanowski M. A., Sigal I. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cDNA for the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple membrane-spanning domains and encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T., Heizmann C. W., Tateishi K., Hamaoka Y., Hama K. An aspect of the organizational principle of the gamma-aminobutyric acidergic system in the cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1987 Apr 21;409(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90732-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosofsky B. E., Molliver M. E., Morrison J. H., Foote S. L. The serotonin and norepinephrine innervation of primary visual cortex in the cynomolgus monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J Comp Neurol. 1984 Dec 1;230(2):168–178. doi: 10.1002/cne.902300203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo T., Fukuda K., Mikami A., Maeda A., Takahashi H., Mishina M., Haga T., Haga K., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Cloning, sequencing and expression of complementary DNA encoding the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):411–416. doi: 10.1038/323411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo T., Maeda A., Sugimoto K., Akiba I., Mikami A., Takahashi H., Haga T., Haga K., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Primary structure of porcine cardiac muscarinic acetylcholine receptor deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):367–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Inagaki S., Kito S., Wu J. Y. Dopaminergic axons directly make synapses with GABAergic neurons in the rat neostriatum. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 17;406(1-2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90779-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y., Nakajima T., Sugimoto T. On the mechanism of activation of muscarinic K+ channels by adenosine in isolated atrial cells: involvement of GTP-binding proteins. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Sep;407(3):264–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00585301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Limbird L. E., Mukherjee C., Caron M. G. The beta-adrenergic receptor and adenylate cyclase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 13;457(1):1–39. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew J. Y., Meller E., Goldstein M. Photoaffinity labeling and purification of solubilized D2 dopamine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 11;113(1):145–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90359-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. L., Weight F. F., Luini A. A guanine nucleotide-binding protein mediates the inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current by somatostatin in a pituitary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9035–9039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Cotecchia S., Regan J. W., DeBernardis J. F., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Mammalian alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Purification and characterization of the native receptor ligand binding subunit. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7710–7716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Yates P. O., Marcyniuk B. Correlation between senile plaque and neurofibrillary tangle counts in cerebral cortex and neuronal counts in cortex and subcortical structures in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1985 May 1;56(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90439-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh P. W., Pinnock R. D., Downes C. P., Goedert M., Hunt S. P. Correlation between inositol phospholipid hydrolysis and substance P receptors in rat CNS. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):795–797. doi: 10.1038/309795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M. Islet activating protein inhibits physiological responses evoked by cardiac muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Role of guanosine triphosphate binding proteins in regulation of potassium permeability. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 17;24(26):7521–7525. doi: 10.1021/bi00347a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney M., Richelson E. Muscarinic responses and binding in a murine neuroblastoma clone (N1E-115): cyclic GMP formation is mediated by a low affinity agonist-receptor conformation and cyclic AMP reduction is mediated by a high affinity agonist-receptor conformation. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Sep;30(3):207–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel T., Winslow J. W., Smith J. A., Seidman J. G., Neer E. J. Molecular cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding the GTP-binding protein alpha i and identification of a related protein, alpha h. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7663–7667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell B., Kirk C. G-protein control of inositol phosphate hydrolysis. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):112–113. doi: 10.1038/323112b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M., Klee W. A. The GTP-binding regulatory proteins of neuroblastoma x glioma, NG108-15, and glioma, C6, cells. Immunochemical evidence of a pertussis toxin substrate that is neither Ni nor No. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley P., Greengard P. Evidence for widespread effects of noradrenaline on axon terminals in the rat frontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):945–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W. Identification and properties of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7532–7536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Bloom F. E. Central catecholamine neuron systems: anatomy and physiology of the dopamine systems. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:129–169. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Bloom F. E. Central catecholamine neuron systems: anatomy and physiology of the norepinephrine and epinephrine systems. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1979;2:113–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.02.030179.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., George S. T., Graziano M. P., Brandwein H. J., Malbon C. C. Mammalian beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Immunological and structural comparisons. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14562–14570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naor Z., Azrad A., Limor R., Zakut H., Lotan M. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone activates a rapid Ca2+-independent phosphodiester hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositides in pituitary gonadotrophs. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12506–12512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Greengard P. Protein phosphorylation in the brain. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):583–588. doi: 10.1038/305583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. L., Barnard E. A. Identification of an opioid receptor subunit carrying the mu binding site. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5385–5389. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Meek J. L., Iadarola M. J., Chuang D. M., Roth B. L., Costa E. Coupling of inositol phospholipid metabolism with excitatory amino acid recognition sites in rat hippocampus. J Neurochem. 1986 Jan;46(1):40–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12922.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Schenker C., Leeman S. E. Substance P as a transmitter candidate. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:227–268. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niznik H. B., Grigoriadis D. E., Seeman P. Photoaffinity labelling of dopamine D2 receptors by [3H]azidomethylspiperone. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 1;209(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Miyata T., Numa S. Primary structure of alpha-subunit precursor of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):793–797. doi: 10.1038/299793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):528–532. doi: 10.1038/302528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Hirose T., Asai M., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Primary structures of beta- and delta-subunit precursors of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequences. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):251–255. doi: 10.1038/301251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Egan T. M. Electrophysiology of peptides in the peripheral nervous system. Br Med Bull. 1982 Sep;38(3):291–296. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W. GABA-benzodiazepine-barbiturate receptor interactions. J Neurochem. 1981 Jul;37(1):1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb05284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W. B., Gardiner T. W., Stricker E. M., Zigmond M. J., Berger T. W. Short-term effects of dopamine-depleting brain lesions on spontaneous activity of striatal neurons: relation to local dopamine concentration and behavior. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 18;376(1):20–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90895-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald R. E., Freeman J. A. Alpha-bungarotoxin binding and central nervous system nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuroscience. 1981;6(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce B., Albrecht J., Morrow C., Murphy S. Astrocyte glutamate receptor activation promotes inositol phospholipid turnover and calcium flux. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Dec 23;72(3):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90537-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Peterson G. L., Smith D. H., Ashkenazi A., Ramachandran J., Schimerlik M. I., Capon D. J. Primary structure and biochemical properties of an M2 muscarinic receptor. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):600–605. doi: 10.1126/science.3107123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L., Herron G. S., Yamaki M., Fullerton D. S., Schimerlik M. I. Purification of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor from porcine atria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4993–4997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer F., Graham D., Betz H. Purification by affinity chromatography of the glycine receptor of rat spinal cord. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9389–9393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J. L., Stern R. Individual cells in the nucleus basalis--diagonal band complex have restricted axonal projections to the cerebral cortex in the rat. Brain Res. 1983 Jun 20;269(2):352–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reader T. A., Ferron A., Descarries L., Jasper H. H. Modulatory role for biogenic amines in the cerebral cortex. Microiontophoretic studies. Brain Res. 1979 Jan 12;160(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redouane K., Sokoloff P., Schwartz J. C., Hamdi P., Mann A., Wermuth C. G., Roy J., Morgat J. L. Photoaffinity labeling of D-2 dopamine binding subunits from rat striatum, anterior pituitary and olfactory bulb with a new probe, [3H]azidosulpride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 15;130(3):1086–1092. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91727-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Nakata H., DeMarinis R. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Purification and characterization of the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3894–3900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson R. T., DeLong M. R. Nucleus basalis of Meynert neuronal activity during a delayed response task in monkey. Brain Res. 1986 Dec 10;399(2):364–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91529-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter A., Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Field P. M., Raisman G. Axotomy causes loss of muscarinic receptors and loss of synaptic contacts in the hypoglossal nucleus. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):734–735. doi: 10.1038/266734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Noma A., Trautwein W. Acetylcholine activation of single muscarinic K+ channels in isolated pacemaker cells of the mammalian heart. Nature. 1983 May 19;303(5914):250–253. doi: 10.1038/303250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. T., Freeman J. A. Electrophysiologic evidence that retinotectal synaptic transmission in the goldfish is nicotinic cholinergic. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 7;187(1):129–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90499-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. T. The laminar organization of optic nerve fibres in the tectum of goldfish. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Aug 1;205(1159):287–306. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt F. O. Molecular regulators of brain function: a new view. Neuroscience. 1984 Dec;13(4):991–1001. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., Dolphin A. C. Regulation of calcium currents by a GTP analogue: potentiation of (-)-baclofen-mediated inhibition. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Aug 15;69(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90414-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds S. H., Strange P. G. Inhibition of inositol phospholipid breakdown by D2 dopamine receptors in dissociated bovine anterior pituitary cells. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Oct 10;60(3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90588-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Burke T. R., Jr, Rice K. C., Jacobson A. E., Klee W. A. Purification of the opiate receptor of NG108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4974–4978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Pin J. P., Récasens M., Bockaert J., Weiss S. Glutamate stimulates inositol phosphate formation in striatal neurones. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):717–719. doi: 10.1038/317717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slivka S. R., Insel P. A. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis and prostaglandin E2 formation in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Possible parallel activation of phospholipase C and phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4200–4207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Childers S. R. Opiate receptors and opioid peptides. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1979;2:35–64. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.02.030179.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., D'Amato R. J. Predicting Parkinson's disease. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):198–199. doi: 10.1038/317198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Parkinson's disease. A cure using brain transplants? 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):824–825. doi: 10.1038/326824b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima M., Noma A. Mode of regulation of the ACh-sensitive K-channel by the muscarinic receptor in rabbit atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00587544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson F. A. Isolation of the gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptor. Biochem Soc Trans. 1985 Dec;13(6):1097–1099. doi: 10.1042/bst0131097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange P. G., Koshland D. E., Jr Receptor interactions in a signalling system: competition between ribose receptor and galactose receptor in the chemotaxis response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):762–766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Ito I., Hirono C. A new type of glutamate receptor linked to inositol phospholipid metabolism. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):531–533. doi: 10.1038/325531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. K., Molinaro S., Schmidt J. Ligand responses of alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites from skeletal muscle and optic lobe of the chick. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8507–8512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watling K. J., Bristow D. R. GABAB receptor-mediated enhancement of vasoactive intestinal peptide-stimulated cyclic AMP production in slices of rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1986 Jun;46(6):1755–1762. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb08493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R., Davidoff R. A., Aprison M. H. Inhibition of motoneurones by iontophoresis of glycine. Nature. 1967 May 13;214(5089):681–683. doi: 10.1038/214681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojcik W. J., Neff N. H. gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptors are negatively coupled to adenylate cyclase in brain, and in the cerebellum these receptors may be associated with granule cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;25(1):24–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Van Dop C., Neer E. J., Snyder S. H. Go, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain resembles distribution of second messenger systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4561–4565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters W., Van Dun J., Laduron P. M. Identification of the serotonin-S2 receptor ligand binding site by photoaffinity labelling with 7-azido-8-[125I]ketanserin ([125I]AZIK). FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 23;213(2):359–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Rodriguez H., Wong S. K., Brandt D. R., May D. C., Burnier J., Harkins R. N., Chen E. Y., Ramachandran J., Ullrich A. The avian beta-adrenergic receptor: primary structure and membrane topology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6795–6799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Direct activation of mammalian atrial muscarinic potassium channels by GTP regulatory protein Gk. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):207–211. doi: 10.1126/science.2432660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimasa T., Sibley D. R., Bouvier M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Cross-talk between cellular signalling pathways suggested by phorbol-ester-induced adenylate cyclase phosphorylation. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):67–70. doi: 10.1038/327067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


