Abstract
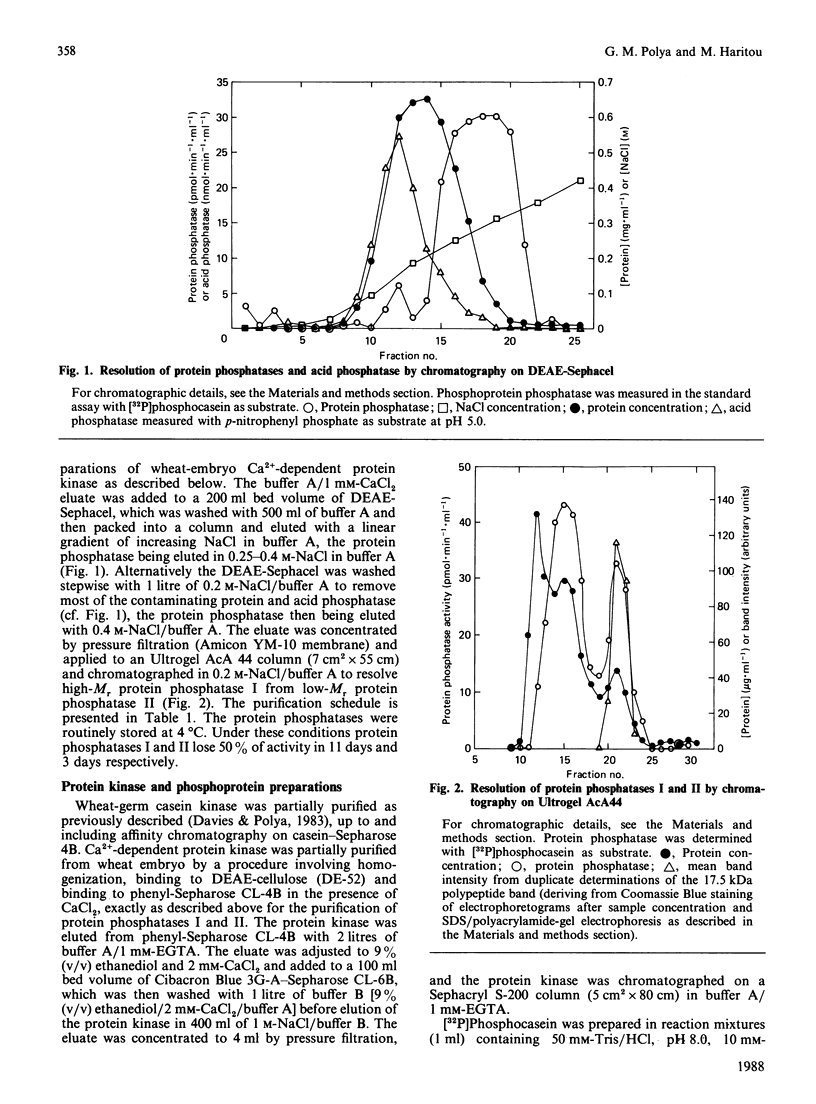
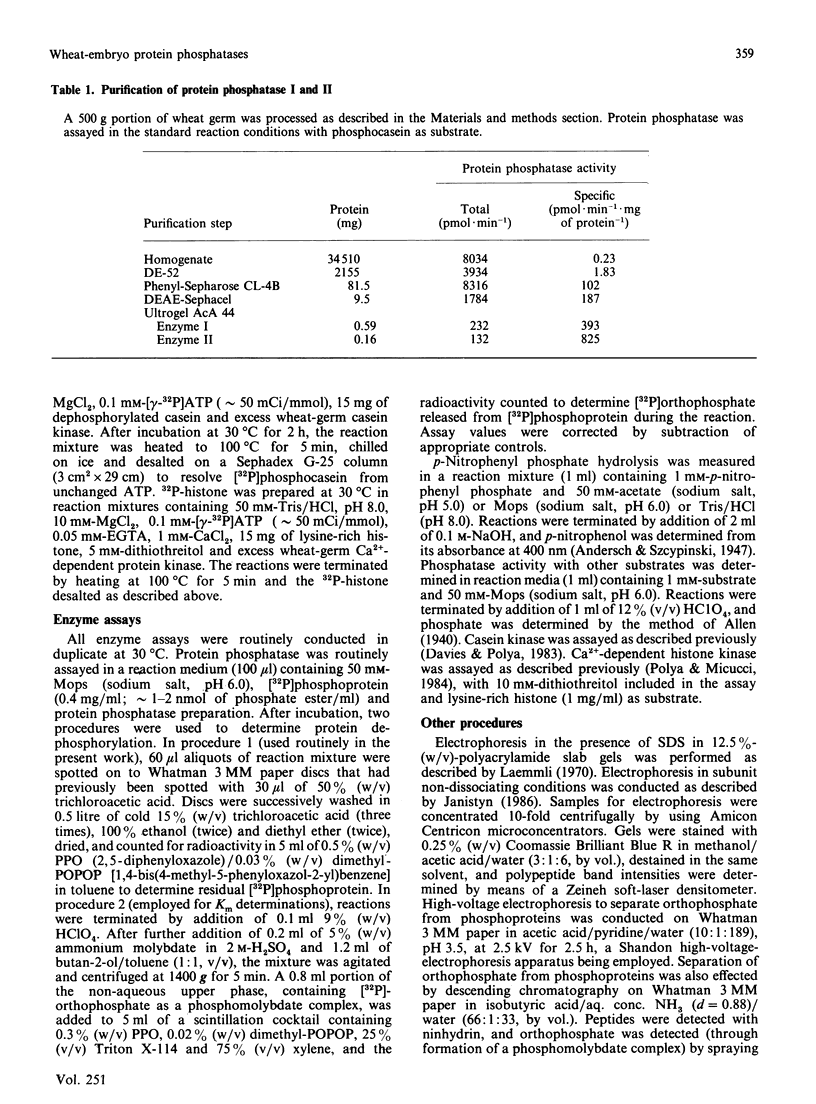
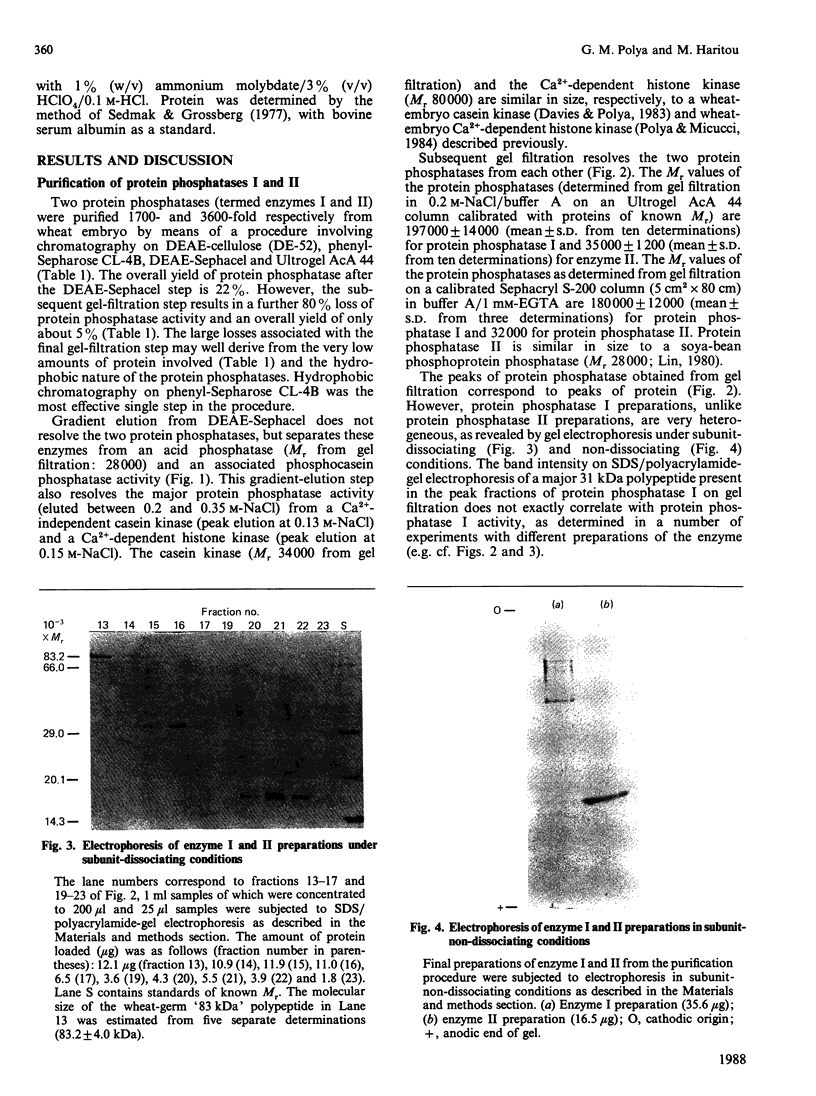
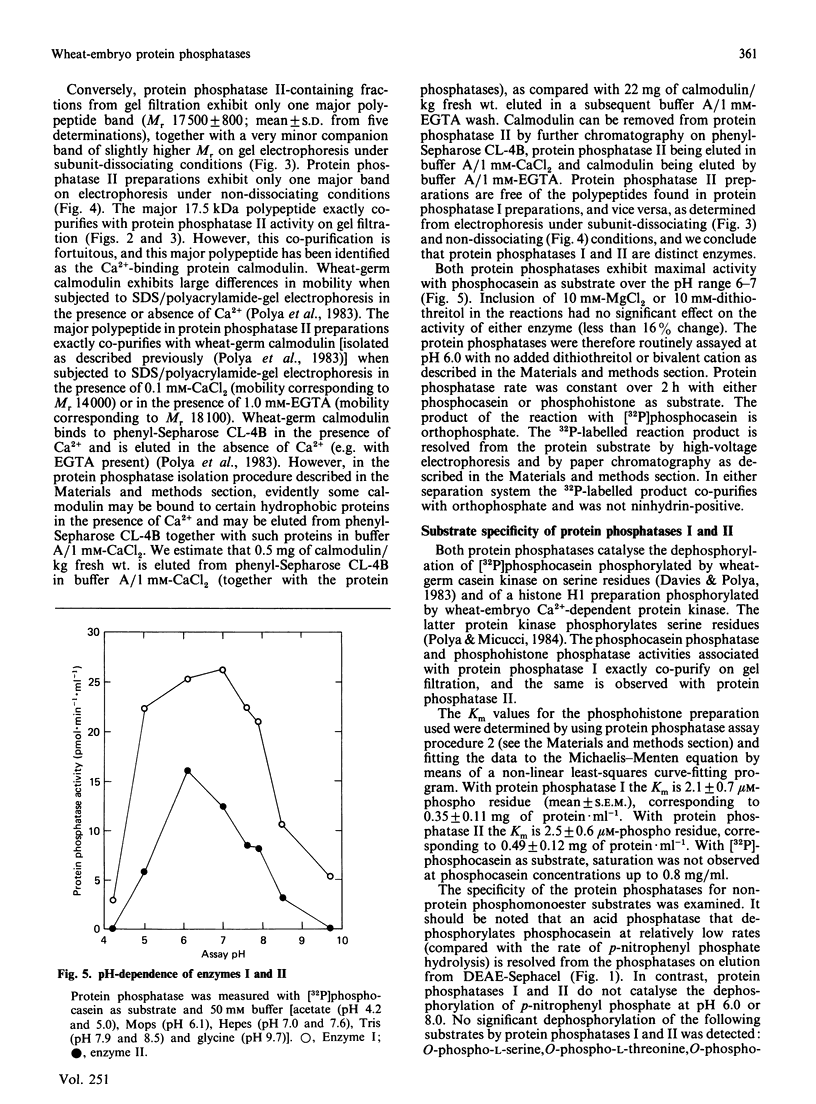
Two protein phosphatases (enzymes I and II) were extensively purified from wheat embryo by a procedure involving chromatography on DEAE-cellulose, phenyl-Sepharose CL-4B, DEAE-Sephacel and Ultrogel AcA 44. Preparations of enzyme I (Mr 197,000) are heterogeneous. Preparations of enzyme II (Mr 35,000) contain only one major polypeptide (Mr 17,500), which exactly co-purifies with protein phosphatase II on gel filtration and is not present in preparations of enzyme I. However, this major polypeptide has been identified as calmodulin. Calmodulin and protein phosphatase II can be separated by further chromatography on phenyl-Sepharose CL-4B. Protein phosphatases I and II do not require Mg2+ or Ca2+ for activity. Both enzymes catalyse the dephosphorylation of phosphohistone H1 (phosphorylated by wheat-germ Ca2+-dependent protein kinase) and of phosphocasein (phosphorylated by wheat-germ Ca2+-independent casein kinase), but neither enzyme dephosphorylates a range of non-protein phosphomonoesters tested. Both enzymes are inhibited by Zn2+, Hg2+, vanadate, molybdate, F-, pyrophosphate and ATP.
Full text
PDF


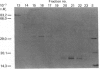
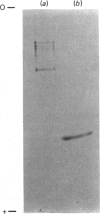
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Villa-Moruzzi E., Fischer E. H. Subunit structure and regulation of phosphorylase phosphatase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1985;27:183–192. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152827-0.50022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The coordinated control of metabolic pathways by broad-specificity protein kinases and phosphatases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1985;27:23–37. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152827-0.50010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in the hormonal control of enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):439–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hardison L. K., Roux S. J. Polyamine stimulation of protein phosphorylation in isolated pea nuclei. Plant Physiol. 1986 Nov;82(3):681–684. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. R., Polya G. M. Purification and properties of a high specific activity protein kinase from wheat germ. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):489–495. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. P. Phosphoprotein Phosphatase of Soybean Hypocotyls: PURIFICATION, PROPERTIES, AND SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITIES . Plant Physiol. 1980 Sep;66(3):368–374. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miernyk J. A., Randall D. D. Some properties of pea mitochondrial phospho-pyruvate dehydrogenase-phosphatase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Feb;83(2):311–315. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.2.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polya G. M., Davies J. R., Micucci V. Properties of a calmodulin-activated Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from wheat germ. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Nov 22;761(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks J. W., Brautigan D. L. Molecular basis for substrate specificity of protein kinases and phosphatases. Int J Biochem. 1986;18(6):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(86)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Lilley R. M., Heldt H. W. Adenine nucleotide levels in the cytosol, chloroplasts, and mitochondria of wheat leaf protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1982 Oct;70(4):971–977. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.4.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veluthambi K., Poovaiah B. W. Polyamine-stimulated phosphorylation of proteins from corn (Zea mays L.) coleoptiles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1374–1380. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]