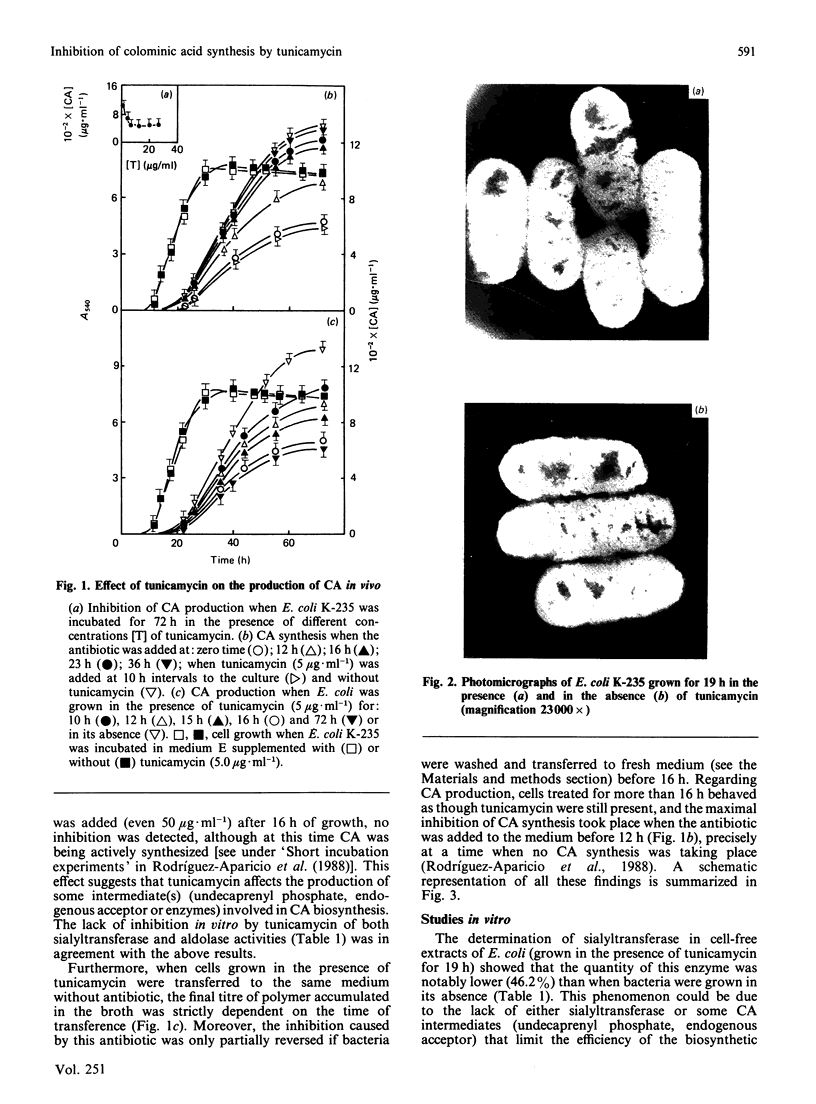
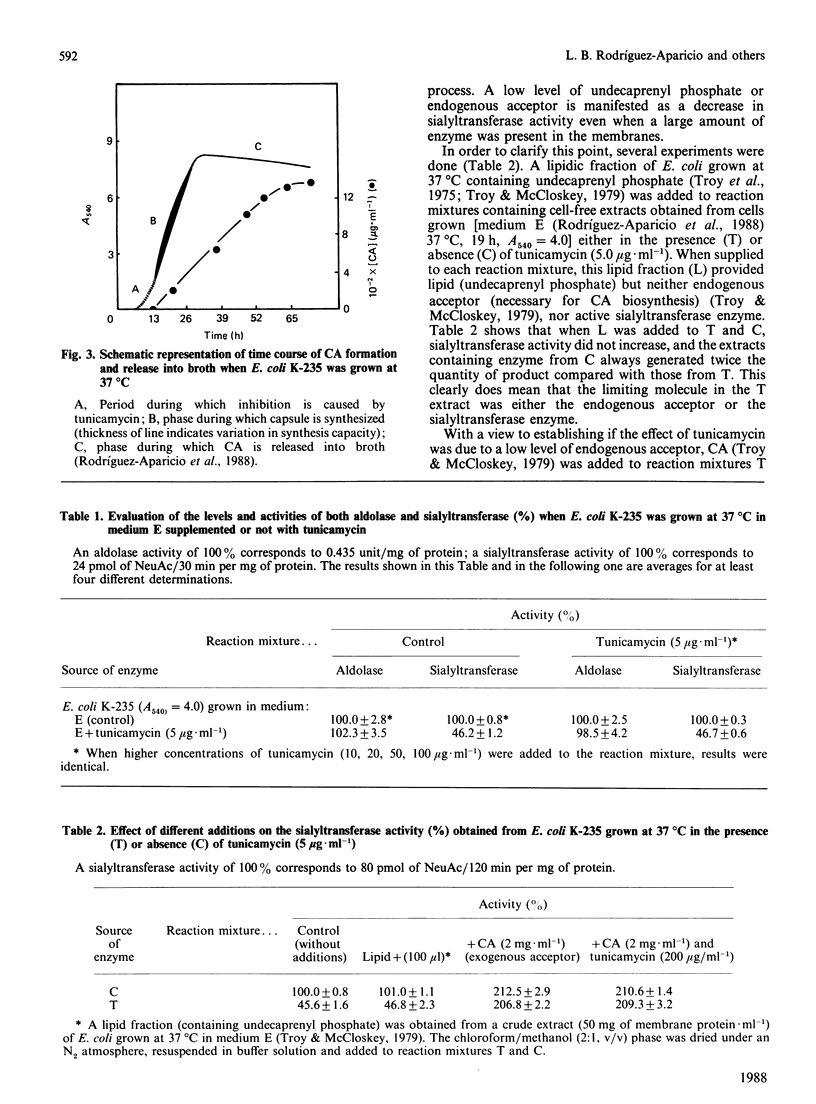
Abstract
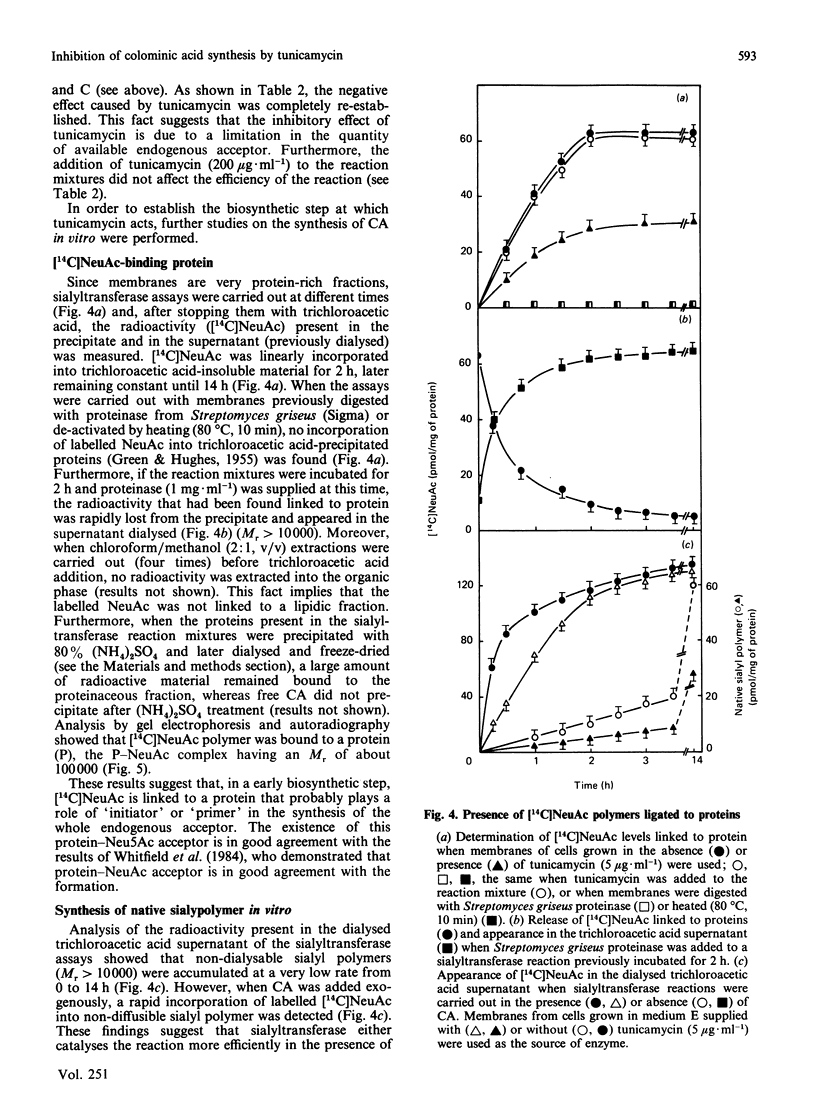
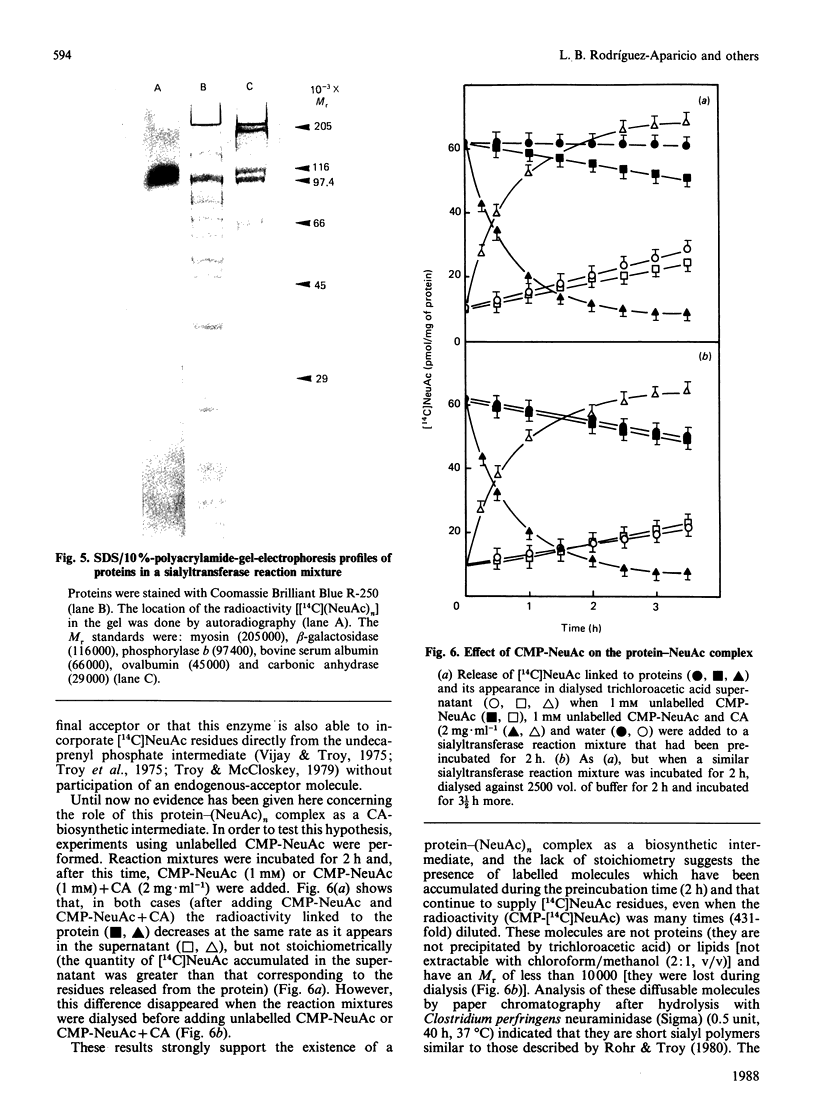
A protein-NeuAc complex involved in colominic acid biosynthesis has been identified in membrane preparations of Escherichia coli K-235. This compound had an Mr (estimated by SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and autoradiography) of about 100,000 and played the role of an 'initiator' or 'primer' (endogenous acceptor) in the synthesis of the whole polymer. Incubations of E. coli membranes with CMP-[14C]NeuAc (CMP-N-[14C]acetylneuraminic acid) pointed to the existence of a protein fraction (primer acceptor) that linked residues of sialic acid (N-acetylneuraminic acid, NeuAc) up to a maximal size, later releasing them as low-Mr sialyl polymers (LMrS, Mr less than 10,000). In the presence of colominic acid (final acceptor) the radioactivity linked to the protein quickly decreased, appearing stoichiometrically bound to the whole polysaccharide. When membrane preparations were previously digested with Streptomyces proteinase or de-activated by heating (80 degrees C, 10 min), no incorporation of labelled NeuAc into trichloroacetic acid-insoluble material was detected. These results suggested that colominic acid molecules are synthesized while they are bound to a proteinaceous acceptor that is subsequently excised in the presence of colominic acid, generating the native protein. The antibiotic tunicamycin inhibited the biosynthesis of colominic acid, affecting the synthesis of this protein-(NeuAc)n intermediate. All these results are described here for the first time.
Full text
PDF



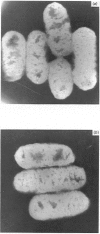
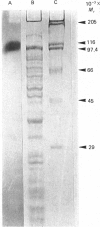
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andaluz E., Guillén A., Larriba G. Preliminary evidence for a glucan acceptor in the yeast Candida albicans. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):495–502. doi: 10.1042/bj2400495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aon M. A., Curtino J. A. Evidence for the glycoprotein nature of retina glycogen. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 2;140(3):557–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aon M. A., Curtino J. A. Protein-bound glycogen is linked to tyrosine residues. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 1;229(1):269–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2290269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T., ABBOTT V., TSAI T. Relationship of colominic acid (poly N-acetylneuraminic acid) to bacteria which contain neuraminic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Oct;29:335–352. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-2-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T. Colominic acid, a polymer of N-acetylneuraminic acid. J Exp Med. 1958 Apr 1;107(4):507–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T., GOEBEL W. F. Colominic acid, a substance of bacterial origin related to sialic acid. Nature. 1957 Jan 26;179(4552):206–206. doi: 10.1038/179206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T., HAMM J. D., GRAHAM M. G. EVALUATION OF COLORIMETRIC METHODS IN THE ESTIMATION OF SIALIC ACID IN BACTERIA. Nature. 1963 Nov 23;200:806–807. doi: 10.1038/200806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T. UN NOUVEAU MUCOPOLYOSIDE DES ENTEROBACT'ERIES. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1965;47:529–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld M. L., Krisman C. R. The initiation of glycogen biosynthesis in rat heart. Studies with a purified preparation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11560–11566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMB D. G., ROSEMAN S. The sialic acids. I. The structure and enzymatic synthesis of N-acetylneuraminic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2529–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan W., Liu T. Y., Dorow D., Cohen J. S., Robbins J. D., Gotschlich E. C., Robbins J. B. Structural studies on the sialic acid polysaccharide antigen of Escherichia coli strain Bos-12. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 9;16(16):3687–3692. doi: 10.1021/bi00635a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifetz A., Keenan R. W., Elbein A. D. Mechanism of action of tunicamycin on the UDP-GlcNAc:dolichyl-phosphate Glc-NAc-1-phosphate transferase. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2186–2192. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedzierska B. N-Acetylneuraminic acid: a constituent of the lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella toucra. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 15;91(2):545–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig J. D., Aminoff D., Roseman S. The sialic acids. XII. Synthesis of colominic acid by a sialyltransferase from Escherichia coli K-235. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2543–2550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Gotschlich E. C., Dunne F. T., Jonssen E. K. Studies on the meningococcal polysaccharides. II. Composition and chemical properties of the group B and group C polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4703–4712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Gotschlich E. C., Egan W., Robbins J. B. Sialic acid-containing polysaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis and Escherichia coli strain Bos-12: structure and immunology. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S71–S77. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luengo J. M., Revilla G., López M. J., Villanueva J. R., Martín J. F. Inhibition and repression of homocitrate synthase by lysine in Penicillium chrysogenum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):869–876. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.869-876.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez I. R., Whelan W. J. A novel glycosyl-amino acid linkage: rabbit-muscle glycogen is covalently linked to a protein via tyrosine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Aparicio L. B., Reglero A., Luengo J. M. Uptake of N-acetylneuraminic acid by Escherichia coli K-235. Biochemical characterization of the transport system. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):287–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2460287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohr T. E., Troy F. A. Structure and biosynthesis of surface polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2332–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. P., Finn C. W., Vann W. F., Aaronson W., Schneerson R., Kretschmer P. J., Garon C. F. Molecular cloning of the K1 capsular polysaccharide genes of E. coli. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):696–698. doi: 10.1038/289696b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., 2nd The chemistry and biosynthesis of selected bacterial capsular polymers. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:519–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., McCloskey M. A. Role of a membranous sialyltransferase complex in the synthesis of surface polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli. Temperature-induced alteration in the assembly process. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7377–7387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., Vijay I. K., McCloskey M. A., Rohr T. E. Synthesis of capsular polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli 07-K1. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:540–548. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., Vijay I. K., Tesche N. Role of undecaprenyl phosphate in synthesis of polymers containing sialic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):156–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijay I. K., Troy F. A. Properties of membrane-associated sialyltransferase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):164–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L., BLACKLOW R. S. The biosynthesis of cytidine 5'-monophospho-n-acetylneuraminic acid by an enzyme from Neisseria meningitidis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3527–3534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L., FELSENFELD H. The biosynthesis of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1421–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield C., Adams D. A., Troy F. A. Biosynthesis and assembly of the polysialic acid capsule in Escherichia coli K1. Role of a low-density vesicle fraction in activation of the endogenous synthesis of sialyl polymers. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12769–12775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]