Abstract
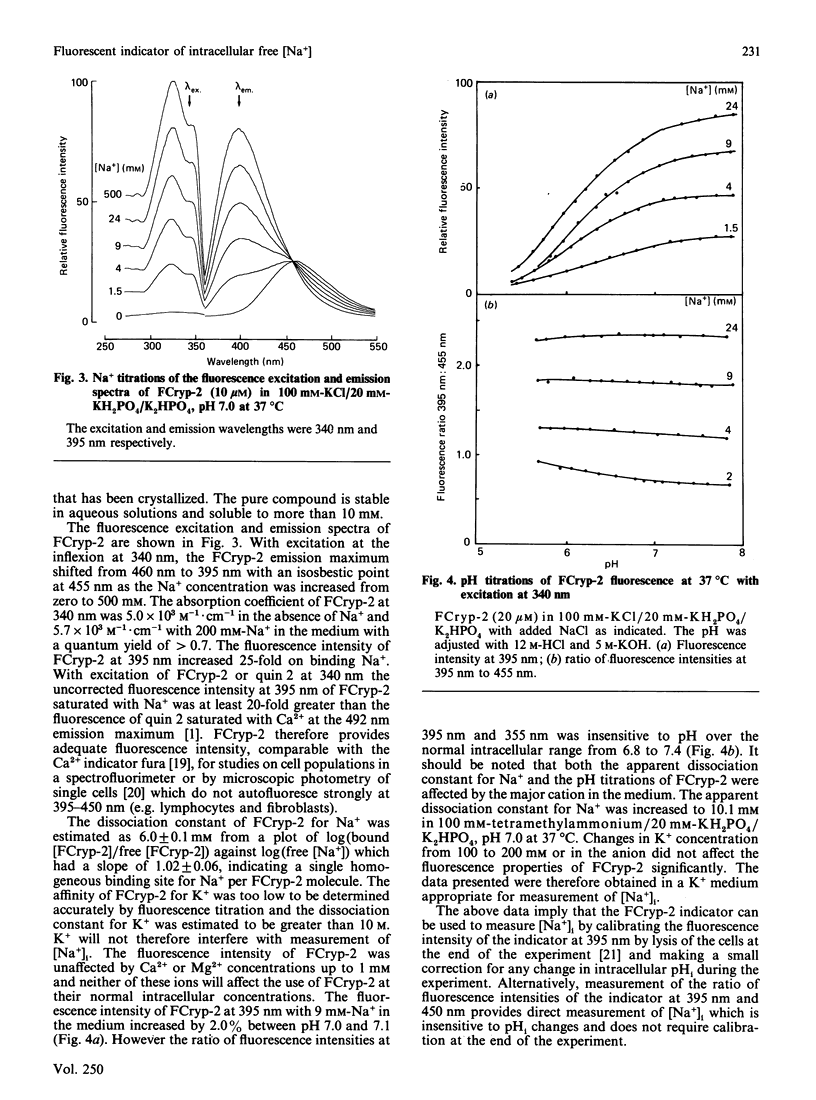
We have recently described a cryptand structure, FCryp-1, with appropriate properties for an indicator of intracellular free Na+ concentration using the 19F-n.m.r. chemical shift of the incorporated 5FBAPTA [1,2-bis-(2-amino-5-fluorophenoxy)ethane-NNN'N'-tetra-acetic acid] reporter group to measure the free cytosolic Na+ concentration [( Na+]i) [Smith, Morris, Hesketh and Metcalfe (1986) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 889, 82-83]. FCryp-1 carries four carboxylate groups to confer aqueous solubility and the indicator is membrane-permeant when the carboxyls are esterified with acetoxymethyl ester groups. Here we describe the synthesis of FCryp-2 to provide a fluorescent indicator of [Na+]i. FCryp-2 retains the parent tribenzo (2:2:1) cryptand structure of FCryp-1, in which the benzenoid ring at C-21 in FCryp-1 is replaced by an indole derivative which acts as the fluorophor in FCryp-2. With excitation at 340 nm, FCryp-2 gives an emission maximum at 460 nm in the absence of Na+ which shifts to 395 nm when FCryp-2 is saturated with Na+, with an isosbestic point at 455 nm. The apparent dissociation constant of FCryp-2 in a buffer solution of 100 mM-KCl/20 mM-KH2PO4/K2HPO4, pH 7.0, at 37 degrees C is 6.0 mM and the free Na+ concentration can be measured either from the calibrated fluorescence intensity at 395 nm, which increases 25-fold when Na+ is bound to FCryp-2, or from the ratio of fluorescence intensities at 395 nm and 455 nm. The measurement of free [Na+] by either method is unaffected by K+, Ca2+ or Mg2+ in the normal intracellular concentration ranges. Free [Na+] measurements by the ratio method are unaffected by pH from 6.6 to 7.6.
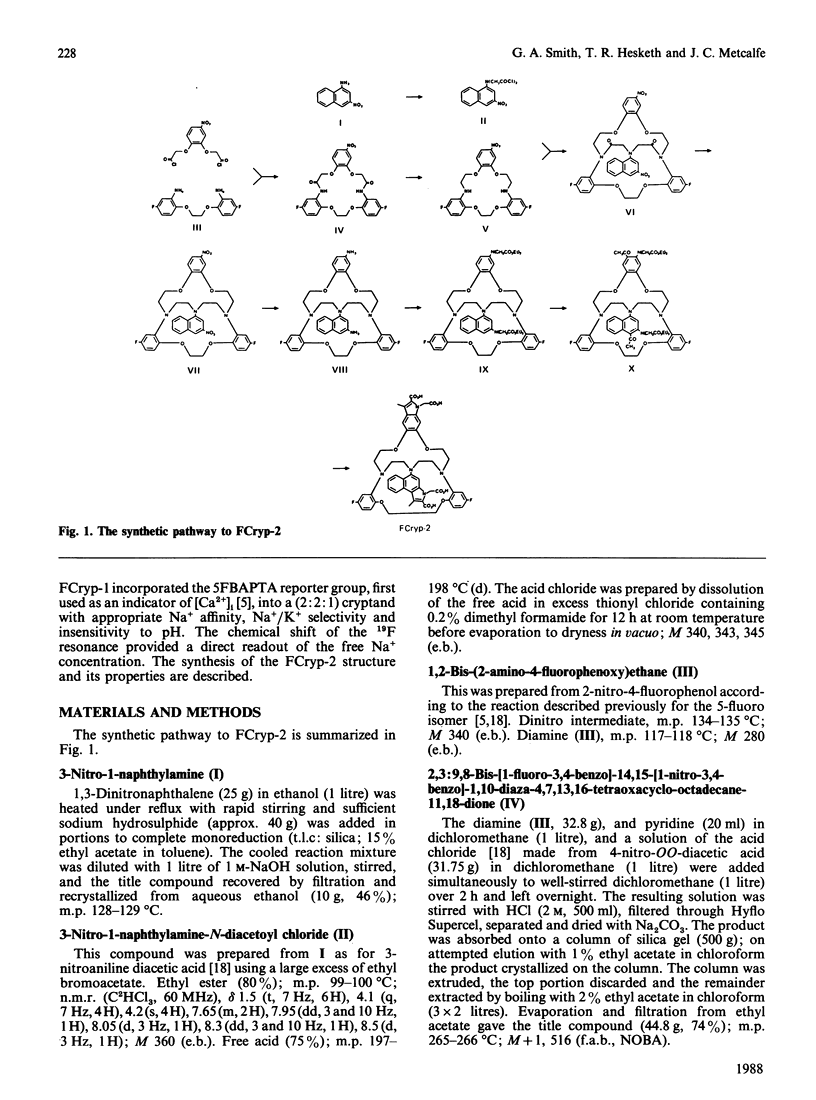
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Besterman J. M., Tyrey S. J., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Cuatrecasas P. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor-induced mitogenesis by amiloride and an analog: evidence against a requirement for Na+/H+ exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6762–6766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. A., Rodrigo G. C., Tunstall J., Yates R. J., Busselen P. Calcium paradox of the heart: a role for intracellular sodium ions. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):H874–H879. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1984.247.5.H874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber S. M., Brand M. D. Concanavalin A causes an increase in sodium permeability and intracellular sodium content of pig lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):893–897. doi: 10.1042/bj2100893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Moore J. P., Morris J. D., Taylor M. V., Rogers J., Smith G. A., Metcalfe J. C. A common sequence of calcium and pH signals in the mitogenic stimulation of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):481–484. doi: 10.1038/313481a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P., Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C. Free cytoplasmic calcium concentration and the mitogenic stimulation of lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4876–4882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I., Metzger H. Initial characterization of the calcium channel activated by the cross-linking of the receptors for immunoglobulin E. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10188–10193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M. S., Partilla J. S., Piñeyro M. A., Schneyer C. R., Gregerman R. I. Salts promote activation of fat cell adenylate cyclase by GTP: special role for sodium ion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7417–7421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe J. C., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A. Free cytosolic Ca2+ measurements with fluorine labelled indicators using 19FNMR. Cell Calcium. 1985 Apr;6(1-2):183–195. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(85)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Todd J. A., Hesketh T. R., Metcalfe J. C. c-fos and c-myc gene activation, ionic signals, and DNA synthesis in thymocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8158–8162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen N. E. Effect of TPA on ion fluxes and DNA synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):454–459. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Chambard J. C., Franchi A., Paris S., Van Obberghen-Schilling E. Growth factor activation of an amiloride-sensitive Na+/H+ exchange system in quiescent fibroblasts: coupling to ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3935–3939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Franchi A., L'Allemain G., Paris S. Cytoplasmic pH, a key determinant of growth factor-induced DNA synthesis in quiescent fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 7;190(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Cytoplasmic pH and free Mg2+ in lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):189–196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Beaven M. A., Metcalfe J. C., Johnson P., Garland P. B. Intracellular pH and free calcium changes in single cells using quene 1 and quin 2 probes and fluorescence microscopy. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 5;161(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80722-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Metcalfe J. C. Intracellular pH of stimulated thymocytes measured with a new fluorescent indicator. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):5994–5997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. A., Hesketh R. T., Metcalfe J. C., Feeney J., Morris P. G. Intracellular calcium measurements by 19F NMR of fluorine-labeled chelators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7178–7182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. A., Morris P. G., Hesketh T. R., Metcalfe J. C. Design of an indicator of intracellular free Na+ concentration using 19F-NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 31;889(1):72–83. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Rozengurt E. Lithium transport by fibroblastic mouse cells: characterization and stimulation by serum and growth factors in quiescent cultures. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Dec;97(3 Pt 2 Suppl 1):441–449. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040970319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. A non-disruptive technique for loading calcium buffers and indicators into cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):527–528. doi: 10.1038/290527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


