Abstract
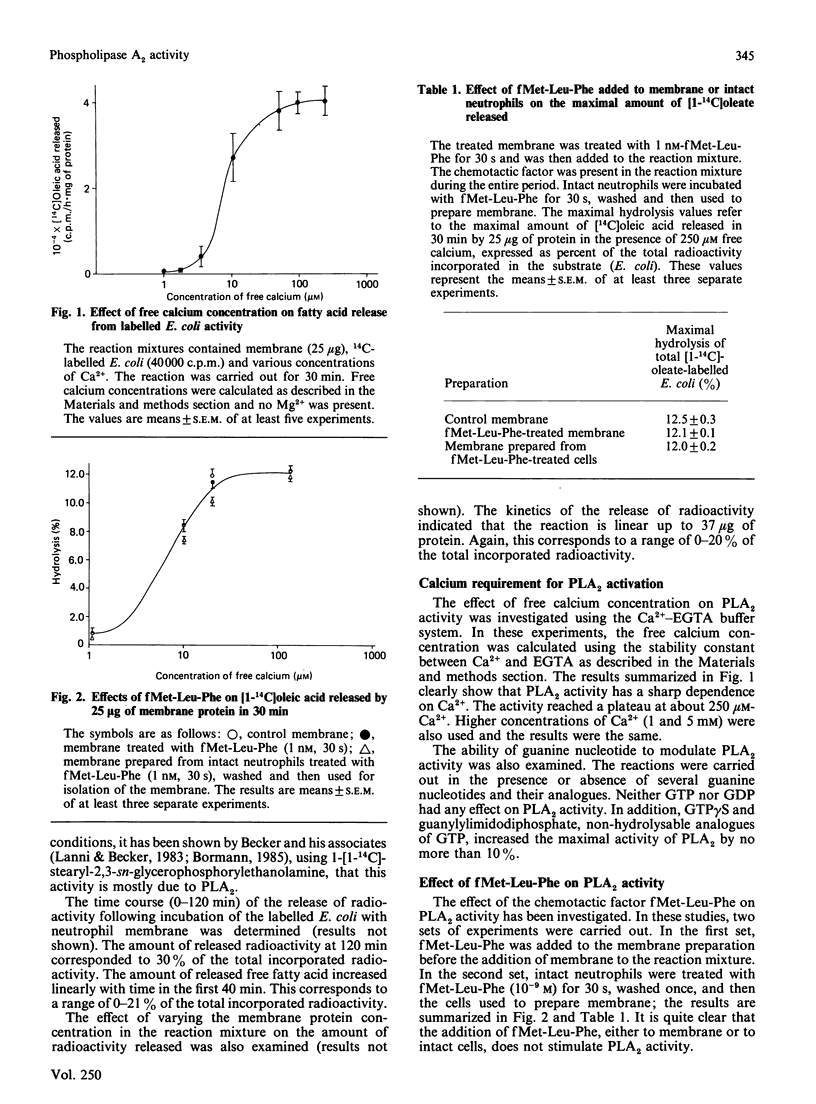
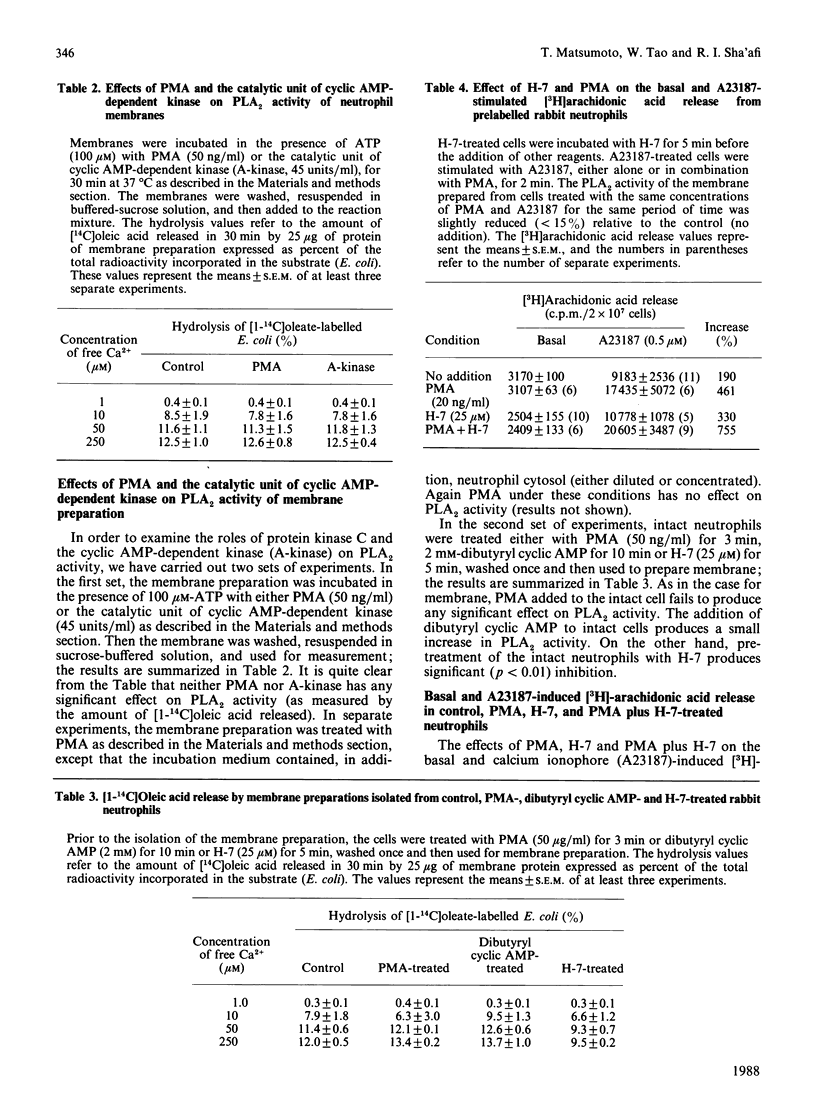
The presence of a phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity in rabbit neutrophil membrane preparation that is able to release [1-14C]oleic acid from labelled Escherichia coli has been demonstrated. The activity is critically dependent on the free calcium concentration and marginally stimulated by GTP gamma S. More than 80% of maximal activity is reached at 10 microM-Ca2+. The chemotactic factor, fMet-Leu-Phe, does not stimulate the PLA2 activity in this membrane preparation. Pretreatment of the membrane preparation, under various experimental conditions, or intact cells, before isolation of the membrane with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), does not affect PLA2 activity. Addition of the catalytic unit of cyclic AMP-dependent kinase to membrane preparation has no effect on PLA2 activity. Pretreatment of the intact neutrophil with dibutyryl-cAMP before isolation of the membrane produces a small but consistent increase in PLA2 activity. The activity of PLA2 in membrane isolated from cells treated with the protein kinase inhibitor 1-(5-isoquinolinesulphonyl)-2-methyl piperazine dihydrochloride (H-7) is significantly decreased. Furthermore, although the addition of PMA to intact rabbit neutrophils has no effect on the release of [3H]arachidonic acid from prelabelled cells, it potentiates significantly the release produced by the calcium ionophore A23187. This potentiation is not due to an inhibition of the acyltransferase activity. H-7 inhibits the basal release of arachidonic acid but does not inhibit the potentiation by PMA. These results suggest several points. (1) fMet-Leu-Phe does not stimulate PLA2 directly, and its ability to release arachidonic acid in intact neutrophils is mediated through its action on phospholipase C. (2) The potentiating effect of PMA on A23187-induced arachidonic acid release is most likely due to PMA affecting either the environment of PLA2 and/or altering the organization of membrane phospholipids in such a way as to increase their susceptibility to hydrolysis. (3) The intracellular level of cyclic AMP probably does not directly affect the activity of PLA2.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso F., Henson P. M., Leslie C. C. A cytosolic phospholipase in human neutrophils that hydrolyzes arachidonoyl-containing phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 12;878(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C activities of platelets. Differential substrate specificity, Ca2+ requirement, pH dependence, and cellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10227–10231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann B. J., Huang C. K., Mackin W. M., Becker E. L. Receptor-mediated activation of a phospholipase A2 in rabbit neutrophil plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):767–770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Luini A., Axelrod J. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C are activated by distinct GTP-binding proteins in response to alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation in FRTL5 thyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7201–7205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Background and discovery of lipocortins. Agents Actions. 1986 Jan;17(3-4):255–262. doi: 10.1007/BF01982616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey R. W., Manzi R. M., Clark M. A., Hoffstein S. T. Stimulus-specific induction of phospholipid and arachidonic acid metabolism in human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):925–932. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halenda S. P., Zavoico G. B., Feinstein M. B. Phorbol esters and oleoyl acetoyl glycerol enhance release of arachidonic acid in platelets stimulated by Ca2+ ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12484–12491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Corcoran B. A., Venkatasubramanian K., Schiffmann E., Axelrod J. Chemoattractants stimulate degradation of methylated phospholipids and release of arachidonic acid in rabbit leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2640–2643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands W. E., Samuelsson B. Phospholipid precursors of prostaglandins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):426–429. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanni C., Becker E. L. Release of phospholipase A2 activity from rabbit peritoneal neutrophils by f-Met-Leu-Phe. Am J Pathol. 1983 Oct;113(1):90–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Molski T. F., Kanaho Y., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. G-protein dissociation, GTP-GDP exchange and GTPase activity in control and PMA treated neutrophils stimulated by fMet-Leu-Phe. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley A., Tai H. H. Synergistic stimulation of thromboxane biosynthesis by calcium ionophore and phorbol ester or thrombin in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):717–723. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90475-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. D. The determination of the stability constant for calcium-EGTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 18;451(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J., Irvine R. F. Liberation of [3H]arachidonic acid and changes in cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated by ionomycin and collagen. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):869–877. doi: 10.1042/bj2350869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P., Sink L. E., Freer R. J. On the relationship between formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine stimulation of arachidonyl phosphatidylinositol turnover and lysosomal enzyme secretion by rabbit neutrophils. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;19(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. M., Jr, Waite M. Phospholipid metabolism in human neutrophil subfractions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Apr;246(1):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90472-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor M., Weiss J., Klempner M. S., Elsbach P. Phospholipase A2 activity in the plasma membrane of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 28;136(2):298–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80639-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Feinstein M. B., Sha'afi R. I. Phorbol 12-myristate, 13-acetate potentiates the action of the calcium ionophore in stimulating arachidonic acid release and production of phosphatidic acid in rabbit neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):594–600. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Yassin R., Tao W., Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I. Leukotriene B4 mobilizes calcium without the breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and the production of phosphatidic acid in rabbit neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5966–5969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


