Abstract
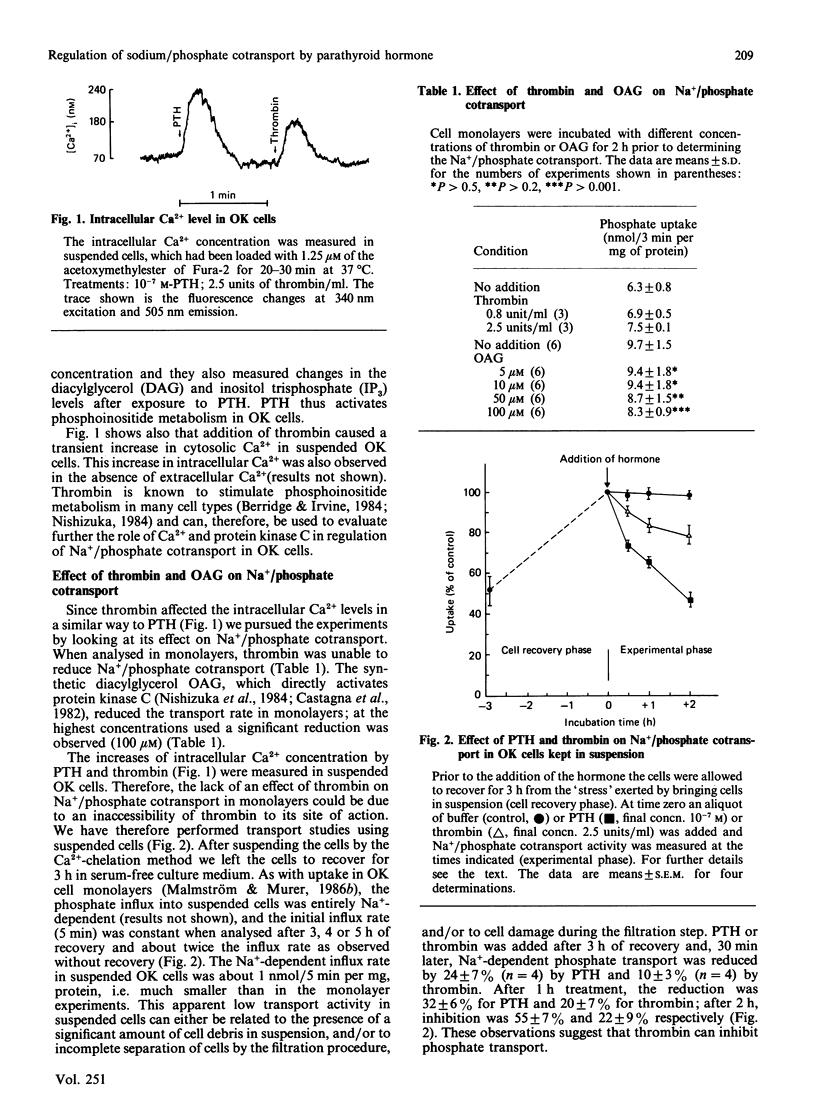
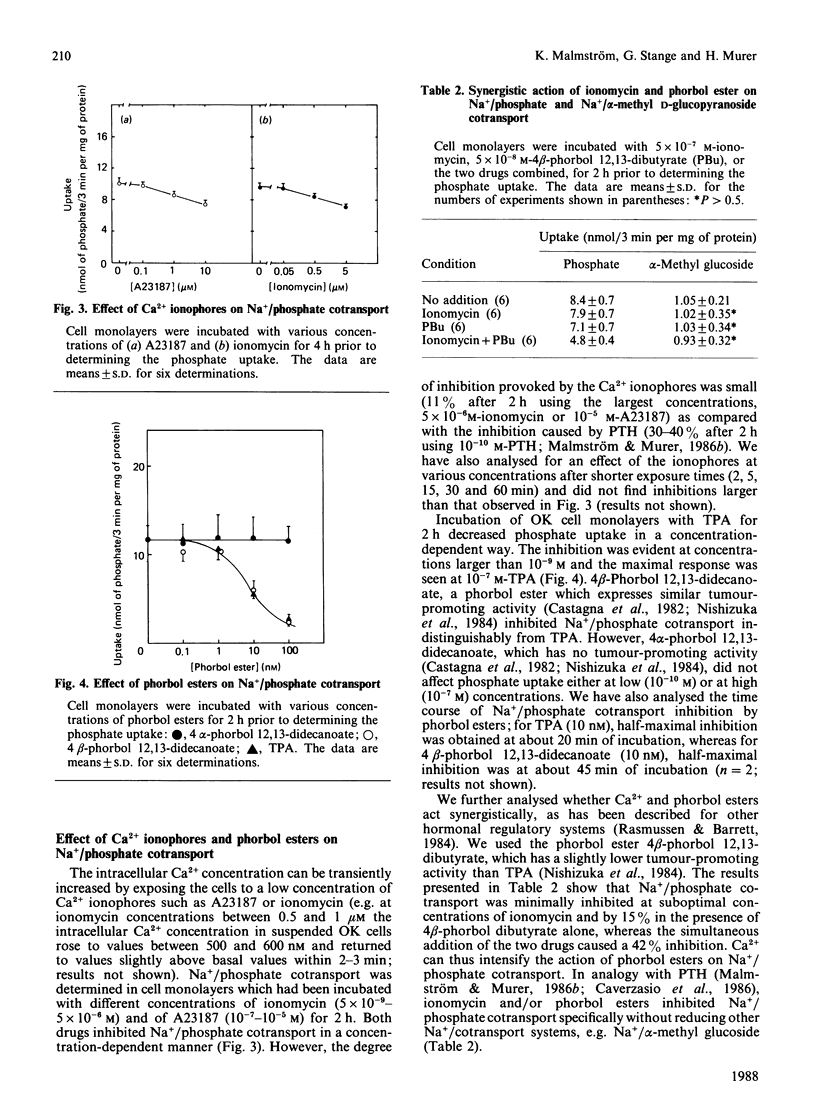
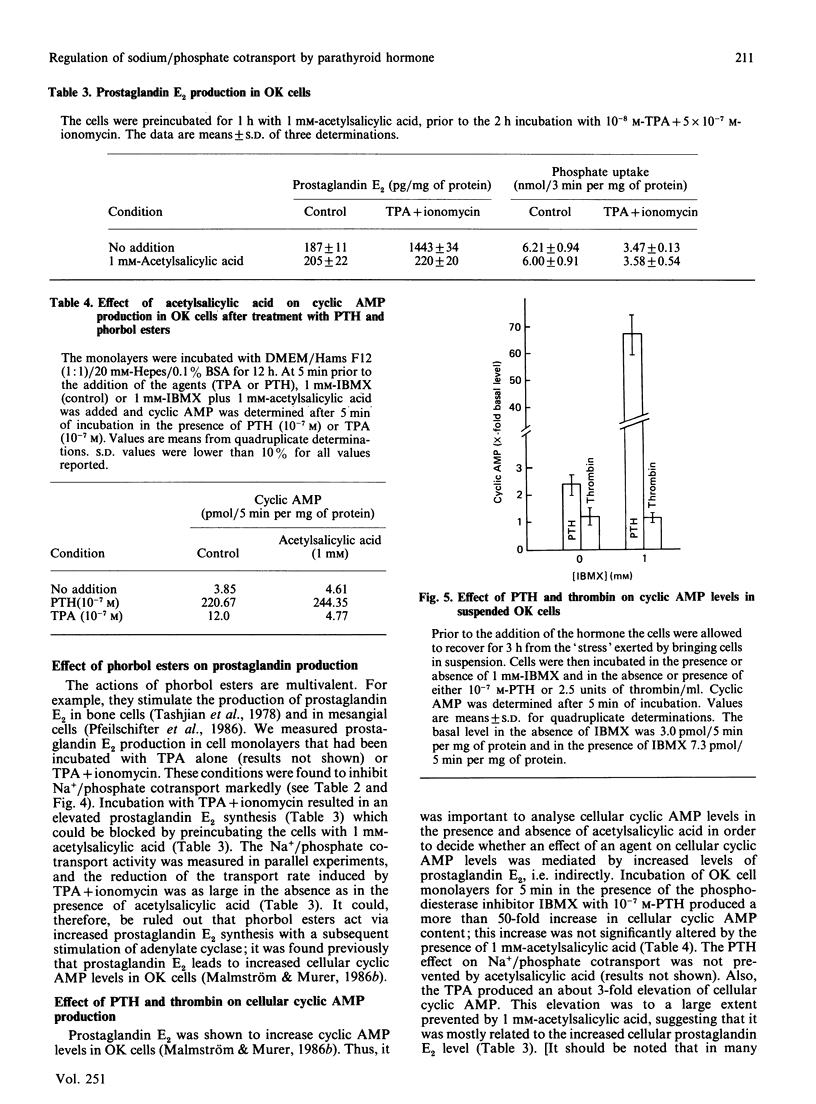
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increased intracellular cyclic AMP and reduces Na+/phosphate cotransport activity in OK cells [Malmström & Murer (1986) Am. J. Physiol. 251, C23-C31; Caverzasio, Rizzoli & Bonjour (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261, 3233-3237]. It was also shown that PTH activates phosphoinositide metabolism in OK cells [Hruska, Moskowitz, Esprit, Civitelli, Westbrook & Huskey (1987) J. Clin. Invest. 79, 230-239]. In the present paper we show that tumour-promoting phorbol esters are effective in reducing Na+/phosphate cotransport. The Ca2+ ionophores A23187 and ionomycin had only a small effect on Na+/phosphate cotransport; added together, A23187 and phorbol esters showed a synergistic action. Phorbol esters and phorbol esters plus ionomycin stimulated prostaglandin synthesis as well as cyclic AMP production; acetylsalicylic acid prevented phorbol-ester-induced prostaglandin synthesis and cyclic AMP production, but had no effect on inhibition of Na+/phosphate cotransport. In suspensions of OK cells, PTH and thrombin produced a rise in intracellular Ca2+. In contrast with PTH, thrombin did not elevate cellular cyclic AMP in suspended OK cells. PTH and thrombin reduced Na+/phosphate cotransport in suspended OK cells. It is suggested that two regulatory cascades are involved in PTH action on Na+/phosphate cotransport: cyclic AMP/kinase A and Ca2+/diacylglycerol/kinase C.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. D., Brunton L. L. Enhancement of adenylate cyclase activity in S49 lymphoma cells by phorbol esters. Withdrawal of GTP-dependent inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12036–12041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. D., Buxton I. L., Brunton L. L. Enhancement of adenylate cyclase activity in S49 lymphoma cells by phorbol esters. Putative effect of C kinase on alpha s-GTP-catalytic subunit interaction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2625–2628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. L., Ekins R. P., Albano J. D. Saturation assay for cyclic AMP using endogenous binding protein. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;2:25–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caverzasio J., Rizzoli R., Bonjour J. P. Sodium-dependent phosphate transport inhibited by parathyroid hormone and cyclic AMP stimulation in an opossum kidney cell line. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3233–3237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. A., Eber S. L., Poelling R. E., Thorne P. K., Forte L. R. A dual mechanism for regulation of kidney phosphate transport by parathyroid hormone. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):E221–E227. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.2.E221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulley J. R., Grieve P. A. A simple technique for eliminating interference by detergents in the Lowry method of protein determination. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):136–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmaj P., Murer H. Cellular mechanisms of inorganic phosphate transport in kidney. Physiol Rev. 1986 Jan;66(1):36–70. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F., Rosenblatt M., Potts J. T., Jr Parathyroid hormone: biochemical aspects of biosynthesis, secretion, action, and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jul;64(3):985–1053. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.3.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Merrill A. H., Jr, Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of protein kinase C activity and of phorbol dibutyrate binding in vitro and in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12604–12609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruska K. A., Moskowitz D., Esbrit P., Civitelli R., Westbrook S., Huskey M. Stimulation of inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol production in renal tubular cells by parathyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):230–239. doi: 10.1172/JCI112788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs K. H., Bauer S., Watanabe Y. Modulation of adenylate cyclase of human platelets by phorbol ester. Impairment of the hormone-sensitive inhibitory pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):425–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita Y., Fukase M., Yamatani T., Hishikawa R., Fujita T. Phorbol esters stimulate phosphate accumulation synergistically with A23187 in cultured renal tubular cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90892-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Raynor R. L., Mazzei G. J., Schatzman R. C., Turner R. S., Kem W. R. Cobra polypeptide cytotoxin I and marine worm polypeptide cytotoxin A-IV are potent and selective inhibitors of phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 7;153(1):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwik C. W., van Leeuwen J. P., van der Meer J. M., van Zeeland J. K., Scheven B. A., Herrmann-Erlee M. P. A two-receptor model for the action of parathyroid hormone on osteoblasts: a role for intracellular free calcium and cAMP. Cell Calcium. 1985 Aug;6(4):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(85)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmström K., Murer H. Parathyroid hormone inhibits phosphate transport in OK cells but not in LLC-PK1 and JTC-12.P3 cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 1):C23–C31. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.1.C23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmström K., Murer H. Parathyroid hormone regulates phosphate transport in OK cells via an irreversible inactivation of a membrane protein. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 1;216(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80701-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohrmann I., Mohrmann M., Biber J., Murer H. Stimulation of Na+/phosphate cotransport in LLC-PK1 cells by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 7;860(1):35–43. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90495-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Yu B., Nishizuka Y. Inhibitory action of chlorpromazine, dibucaine, and other phospholipid-interacting drugs on calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8378–8380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai M., Kinoshita Y., Fukase M., Fujita T. Phorbol esters inhibit phosphate uptake in opossum kidney cells: a model of proximal renal tubular cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Kikkawa U., Kaibuchi K. Phospholipid turnover in hormone action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1984;40:301–345. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571140-1.50012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Kurtz A., Bauer C. Role of phospholipase C and protein kinase C in vasoconstrictor-induced prostaglandin synthesis in cultured rat renal mesangial cells. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):125–130. doi: 10.1042/bj2340125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Barrett P. Q. Calcium messenger system: an integrated view. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jul;64(3):938–984. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.3.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Murray M., Zachary I., Collins M. Protein kinase C activation enhances cAMP accumulation in Swiss 3T3 cells: inhibition by pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2282–2286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Wise B. C., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent protein kinase: inhibition by antipsychotic drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 12;98(3):669–676. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Ivey J. L., Delclos B., Levine L. Stimulation of prostaglandin production in bone by phorbol diesters and melittin. Prostaglandins. 1978 Aug;16(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(78)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum A. P., Strewler G. J. Parathyroid hormone receptors coupled to cyclic adenosine monophosphate formation in an established renal cell line. Endocrinology. 1984 Mar;114(3):980–985. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-3-980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimasa T., Sibley D. R., Bouvier M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Cross-talk between cellular signalling pathways suggested by phorbol-ester-induced adenylate cyclase phosphorylation. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):67–70. doi: 10.1038/327067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


