Abstract
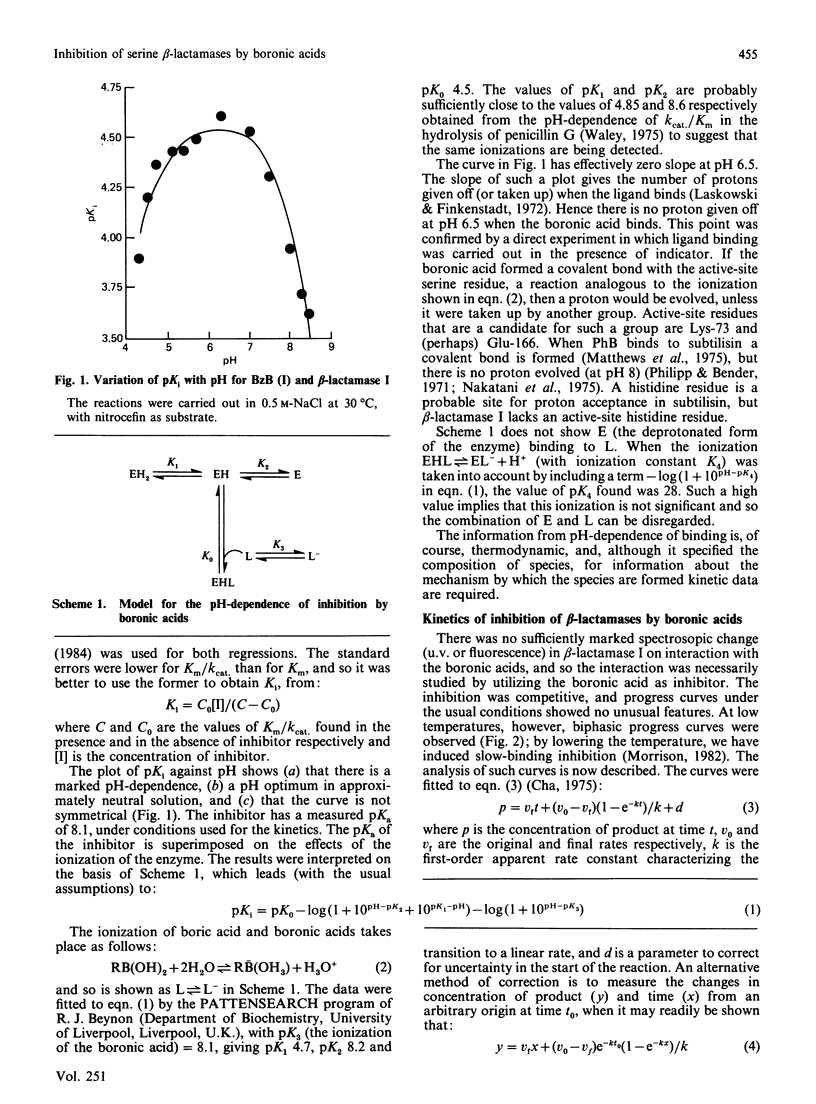
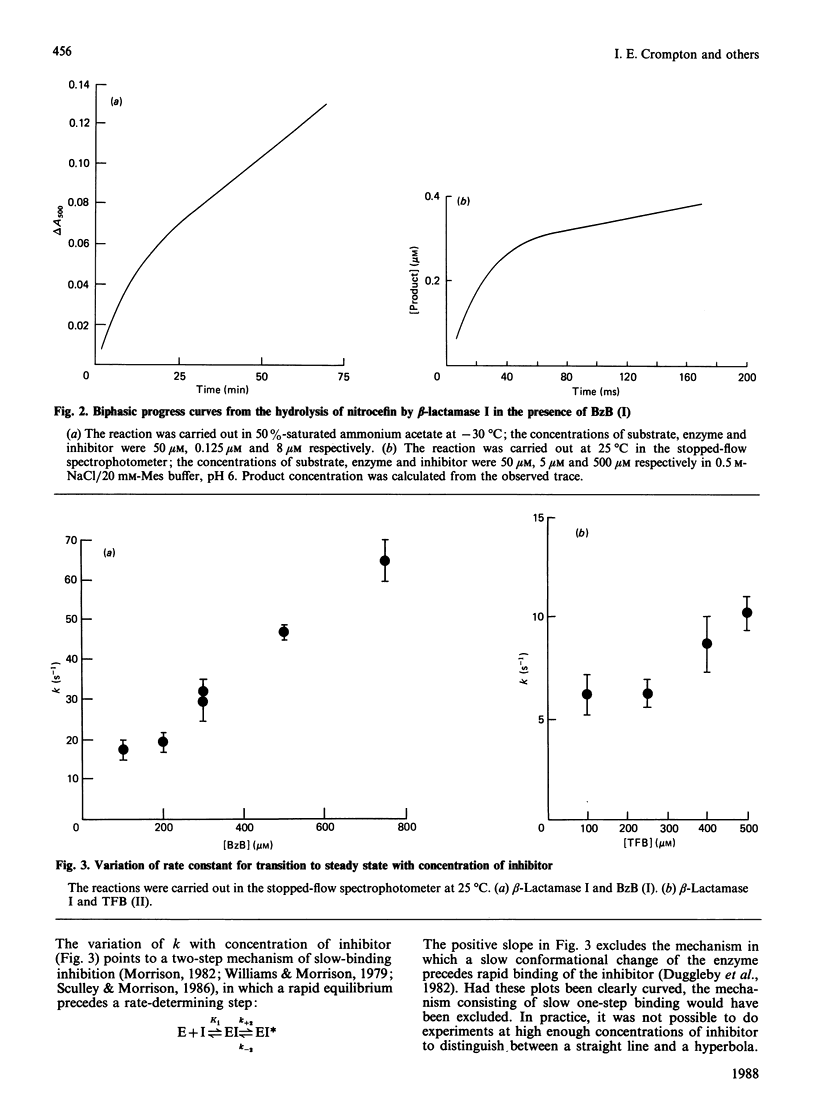
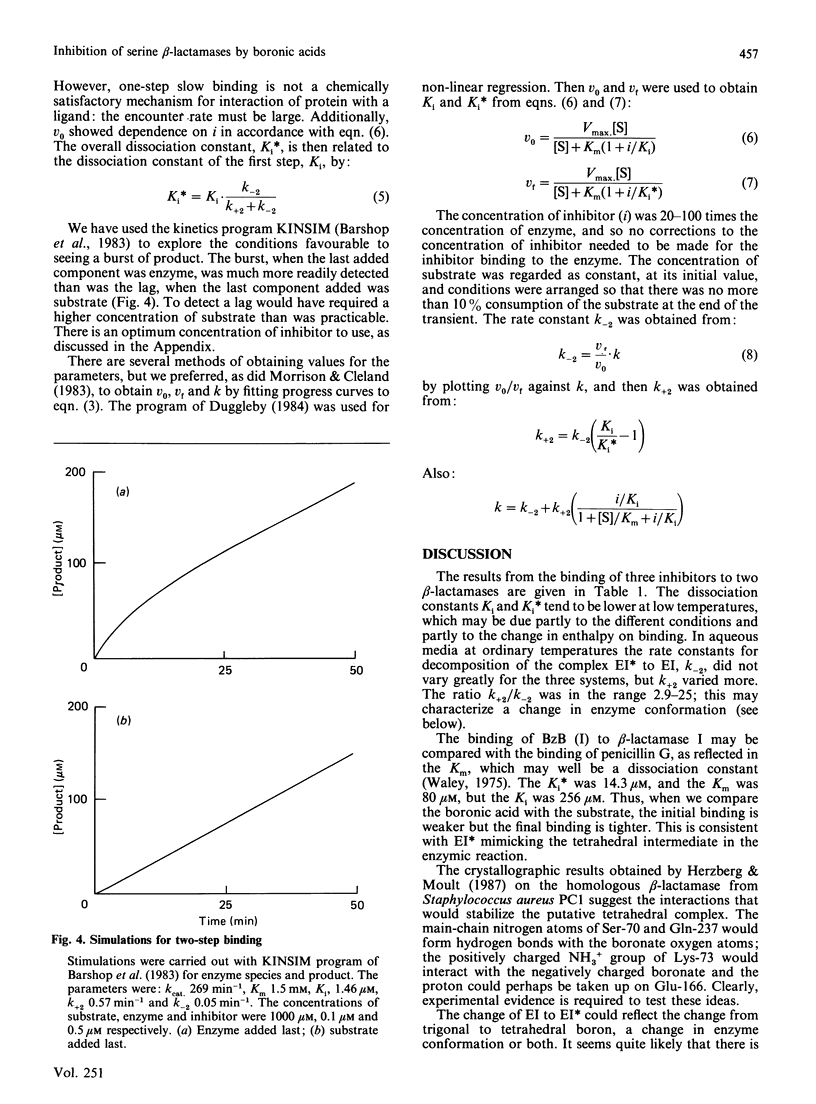
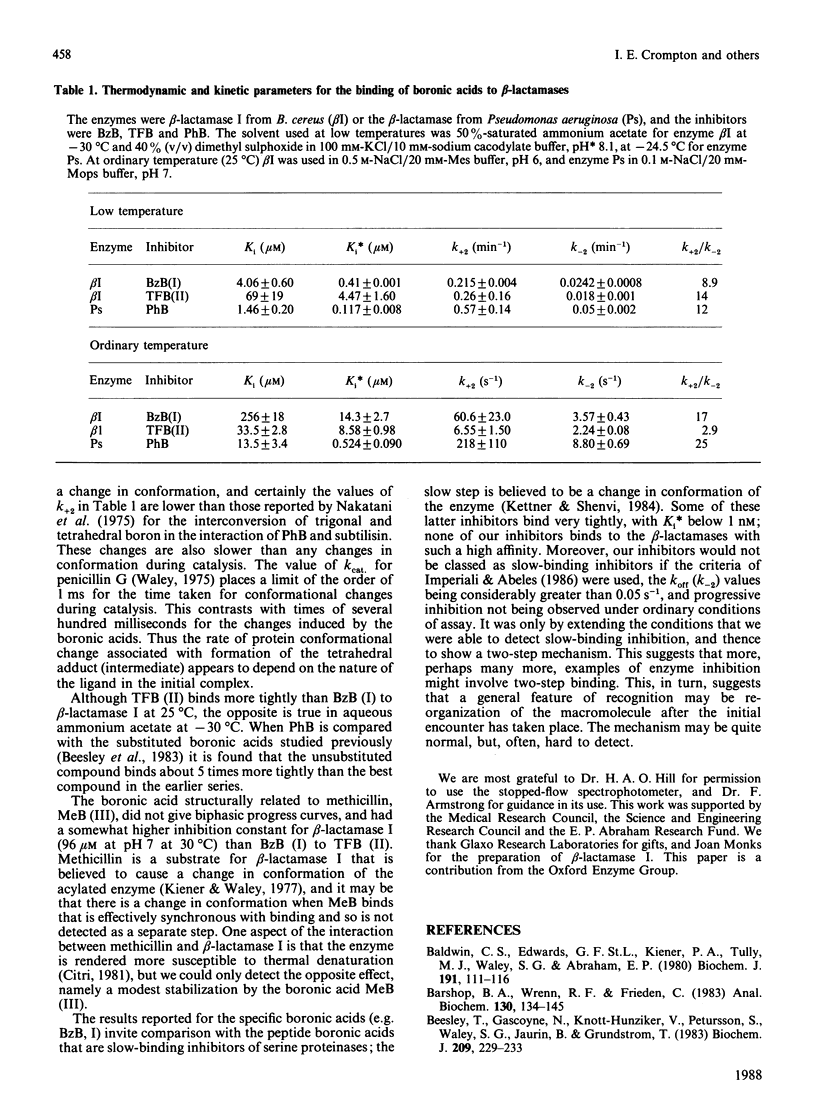
Many beta-lactamases have active-site serine residues, and are competitively inhibited by boronic acids. Hitherto, the boronic acids used have lacked any structural resemblance to the substrates of beta-lactamases. Phenylacetamidomethaneboronic acid, trifluoroacetamidomethaneboronic acid and 2,6-dimethoxybenzamidomethaneboronic acid have now been synthesized. The first of these contains the side-chain moiety of penicillin G, and the last that of methicillin. The pH-dependence of binding of the first inhibitor to beta-lactamase I from Bacillus cereus revealed pK values of 4.7 and 8.2 for (presumably) active-site groups in the enzyme. The kinetics of inhibition were studied by cryoenzymology and by stopped-flow spectrophotometry. These techniques provided evidence for a two-step mechanism of binding of the first two boronic acids mentioned above to beta-lactamase I, and for benzeneboronic acid to a beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The slower step is probably associated with a change in enzyme conformation as well as the formation of an O-B bond between the active-site serine hydroxy group and the boronic acid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAHAM E. P., NEWTON G. G. Experiments on the degradation of cephalosporin C. Biochem J. 1956 Apr;62(4):658–665. doi: 10.1042/bj0620658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin G. S., Edwards G. F., Kiener P. A., Tully M. J., Waley S. G., Abraham E. P. Production of a variant of beta-lactamase II with selectively decreased cephalosporinase activity by a mutant of Bacillus cereus 569/H/9. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):111–116. doi: 10.1042/bj1910111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barshop B. A., Wrenn R. F., Frieden C. Analysis of numerical methods for computer simulation of kinetic processes: development of KINSIM--a flexible, portable system. Anal Biochem. 1983 Apr 1;130(1):134–145. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90660-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley T., Gascoyne N., Knott-Hunziker V., Petursson S., Waley S. G., Jaurin B., Grundström T. The inhibition of class C beta-lactamases by boronic acids. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):229–233. doi: 10.1042/bj2090229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berks M., Redhead K., Abraham E. P. Isolation and properties of an inducible and a constitutive beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jan;128(1):155–159. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R., Waley S. G. Cryoenzymology of Bacillus cereus beta-lactamase II. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):6876–6887. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright S. J., Waley S. G. Cryoenzymology of beta-lactamases. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5329–5337. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright S. J., Waley S. G. Purification of beta-lactamases by affinity chromatography on phenylboronic acid-agarose. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):505–512. doi: 10.1042/bj2210505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cha S. Tight-binding inhibitors-I. Kinetic behavior. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Dec 1;24(23):2177–2185. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. B., Abraham E. P. Separation, purification and properties of beta-lactamase I and beta-lactamase II from Bacillus cereus 569/H/9. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):115–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1430115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobozy O., Mile I., Ferencz I., Csányi V. Effect of electrolytes on the activity and iodine sensitivity of penicillinase from B. cereus. Acta Biochim Biophys Acad Sci Hung. 1971;6(2):97–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby R. G., Attwood P. V., Wallace J. C., Keech D. B. Avidin is a slow-binding inhibitor of pyruvate carboxylase. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 6;21(14):3364–3370. doi: 10.1021/bi00257a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby R. G. Estimation of the initial velocity of enzyme-catalysed reactions by non-linear regression analysis of progress curves. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):55–60. doi: 10.1042/bj2280055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby R. G. Regression analysis of nonlinear Arrhenius plots: an empirical model and a computer program. Comput Biol Med. 1984;14(4):447–455. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(84)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flett F., Curtis N. A., Richmond M. H. Mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 18S that synthesizes type Id beta-lactamase constitutively. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1585–1586. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1585-1586.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., Moult J. Bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics: crystal structure of beta-lactamase from Staphylococcus aureus PC1 at 2.5 A resolution. Science. 1987 May 8;236(4802):694–701. doi: 10.1126/science.3107125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiali B., Abeles R. H. Inhibition of serine proteases by peptidyl fluoromethyl ketones. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3760–3767. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C. A., Shenvi A. B. Inhibition of the serine proteases leukocyte elastase, pancreatic elastase, cathepsin G, and chymotrypsin by peptide boronic acids. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15106–15114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiener P. A., Waley S. G. Reversible inhibitors of penicillinases. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):197–204. doi: 10.1042/bj1690197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiener P. A., Waley S. G. Substrate-induced deactivation of penicillinases. Studies of beta-lactamase I by hydrogen exchange. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):279–285. doi: 10.1042/bj1650279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, finkenstadt W. R. Study of protein-protein and of protein-ligand interactions by potentiometric methods. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:193–277. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist R. N., Nguyen A. C. Aminomethaneboronic acids. Synthesis and inhibition of boron analogue of esterase substrates. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Sep 14;99(19):6435–6437. doi: 10.1021/ja00461a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. A., Alden R. A., Birktoft J. J., Freer S. T., Kraut J. X-ray crystallographic study of boronic acid adducts with subtilisin BPN' (Novo). A model for the catalytic transition state. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7120–7126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani H., Uehara Y., Hiromi K. Elementary processes in the interaction of serine protease with a possible transition state analog. Subtillisin-benzeneboronic acid system. J Biochem. 1975 Sep;78(3):611–616. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp M., Bender M. L. Inhibition of serine proteases by arylboronic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):478–480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn M. J. A simple test for inactivation of an enzyme during assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 29;105(1):193–195. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G. The pH-dependence and group modification of beta-lactamase I. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):547–551. doi: 10.1042/bj1490547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. W., Morrison J. F. The kinetics of reversible tight-binding inhibition. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:437–467. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


