Abstract
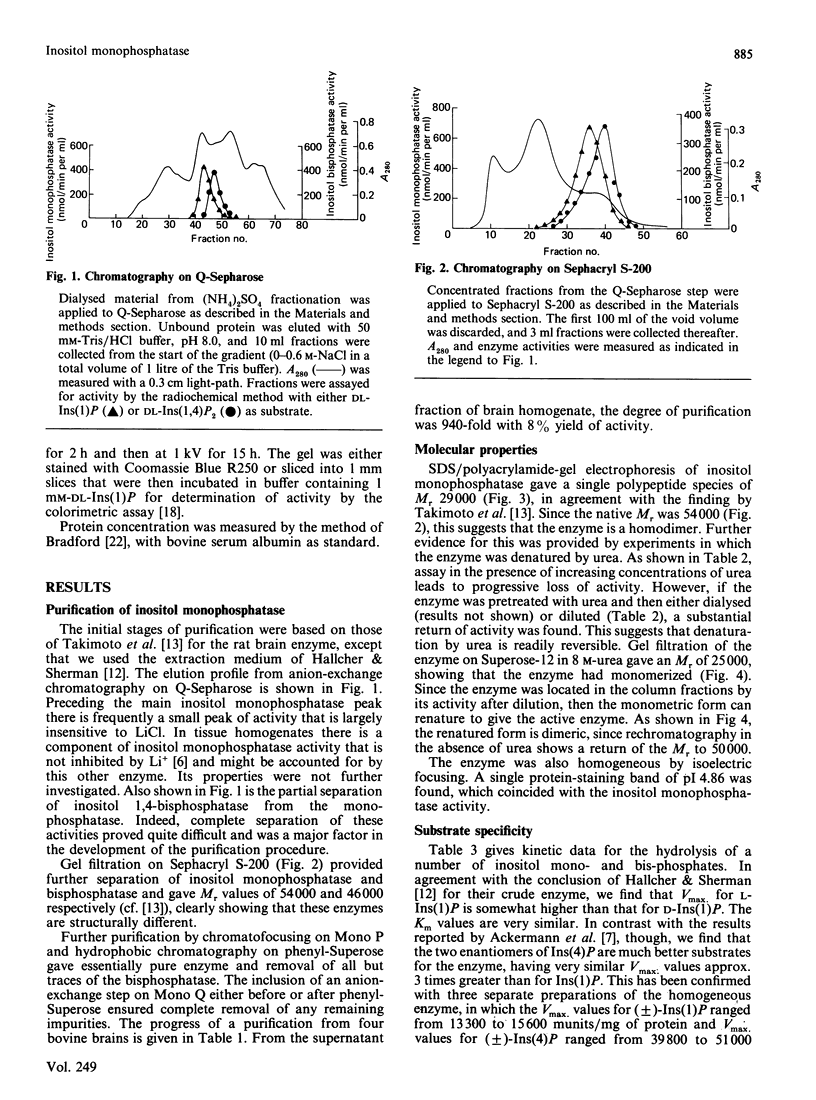
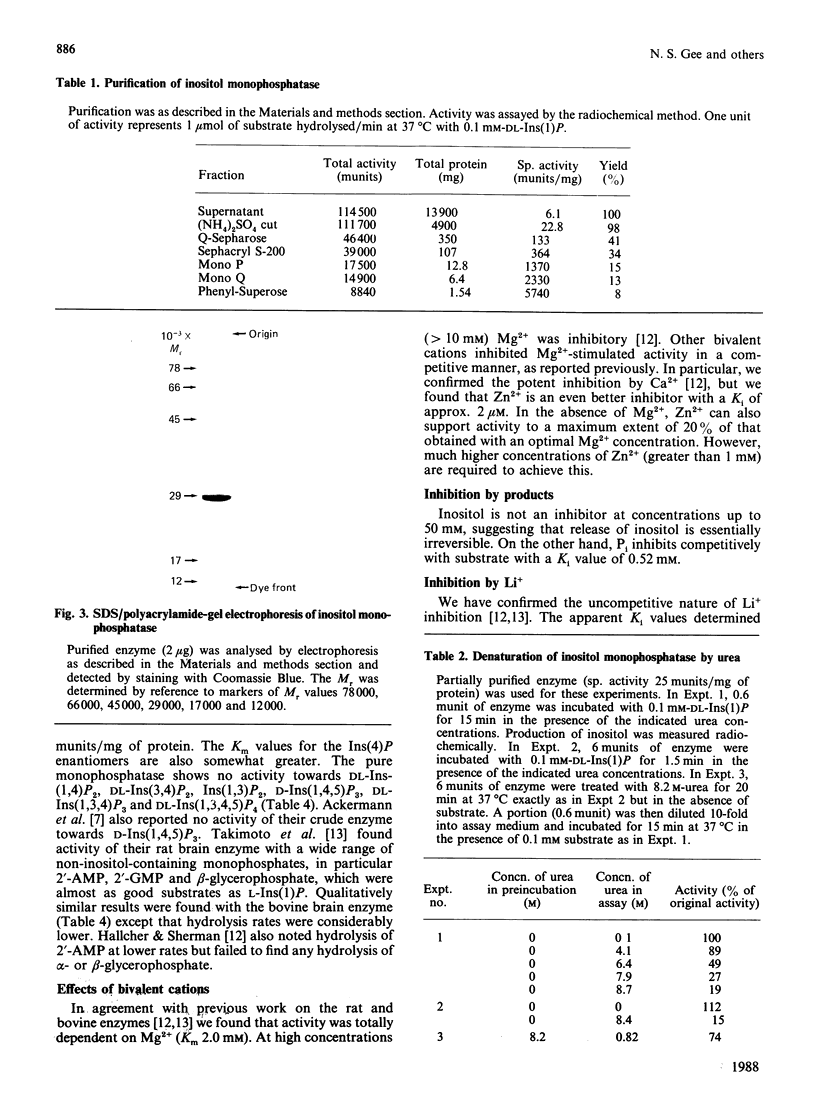
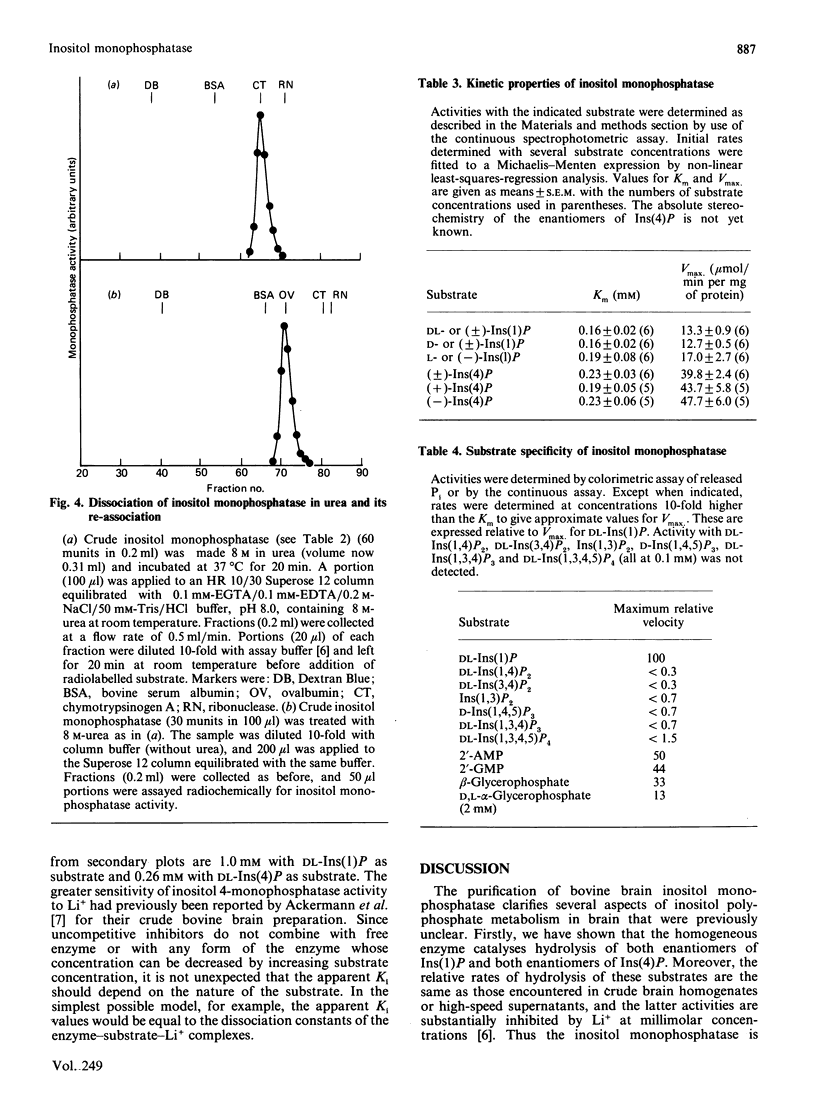
1. An inositol monophosphatase was purified to homogeneity from bovine brain. 2. The enzyme is a dimer of subunit Mr 29,000. 3. The enzyme hydrolyses both enantiomers of myo-inositol 1-phosphate and both enantiomers of myo-inositol 4-phosphate, but has no activity towards inositol bisphosphates, inositol trisphosphates or inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate. 4. Several non-inositol-containing monophosphates are also substrates. 5. The enzyme requires Mg2+ for activity, and Zn2+ supports activity to a small extent. 6. Other bivalent cations (including Zn2+) are inhibitors, competitive with Mg2+. 7. Phosphate, but not inositol, is an inhibitor competitive with substrate. 8. Li+ inhibits hydrolysis of inositol 1-phosphate and inositol 4-phosphate uncompetitively with different apparent Ki values (1.0 mM and 0.26 mM respectively).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Latif A. A. Calcium-mobilizing receptors, polyphosphoinositides, and the generation of second messengers. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Sep;38(3):227–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann K. E., Gish B. G., Honchar M. P., Sherman W. R. Evidence that inositol 1-phosphate in brain of lithium-treated rats results mainly from phosphatidylinositol metabolism. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):517–524. doi: 10.1042/bj2420517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balla T., Baukal A. J., Guillemette G., Morgan R. O., Catt K. J. Angiotensin-stimulated production of inositol trisphosphate isomers and rapid metabolism through inositol 4-monophosphate in adrenal glomerulosa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9323–9327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A. Why is uncompetitive inhibition so rare? A possible explanation, with implications for the design of drugs and pesticides. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 14;203(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Stone M. A. Lithium-induced reduction in intracellular inositol supply in cholinergically stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):199–204. doi: 10.1042/bj2340199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A. H., Raeburn C. A. The interaction of lithium with thyrotropin-releasing hormone-stimulated lipid metabolism in GH3 pituitary tumour cells. Enhancement of stimulated 1,2-diacylglycerol formation. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):129–136. doi: 10.1042/bj2240129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg F., Jr D-myoinositol 1-phosphate as product of cyclization of glucose 6-phosphate and substrate for a specific phosphatase in rat testis. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1375–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallcher L. M., Sherman W. R. The effects of lithium ion and other agents on the activity of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10896–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Mah S., Williamson J. R. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8100–8103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Downes C. P. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands may both result indirectly from receptor-stimulated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2380507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inhorn R. C., Bansal V. S., Majerus P. W. Pathway for inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate and 1,4-bisphosphate metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2170–2174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itaya K., Ui M. A new micromethod for the colorimetric determination of inorganic phosphate. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Sep;14(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek J. L. Inositol bis-, tris-, and tetrakis(phosphate)s: analysis in tissues by HPLC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4162–4166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragan C. I., Watling K. J., Gee N. S., Aspley S., Jackson R. G., Reid G. G., Baker R., Billington D. C., Barnaby R. J., Leeson P. D. The dephosphorylation of inositol 1,4-bisphosphate to inositol in liver and brain involves two distinct Li+-sensitive enzymes and proceeds via inositol 4-phosphate. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):143–148. doi: 10.1042/bj2490143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B., Storey D. J., Morris A. J., Cubitt A. B., Parry J. B., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Dephosphorylation of myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and myo-inositol 1,3,4-triphosphate. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):393–402. doi: 10.1042/bj2420393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. R., Munsell L. Y., Gish B. G., Honchar M. P. Effects of systemically administered lithium on phosphoinositide metabolism in rat brain, kidney, and testis. J Neurochem. 1985 Mar;44(3):798–807. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb12886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. J., Shears S. B., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. Stepwise enzymatic dephosphorylation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to inositol in liver. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):374–376. doi: 10.1038/312374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagahara I., Yamauti J., Fujii K., Yamashita J., Horio T. Theoretical and experimental analyses of coupled enzyme reactions. J Biochem. 1983 Apr;93(4):1145–1157. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto K., Okada M., Matsuda Y., Nakagawa H. Purification and properties of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from rat brain. J Biochem. 1985 Aug;98(2):363–370. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Neufeld E. J., Majerus P. W. Phosphoinositide interconversion in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1046–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot H., de Groot H., Noll T. Enzymic determination of inorganic phosphates, organic phosphates and phosphate-liberating enzymes by use of nucleoside phosphorylase-xanthine oxidase (dehydrogenase)-coupled reactions. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):255–260. doi: 10.1042/bj2300255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



