Abstract
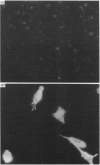
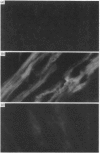
The 67 k calcimedin is a Ca2+-binding protein present in both muscle cells and peritoneal macrophages. Many tissues, including lymphoid tissues, liver and lymphocytes, have been shown to contain Ca2+-binding proteins of similar molecular size, such as the p67(67 kDa) calelectrin or the 68 kDa lymphocyte protein. We have tested affinity-purified antibodies raised to the smooth-muscle 67 k calcimedin in these several tissues and here report that the 67 k calcimedin is not detectable in liver, thymus, spleen or thymic lymphocytes. These findings support recent biochemical evidence, discussed here, suggesting that the 67 k calcimedin is a protein different from calelectrin and the 68 kDa lymphocyte protein. The more limited tissue distribution of the 67 k calcimedin, which includes muscle and macrophages, suggests that the 67 k calcimedin may function in Ca2+-mediated events special to these cell types. The affinity-purified antibodies to the 67 k calcimedin will be useful in obtaining information concerning the special roles of this Ca2+-binding protein in these cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davies A. A., Crumpton M. J. Identification of calcium-binding proteins associated with the lymphocyte plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):571–577. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel J., Vicendo P., Roques V., Ragab-Thomas J., Granier C., Vilgrain I., Chambaz E., Rochat H., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Isolation of two 67 kDa calcium-binding proteins from pig lung differing in affinity for phospholipids and in anti-phospholipase A2 activity. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 14;221(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80963-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M., Childs J., Dash B., Harris A., Panayotou G., Südhof T., Walker J. H. Cellular distribution of three mammalian Ca2+-binding proteins related to Torpedo calelectrin. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2969–2974. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02242.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew J. K., Krolak J. M., Dedman J. R. Calcimedins: purification and characterization from chicken gizzard and rat and bovine livers. J Cell Biochem. 1986;32(3):223–234. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240320309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B. 67 kDa calcimedin, a new Ca2+-binding protein. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):49–54. doi: 10.1042/bj2380049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Dedman J. R. Calcium-dependent protein binding to phenothiazine columns. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9663–9667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B. Isolation and purification of an antibody to 67-KD calcimedin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Feb;36(2):185–192. doi: 10.1177/36.2.2961799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Kraus-Friedmann N., Dedman J. R. Unique calcium-dependent hydrophobic binding proteins: possible independent mediators of intracellular calcium distinct from calmodulin. J Cell Sci. 1984 Dec;72:121–133. doi: 10.1242/jcs.72.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. S., Moore P. B. Effect of nifedipine on 67k calcimedin in cultured macrophages and smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 15;145(2):726–732. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. J., Crumpton M. J. Isolation and characterization of a novel 68,000-Mr Ca2+-binding protein of lymphocyte plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 1;219(1):309–316. doi: 10.1042/bj2190309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads A. R., Lulla M., Moore P. B., Jackson C. E. Characterization of calcium-dependent membrane binding proteins of brain cortex. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 1;229(3):587–593. doi: 10.1042/bj2290587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith V. L., Dedman J. R. An immunological comparison of several novel calcium-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15815–15818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohar I., Bird J. W., Moore P. B. Calcium-dependent proteolysis of calcium-binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1269–1275. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C. Calelectrins are a ubiquitous family of Ca2+-binding proteins purified by Ca2+-dependent hydrophobic affinity chromatography by a mechanism distinct from that of calmodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):100–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90385-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Ebbecke M., Walker J. H., Fritsche U., Boustead C. Isolation of mammalian calelectrins: a new class of ubiquitous Ca2+-regulated proteins. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 13;23(6):1103–1109. doi: 10.1021/bi00301a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Zimmermann C. W., Walker J. H. Calelectrin in human blood cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 May;30(2):214–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]