Abstract
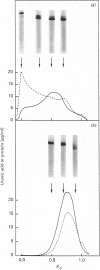
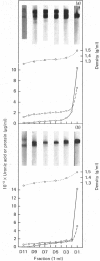
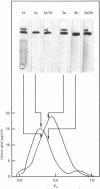
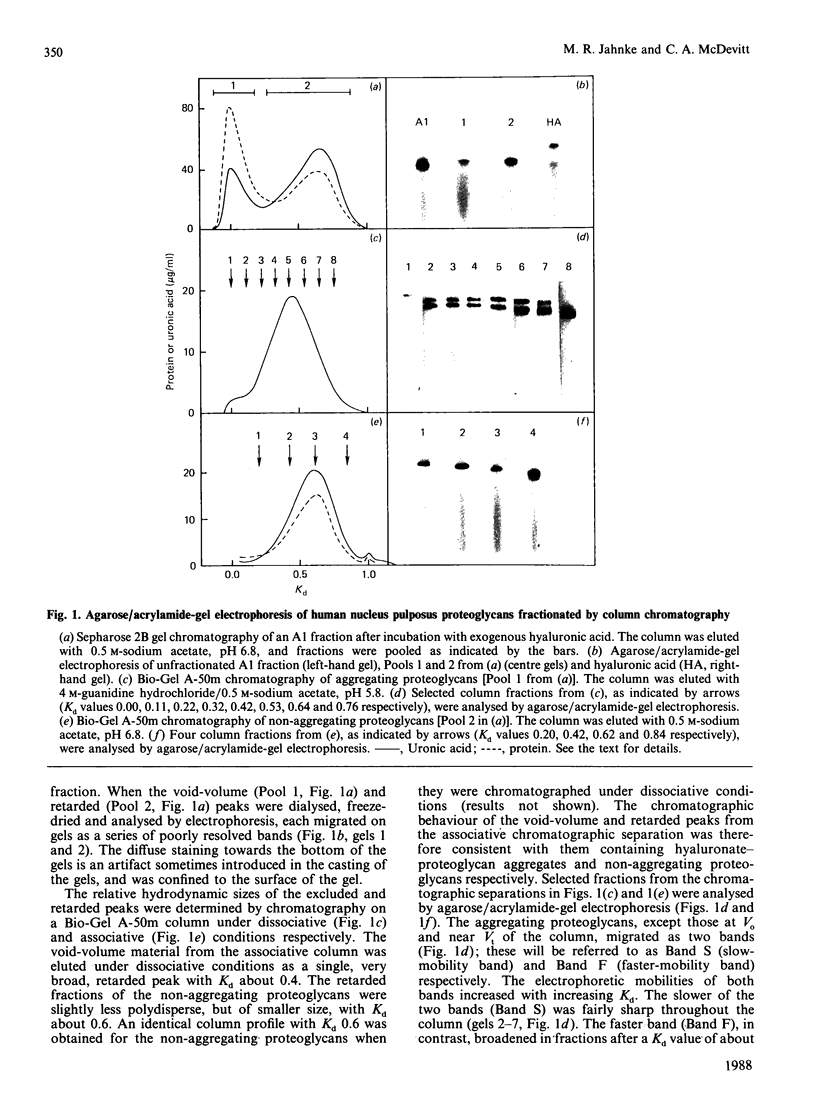
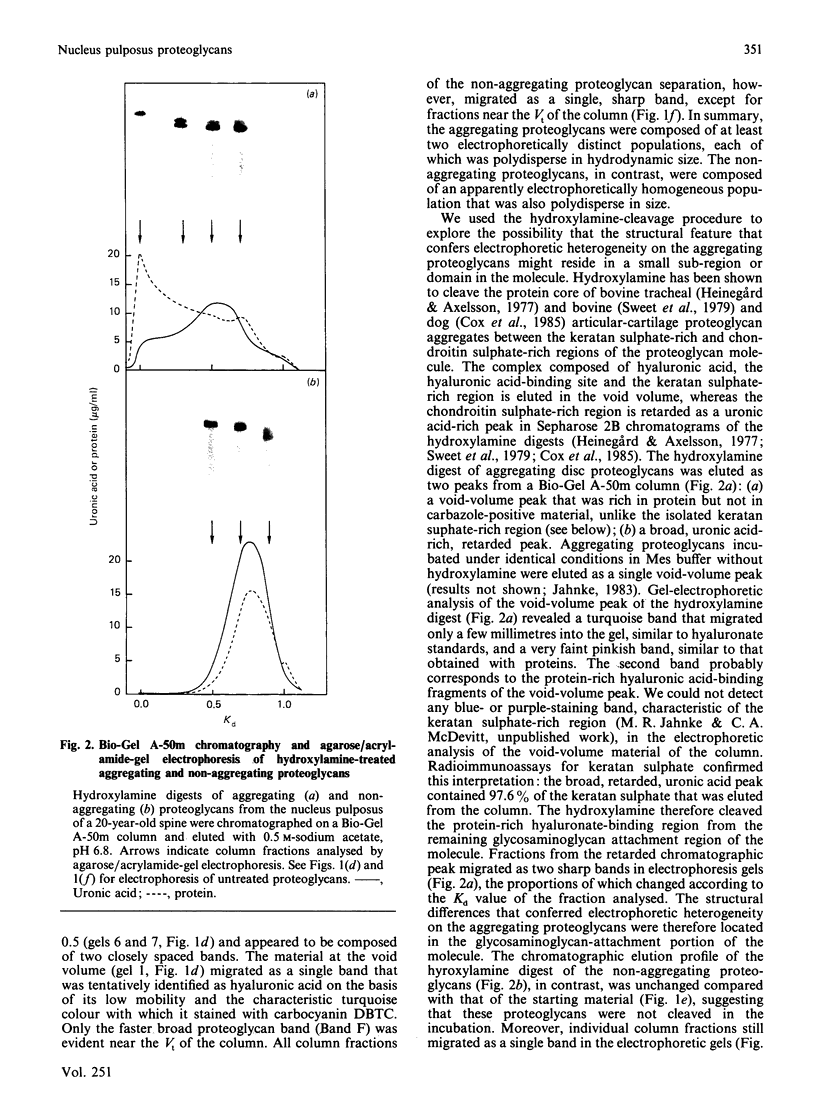
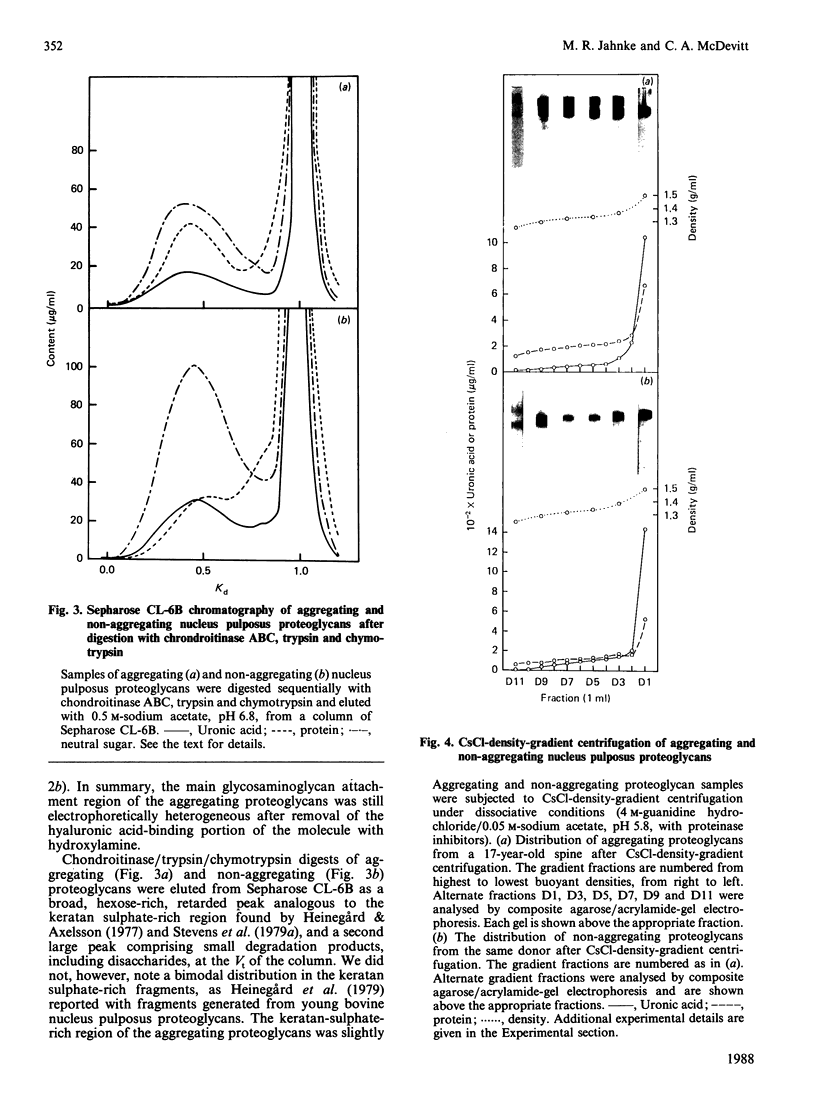
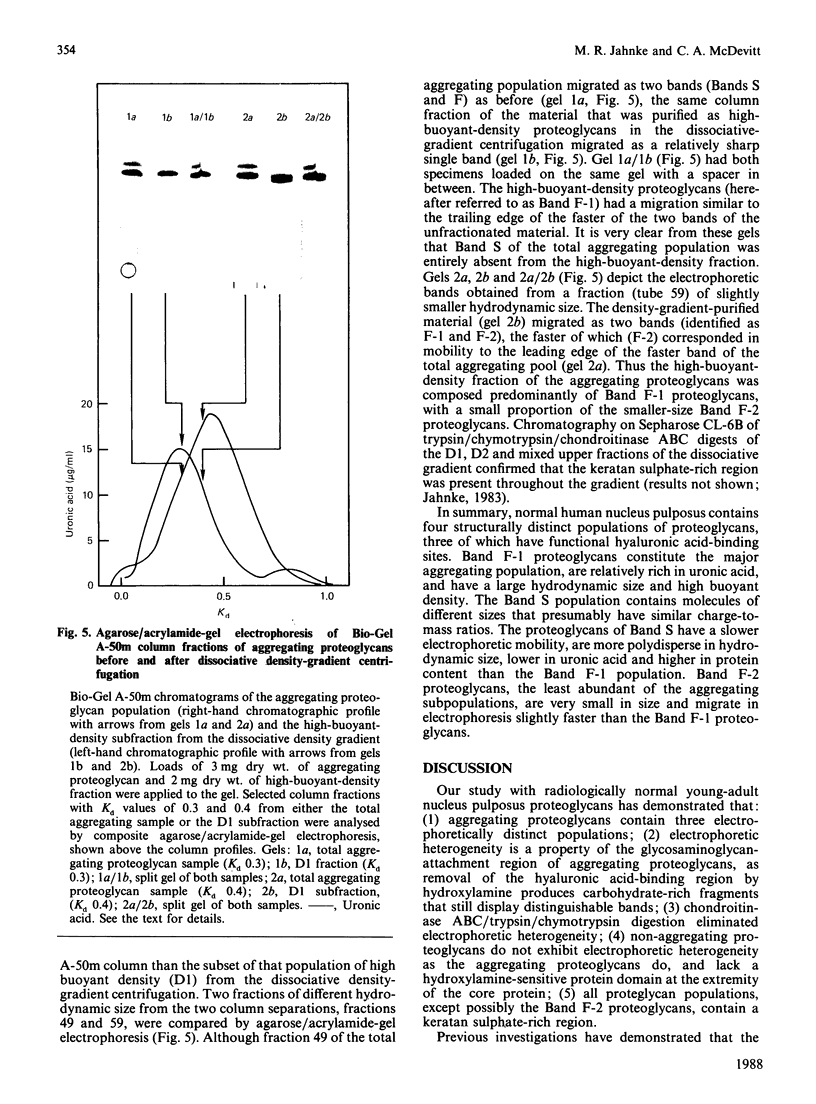
Nuclei pulposi were dissected from lumbar discs of radiologically normal human spines of cadavers aged 17, 20 and 21 years. Proteoglycans were extracted with 4 M guanidine hydrochloride (dissociative conditions) with proteinase inhibitors and isolated as A1 fractions by associative density-gradient centrifugation. Aggregating and non-aggregating proteoglycans were separated by Sepharose 2B chromatography. Both aggregating and non-aggregating proteoglycans contained a keratan sulphate-rich region as isolated by chondroitinase/trypsin/chymotrypsin digestion and Sepharose CL-6B chromatography. Agarose/acrylamide-gel electrophoresis of individual fractions of a Bio-Gel A-50m dissociative-column separation of the aggregating proteoglycans revealed two, well-separated bands: S and F, the slower and faster migrating bands respectively. The non-aggregating proteoglycan fractions were eluted under associative conditions (0.5 M-sodium acetate, pH 6.8) and migrated as a single band in the electrophoretic system. The gel-electrophoretic heterogeneity of the aggregating proteoglycans was still evident after hydroxylamine fragmentation and removal of the hyaluronate-binding portion of the molecule. Dissociative density-gradient centrifugation of the aggregating proteoglycans partially separated the Band-S proteoglycans from the Band-F population. Subsequent dissociative chromatography of the high-buoyant-density Band F proteoglycans permitted discrimination of this band into two gel-electrophoresis-distinguishable populations (Bands F-1 and F-2). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with a monoclonal antibody that recognized keratan sulphate demonstrated that the D1 fraction containing the Band F-1 proteoglycans was enriched in keratan sulphate compared with the total aggregating or non-aggregating pool of proteoglycans. The proteoglycans of young adult nucleus pulposus could then be ascribed to one of four structurally and/or electrophoretically distinct populations: (1) the non-aggregating population, which comprised about 70% of the total extractable proteoglycans; (2) the aggregating pool, comprising: (a) Band F-1 proteoglycans, which had a relatively large hydrodynamic size, uronate/protein weight ratio, were enriched in keratan sulphate and had a high buoyant density; (b) Band S proteoglycans, which migrated slower in agarose/acrylamide gels, had a smaller hydrodynamic size, lower buoyant density and a lower uronate/protein ratio than the Band F-1 population; (c) Band F-2 proteoglycans, which were lower in buoyant density, smaller in hydrodynamic size and slightly faster in electrophoretic mobility than the Band F-1 proteoglycans.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. E., Grant M. D., Ho A. Cartilage proteoglycan changes in experimental canine osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1987 May;14(Spec No):107–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P., Muir H. Qualitative changes with age of proteoglycans of human lumbar discs. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Aug;35(4):289–296. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.4.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss M. T., Ali S. Y. Age-related changes in the composition and structure of human articular-cartilage proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):683–693. doi: 10.1042/bj1760683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss M. T., Urban J. P., Johnstone B., Holm S. In vitro method for measuring synthesis rates in the intervertebral disc. J Orthop Res. 1986;4(1):10–17. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100040102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Balian G. The specific nonenzymatic cleavage of bovine ribonuclease with hydroxylamine. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4854–4856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J., Oldberg A., Ruoslahti E., Brown K., Schwartz N. Immunological evidence for two distinct chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan core proteins: differential expression in cartilage matrix deficient mice. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90342-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Christner J. E., Baker J. R., Couchman J. R. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against connective tissue proteoglycans. Fed Proc. 1985 Feb;44(2):386–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Christner J. E., Baker J. R. Identification of a monoclonal antibody that specifically recognizes corneal and skeletal keratan sulfate. Monoclonal antibodies to cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8848–8854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. C., Burkhardt D., Frost L., Ghosh P. The proteoglycans of the canine intervertebral disc. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 17;839(2):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. C., Ghosh P., Taylor T. K. Variations of the proteoglycans of the canine intervertebral disc with ageing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 19;880(2-3):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. J., McDevitt C. A., Arnoczky S. P., Warren R. F. Changes in the chondroitin sulfate-rich region of articular cartilage proteoglycans in experimental osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 18;840(2):228–234. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON E. A., WOODHALL B. Biochemical alterations in herniated intervertebral disks. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2951–2954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg A. E., Dingman C. W., Peacock A. C. Electrophoretic characterization of bacterial polyribosomes in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr 14;41(1):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFabio J. L., Pearce R. H., Caterson B., Hughes H. The heterogeneity of the non-aggregating proteoglycans of the human intervertebral disc. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):27–33. doi: 10.1042/bj2440027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emes J. H., Pearce R. H. The proteoglycans of the human intervertebral disc. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):549–556. doi: 10.1042/bj1450549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Axelsson I. Distribution of keratan sulfate in cartilage proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1971–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Axelsson I., Inerot S. Skeletal keratan sulfate from different tissues. Characterization and alkaline degradation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 23;581(1):122–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Extraction, fractionation and characterization of proteoglycans from bovine tracheal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Gardell S. Studies on protein-polysaccharide complex (proteoglycan) from human nucleus pulposus. I. Isolation and preliminary characterisation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 9;148(1):164–171. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Wieslander J., Sheehan J., Paulsson M., Sommarin Y. Separation and characterization of two populations of aggregating proteoglycans from cartilage. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 1;225(1):95–106. doi: 10.1042/bj2250095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inerot S., Heinegård D., Audell L., Olsson S. E. Articular-cartilage proteoglycans in aging and osteoarthritis. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):143–156. doi: 10.1042/bj1690143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inerot S., Heinegård D. Bovine tracheal cartilage proteoglycans. Variations in structure and composition with age. Coll Relat Res. 1983 May;3(3):245–262. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(83)80007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau C. K., Fujitaki J. M. An improved method of microdialysis. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):144–145. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90125-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowther D. A., Baxter E. Isolation of a chondroitin sulphate protein complex from bovine intervertebral disks. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):595–597. doi: 10.1038/211595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt C. A., Muir H. Gel electrophoresis of proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans on large-pore composite polyacrylamide-agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1971 Dec;44(2):612–622. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehmet H., Scudder P., Tang P. W., Hounsell E. F., Caterson B., Feizi T. The antigenic determinants recognized by three monoclonal antibodies to keratan sulphate involve sulphated hepta- or larger oligosaccharides of the poly(N-acetyllactosamine) series. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jun 2;157(2):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Bradford D. S., Cooper K. M. Aggregated proteoglycan synthesis in organ cultures of human nucleus pulposus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10579–10581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6151–6159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosta G. M., Mathewson N. S., Catravas G. N. Optimization of Folin--Ciocalteu Reagent concentration in an automated Lowry protein assay. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90723-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce R. H., Grimmer B. J., Adams M. E. Degeneration and the chemical composition of the human lumbar intervertebral disc. J Orthop Res. 1987;5(2):198–205. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. P., Mason R. M. The stability of bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycans during isolation and storage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 23;498(1):176–188. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrini V. Electrophoretic heterogeneity of proteinpolysaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1540–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Berg R., Martin G. R., Foidart J. M., Robey P. G. Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) for connective tissue components. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., Mason R. M. The electrophoretic heterogeneity of bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):357–367. doi: 10.1042/bj1570357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., White R. J. Age-related changes in the structure of the proteoglycan subunits from human articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., White R. J. The use of caesium sulphate density gradient centrifugation to analyse proteoglycans from human articular cartilages of different ages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 23;759(1-2):58–66. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90189-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanescu V., Maroteaux P., Sobczak E. Proteoglycan populations of baboon (Papio papio) articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 1;163(1):103–109. doi: 10.1042/bj1630103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanescu V., Maroteaux P., Sobczak E. Proteoglycan populations of baboon (Papio papio) cartilages from different anatomical sites: gel electrophoretic analysis of dissociated proteoglycans and of fractions obtained by density gradient centrifugation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 7;629(2):371–381. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Dondi P. G., Muir H. Proteoglycans of the intervertebral disc. Absence of degradation during the isolation of proteoglycans from the intervertebral disc. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):573–578. doi: 10.1042/bj1790573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Ewins R. J., Revell P. A., Muir H. Proteoglycans of the intervertebral disc. Homology of structure with laryngeal proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):561–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1790561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet M. B., Thonar E. J., Marsh J. Age-related changes in proteoglycan structure. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Dec;198(2):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90518-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tengblad A., Pearce R. H., Grimmer B. J. Demonstration of link protein in proteoglycan aggregates from human intervertebral disc. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):85–92. doi: 10.1042/bj2220085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triphaus G. F., Schmidt A., Buddecke E. Age-related changes in the incorporation of [35S]sulfate into two proteoglycan populations from human cartilage. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 Dec;361(12):1773–1779. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1980.361.2.1773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander J., Heinegård D. Immunochemical analysis of cartilage proteoglycans. Cross-reactivity of molecules isolated from different species. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 1;199(1):81–87. doi: 10.1042/bj1990081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]