Abstract
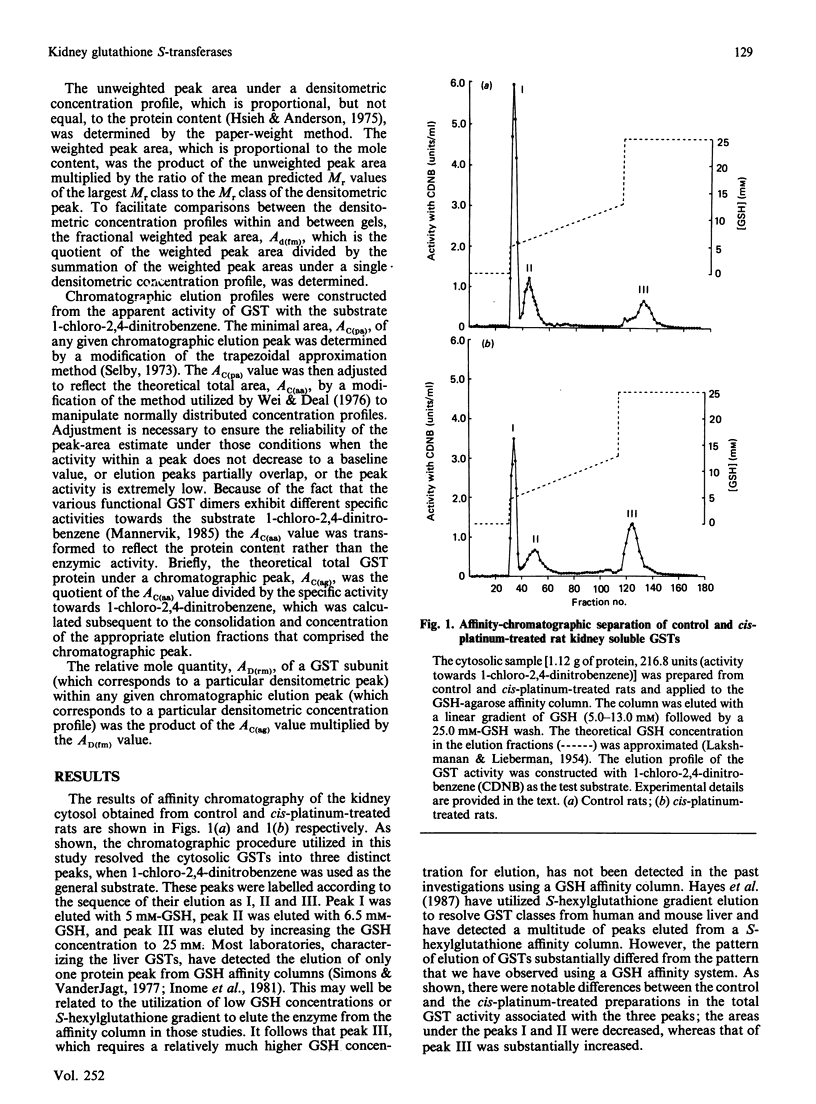
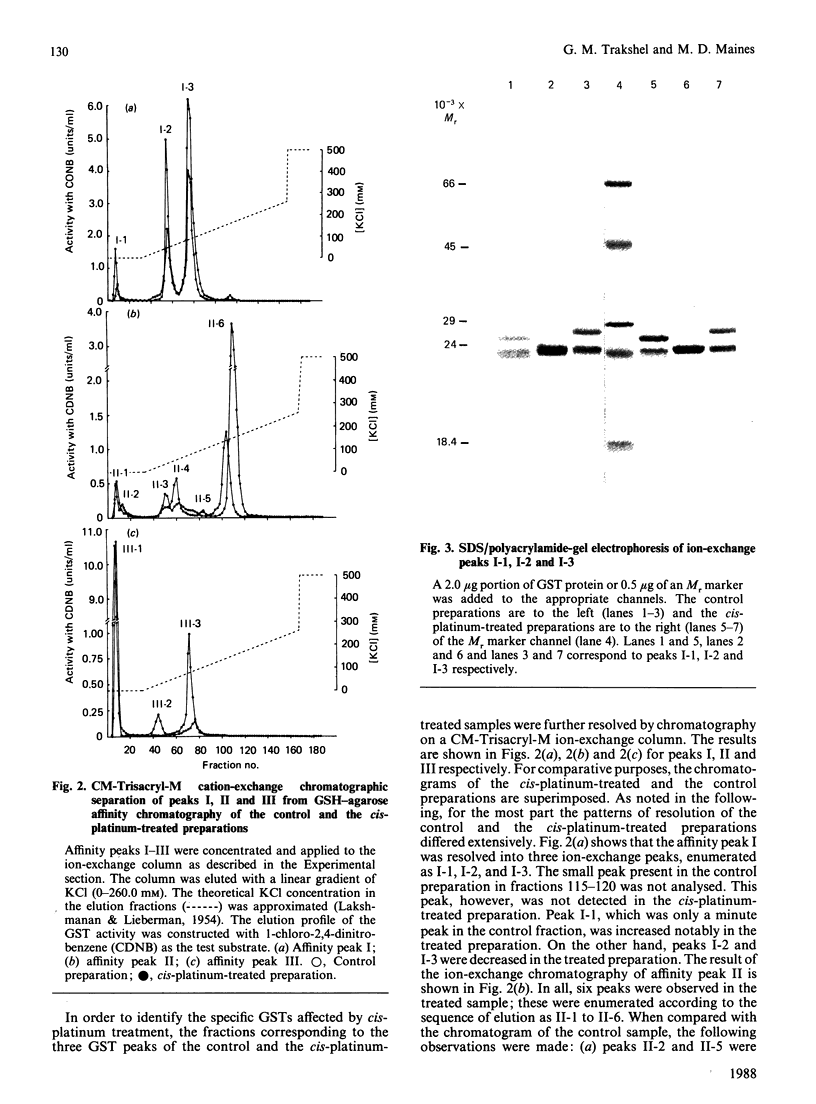
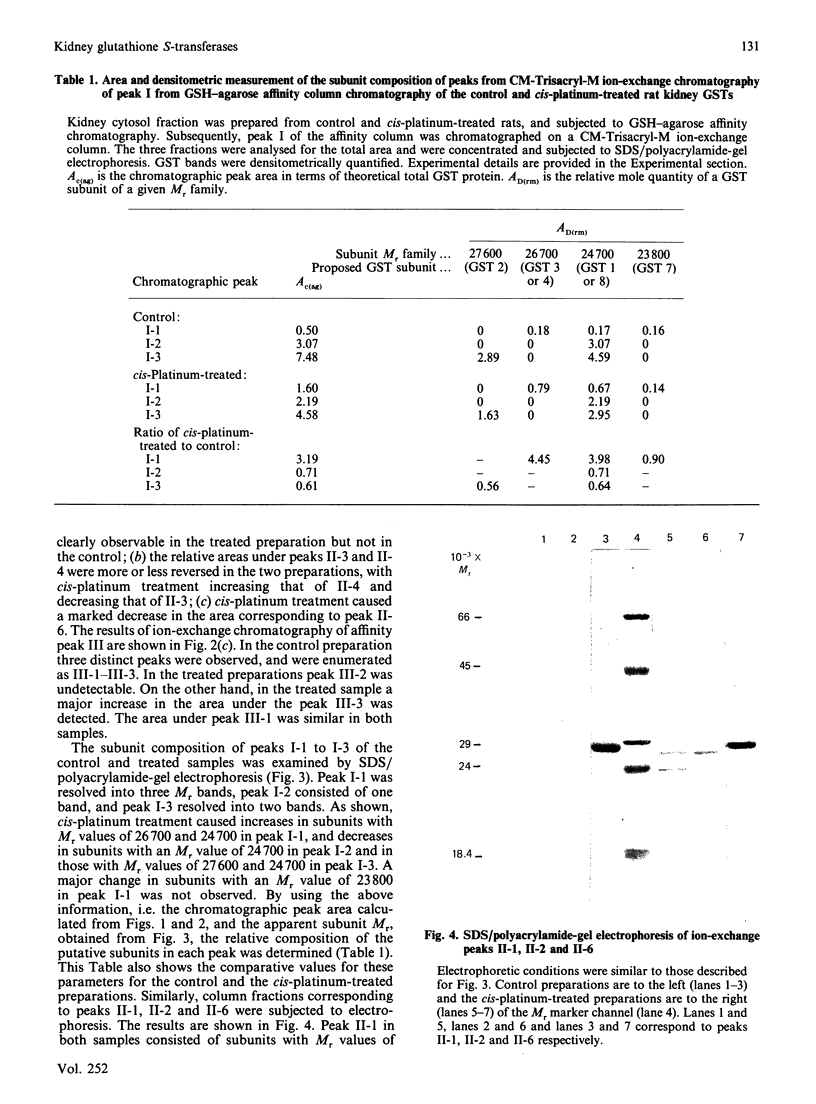
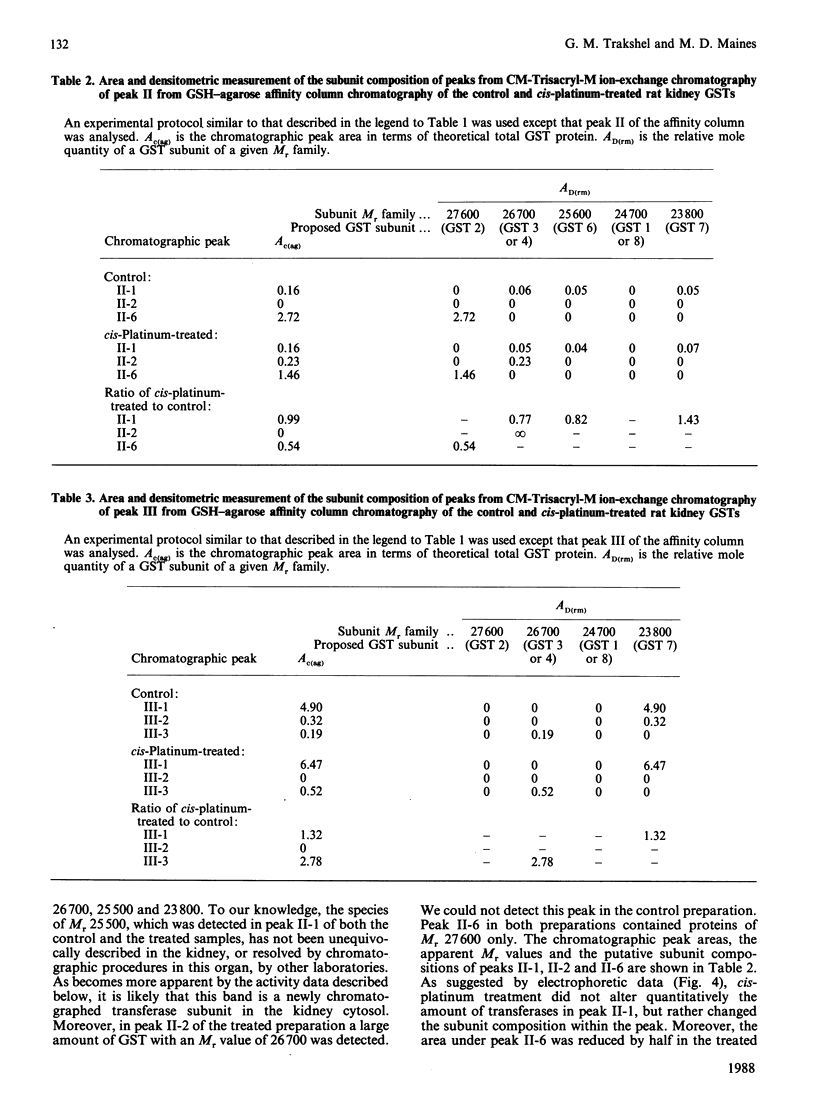
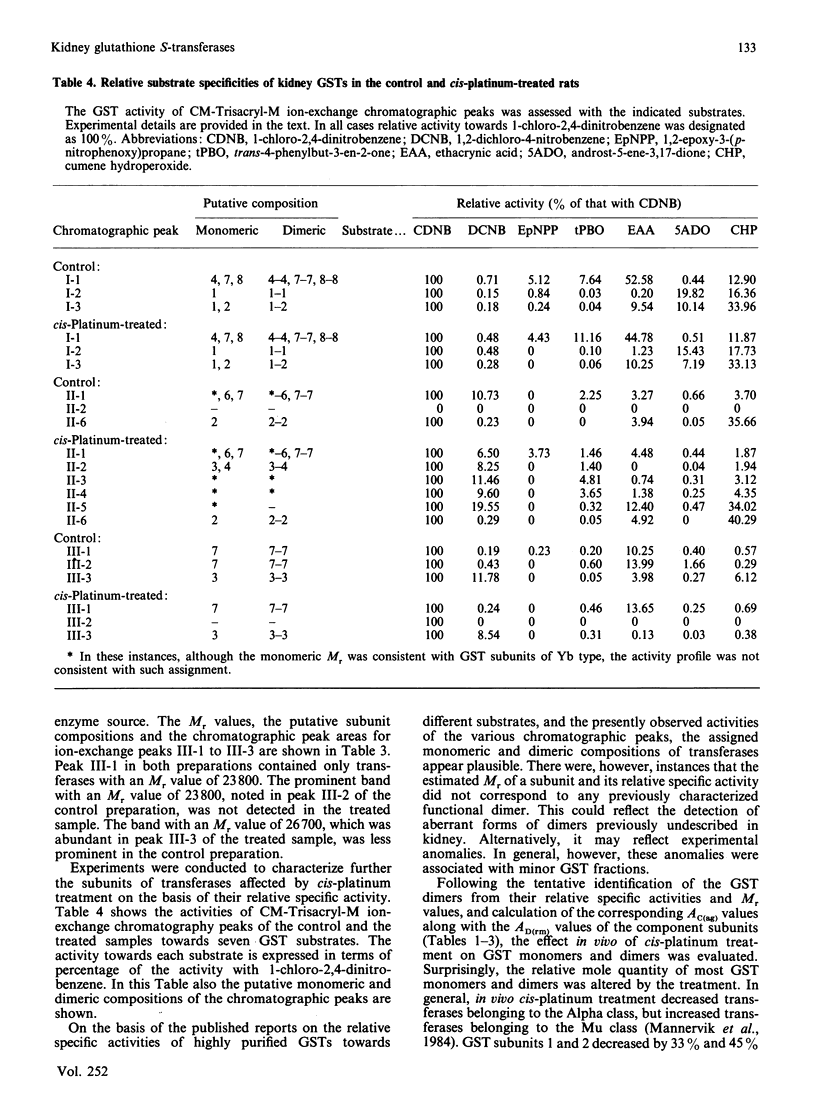
We have developed chromatographic and mathematical protocols that allowed the high resolution of glutathione S-transferase (GST) subunits, and the identification of a previously unresolved GST monomer in rat kidney cytosol; the monomer was identified tentatively as subunit 6. Also, an aberrant form of GST 7-7 dimer appeared to be present in the kidney. This development was utilized to illustrate the response of rat kidney GST following cis-platinum treatment in vivo. Rat kidney cytosol was separated into three 'affinity families' of GST activity after elution from a GSH-agarose matrix. The affinity peaks were characterized by quantitative differences in their subunit and dimeric compositions as determined by subsequent chromatography on a cation-exchange matrix and specific activity towards substrates. By use of these criteria, the major GST dimers of affinity peaks were tentatively identified. The major GST dimers in peak I were GST 1-1 and 1-2, in affinity peak II it was GST 2-2, and in peak III they were GST 3-3 and 7-7. GST 3-6 and/or 4-6, which have not been previously resolved in kidney cytosol, were also present in peak II. Alterations in the kidney cytosolic GST composition of male rats were detected subsequent to the administration of cis-platinum (7.0 mg/kg subcutaneously, 6 days). This treatment caused a pronounced alteration in the GST profile, and the pattern of alteration was markedly different from that reported for other chemicals in the kidney or in the liver. In general, the cellular contents of the GSTs of the Alpha and the Mu classes decreased and increased respectively. It is postulated that the decrease in the Alpha class of GSTs by cis-platinum treatment may be related to renal cortical damage and the loss of GSTs in the urine. The increase in the Mu class of GSTs could potentially stem from a lowered serum concentration of testosterone; the latter is a known effect of cis-platinum treatment.
Full text
PDF




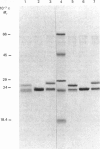
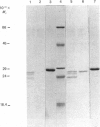
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson A. M., Barretto P. B. Effects of disulfiram, diethyldithiocarbamate, bisethylxanthogen, and benzyl isothiocyanate on glutathione transferase activities in mouse organs. Cancer Res. 1985 Sep;45(9):4219–4223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer T. D. Covalent labeling of the nonsubstrate ligand-binding site of glutathione S-transferases with bilirubin-Woodward's reagent K. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5363–5367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer T. D., Kenney W. C. Acidic glutathione S-transferases of rat testis. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):125–132. doi: 10.1042/bj2300125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding G. J., Ding V. D., Rodkey J. A., Bennett C. D., Lu A. Y., Pickett C. B. Rat liver glutathione S-transferases. DNA sequence analysis of a Yb2 cDNA clone and regulation of the Yb1 and Yb2 mRNAs by phenobarbital. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7952–7957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthenberg C., Jensson H., Nyström L., Osterlund E., Tahir M. K., Mannervik B. Isoenzymes of glutathione transferase in rat kidney cytosol. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 15;230(3):609–615. doi: 10.1042/bj2300609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habig W. H., Jakoby W. B. Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-transferases. Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:398–405. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)77053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. F., Jaeger V., Neims A. H. Isoelectric focusing of glutathione S-transferases from rat liver and kidney. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):937–943. doi: 10.1042/bj1750937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. F., Jain R., Robaire B. Differential regulation of male rat liver glutathione S-transferases. Effects of orchidectomy and hormone replacement. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 15;31(14):2389–2393. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Clarkson G. H. Purification and characterization of three forms of glutathione S-transferase A. A comparative study of the major YaYa-, YbYb- and YcYc-containing glutathione S-transferases. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):459–470. doi: 10.1042/bj2070459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Mantle T. J. Anomalous electrophoretic behaviour of the glutathione S-transferase Ya and Yk subunits isolated from man and rodents. A potential pitfall for nomenclature. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):731–740. doi: 10.1042/bj2370731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Mantle T. J. Use of immuno-blot techniques to discriminate between the glutathione S-transferase Yf, Yk, Ya, Yn/Yb and Yc subunits and to study their distribution in extrahepatic tissues. Evidence for three immunochemically distinct groups of transferase in the rat. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):779–788. doi: 10.1042/bj2330779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D. Purification and characterization of glutathione S-transferases P, S and N. Isolation from rat liver of Yb1 Yn protein, the existence of which was predicted by subunit hybridization in vitro. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):839–852. doi: 10.1042/bj2240839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D. Purification and physical characterization of glutathione S-transferase K. Differential use of S-hexylglutathione and glutathione affinity matrices to isolate a novel glutathione S-transferase from rat liver. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):789–798. doi: 10.1042/bj2330789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh W. C., Anderson R. E. Quantitation of stained proteins in SDS polyacrylamide gels with lysozyme as internal standard. Anal Biochem. 1975 Dec;69(2):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Hara M., Nagashima F., Matsui S., Mitsuyasu N., Morino Y. Affinity chromatography of hepatic glutathione S-transferases on omega-aminoalkyl sepharose derivatives of glutathione. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 15;659(2):362–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagt D. L., Wilson S. P., Dean V. L., Simons P. C. Bilirubin binding to rat liver ligandins (glutathione S-transferases A and B). Relationship between bilirubin binding and transferase activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1997–2001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensson H., Guthenberg C., Alin P., Mannervik B. Rat glutathione transferase 8-8, an enzyme efficiently detoxifying 4-hydroxyalk-2-enals. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 28;203(2):207–209. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80743-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jollie D. R., Maines M. D. Effect of cis-platinum on kidney cytochrome P-450 and heme metabolism: evidence for the regulatory role of the pituitary hormones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jul;240(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketterer B., Srai K. S., Christodoulides L. Haem-binding proteins of the rat liver cytosol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 28;428(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKSHMANAN T. K., LIEBERMAN S. An improved method of gradient elution chromatography and its application to the separation of urinary ketosteroids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Nov;53(1):258–281. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. A., Burk R. F. Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):952–958. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90747-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litterst C. L., Mimnaugh E. G., Reagan R. L., Gram T. E. Comparison of in vitro drug metabolism by lung, liver, and kidney of several common laboratory species. Drug Metab Dispos. 1975 Jul-Aug;3(4):259–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maines M. D. Differential effect of cis-platinum (cis-diamminedichloroplatinum) on regulation of liver and kidney haem and haemoprotein metabolism. Possible involvement of gamma-glutamyl-cycle enzymes. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):713–721. doi: 10.1042/bj2370713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maines M. D., Mayer R. D. Inhibition of testicular cytochrome P-450-dependent steroid biosynthesis by cis-platinum. Reversal by human chorionic gonadotropin. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6063–6068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Guthenberg C. Glutathione transferase (human placenta). Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:231–235. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)77030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B. The isoenzymes of glutathione transferase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1985;57:357–417. doi: 10.1002/9780470123034.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama H., Listowsky I. Preferential binding of steroids by anionic forms of rat glutathione S-transferase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12449–12455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Beale D., Tan K. H., Coles B., Ketterer B. Glutathione transferases in primary rat hepatomas: the isolation of a form with GSH peroxidase activity. FEBS Lett. 1985 May 6;184(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80670-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. C., Li N., Tu C. P. Identification of a new glutathione S-transferase from rat liver cytosol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 29;121(3):1014–1020. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90778-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Estimation of molecular radius, free mobility, and valence using polyacylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Mar;40(1):95–134. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safirstein R., Miller P., Dikman S., Lyman N., Shapiro C. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats: defect in papillary hypertonicity. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):F175–F185. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.2.F175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Kitahara A., Satoh K., Ishikawa T., Tatematsu M., Ito N. The placental form of glutathione S-transferase as a new marker protein for preneoplasia in rat chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Gan. 1984 Mar;75(3):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh K., Kitahara A., Soma Y., Inaba Y., Hatayama I., Sato K. Purification, induction, and distribution of placental glutathione transferase: a new marker enzyme for preneoplastic cells in the rat chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3964–3968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan D., Mantle T. J. Evidence for two forms of ligandin (YaYa dimers of glutathione S-transferase) in rat liver and kidney. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):893–897. doi: 10.1042/bj2180893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons P. C., Vander Jagt D. L. Purification of glutathione S-transferases from human liver by glutathione-affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):334–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei G. J., Deal W. C., Jr Rapid determination of areas of Gaussian curves and diffusion coefficients. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]