Abstract
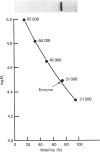
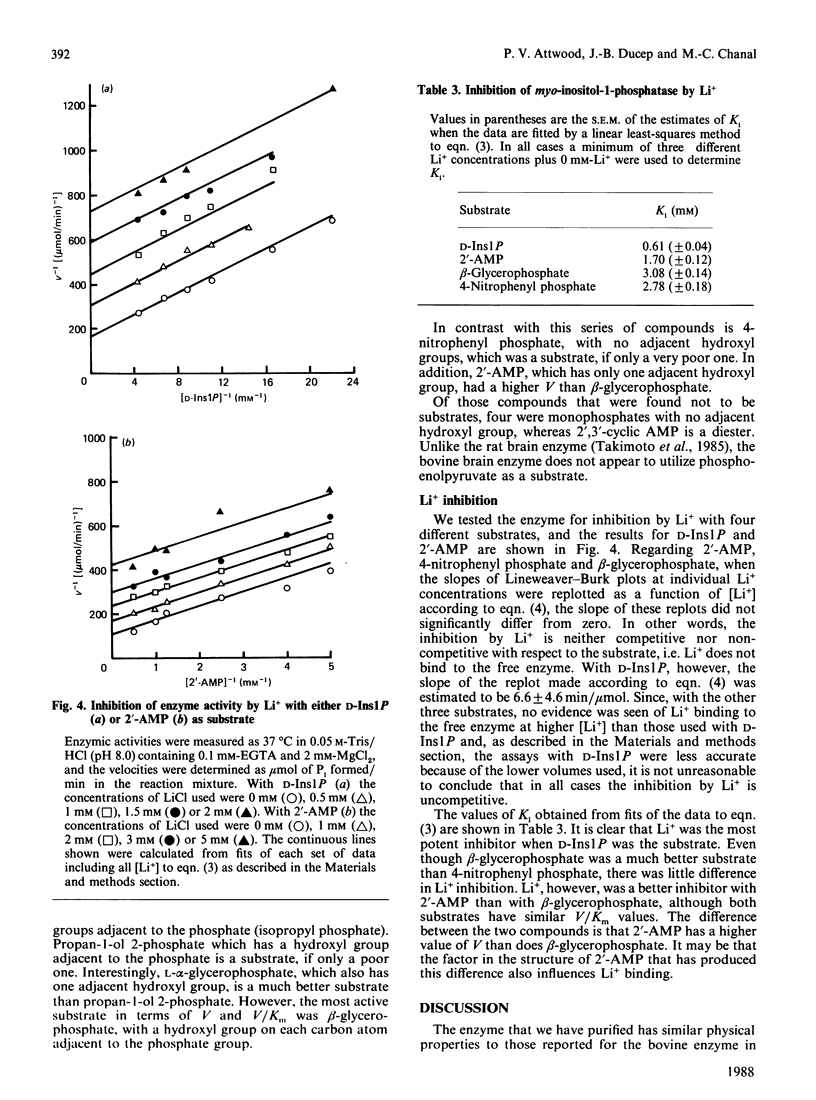
myo-Inositol-1-phosphatase from bovine brain was purified over 2000-fold. The native enzyme has a Mr of 59,000, and on SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis the subunit Mr was 31,000. Thus the native enzyme is a dimer of two apparently identical subunits. The enzyme, purified to a specific activity of more than 300 units/mg of protein (1 unit of enzyme activity corresponds to the release of 1 mumol of Pi/h at 37 degrees C), catalysed the hydrolysis of a variety of phosphorylated compounds, the best one, in terms of V/Km, being D-myo-inositol 1-phosphate. Kinetic constants of compounds tested, including both isomers of glycerophosphate and two deoxy forms of beta-glycerophosphate, were measured. They show the importance of the two hydroxyl groups which are adjacent to the phosphate in myo-inositol 1-phosphate. With a wide variety of substrates Li+ was found to be an uncompetitive inhibitor whose Ki varied with substrate structure.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann K. E., Gish B. G., Honchar M. P., Sherman W. R. Evidence that inositol 1-phosphate in brain of lithium-treated rats results mainly from phosphatidylinositol metabolism. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):517–524. doi: 10.1042/bj2420517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison J. H., Blisner M. E., Holland W. H., Hipps P. P., Sherman W. R. Increased brain myo-inositol 1-phosphate in lithium-treated rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 26;71(2):664–670. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90839-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Ernst Klenk Lecture, November 1985. Intracellular signalling through inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Jun;367(6):447–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M. J., Jones M. E. Inorganic phosphate determination in the presence of a labile organic phosphate: assay for carbamyl phosphate phosphatase activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Nov;135(1):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90756-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. W., Charalampous C. F. Biochemical studies on inositol. IX. D-Inositol 1-phosphate as intermediate in the biosynthesis of inositol from glucose 6-phosphate, and characteristics of two reactions in this biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2194–2199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby R. G. A nonlinear regression program for small computers. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg F., Jr D-myoinositol 1-phosphate as product of cyclization of glucose 6-phosphate and substrate for a specific phosphatase in rat testis. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1375–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallcher L. M., Sherman W. R. The effects of lithium ion and other agents on the activity of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10896–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie S., Sezaki M., Kato Y. A faithful double stain of proteins in the polyacrylamide gels with Coomassie blue and silver. Anal Biochem. 1982 Nov 1;126(2):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90526-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck L. A., Wong Y. H., Sherman W. R. L-myo-Inositol-1-phosphate synthase from bovine testis: purification to homogeneity and partial characterization. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3623–3629. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motoyama N., Takimoto K., Okada M., Nakagawa H. Phosphotyrosine phosphatase: a novel phosphatase specific for phosphotyrosine, 2'-AMP and p-nitrophenylphosphate in rat brain. J Biochem. 1987 Apr;101(4):939–947. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccarato W. F., Ray R. E., Wells W. W. Biosynthesis of myo-inositol in rat mammary gland. Isolation and properties of the enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Sep;164(1):194–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULUS H., KENNEDY E. P. The enzymatic synthesis of inositol monophosphatide. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1303–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. R., Leavitt A. L., Honchar M. P., Hallcher L. M., Phillips B. E. Evidence that lithium alters phosphoinositide metabolism: chronic administration elevates primarily D-myo-inositol-1-phosphate in cerebral cortex of the rat. J Neurochem. 1981 Jun;36(6):1947–1951. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb10819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto K., Okada M., Matsuda Y., Nakagawa H. Purification and properties of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from rat brain. J Biochem. 1985 Aug;98(2):363–370. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]