Abstract
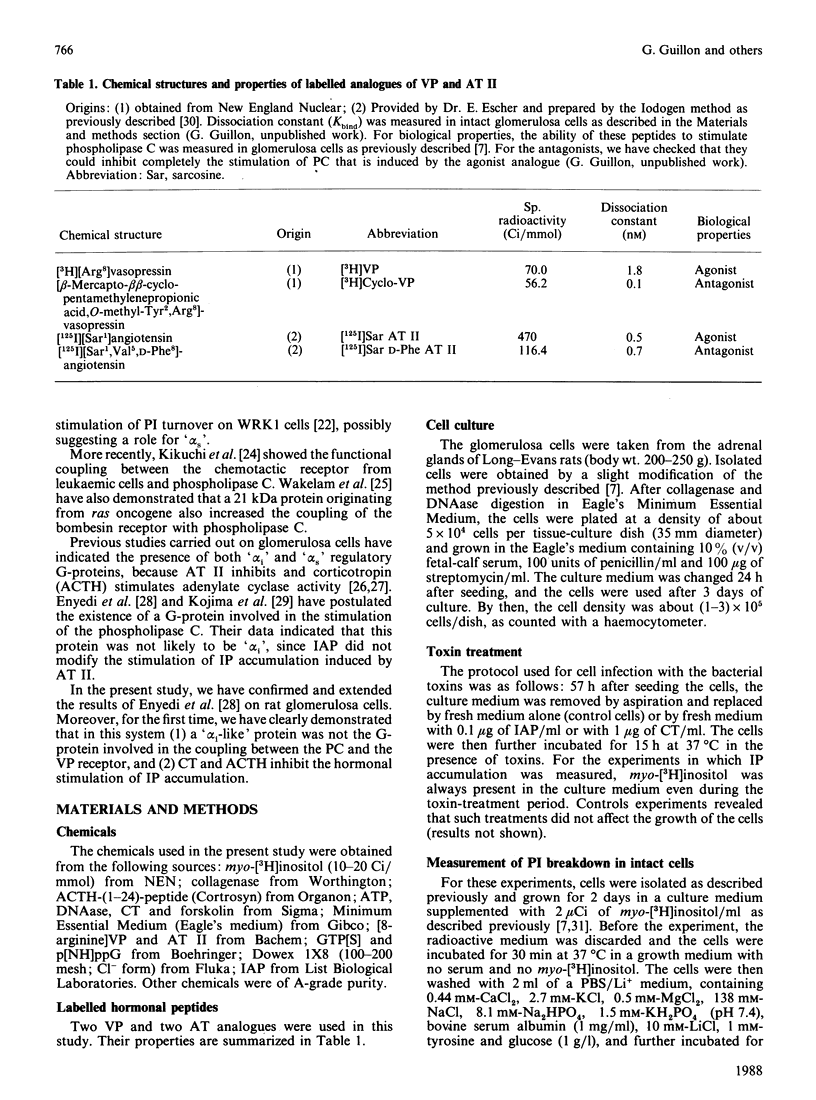
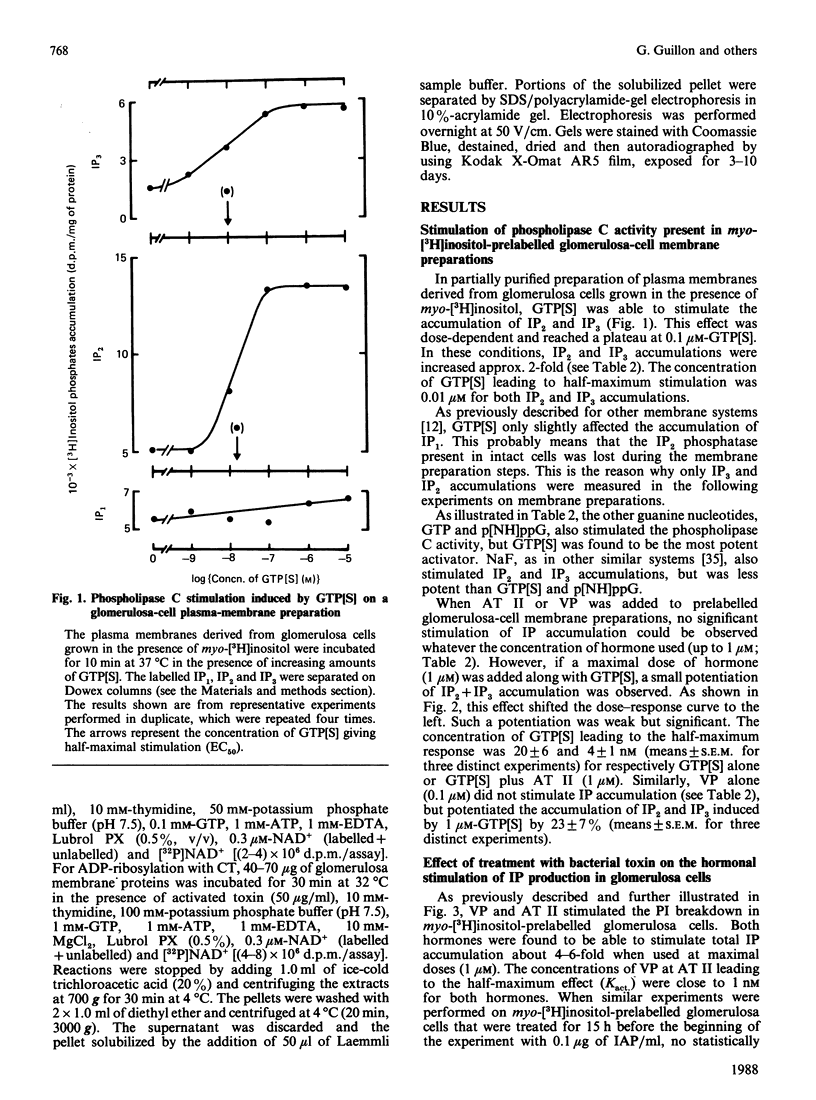
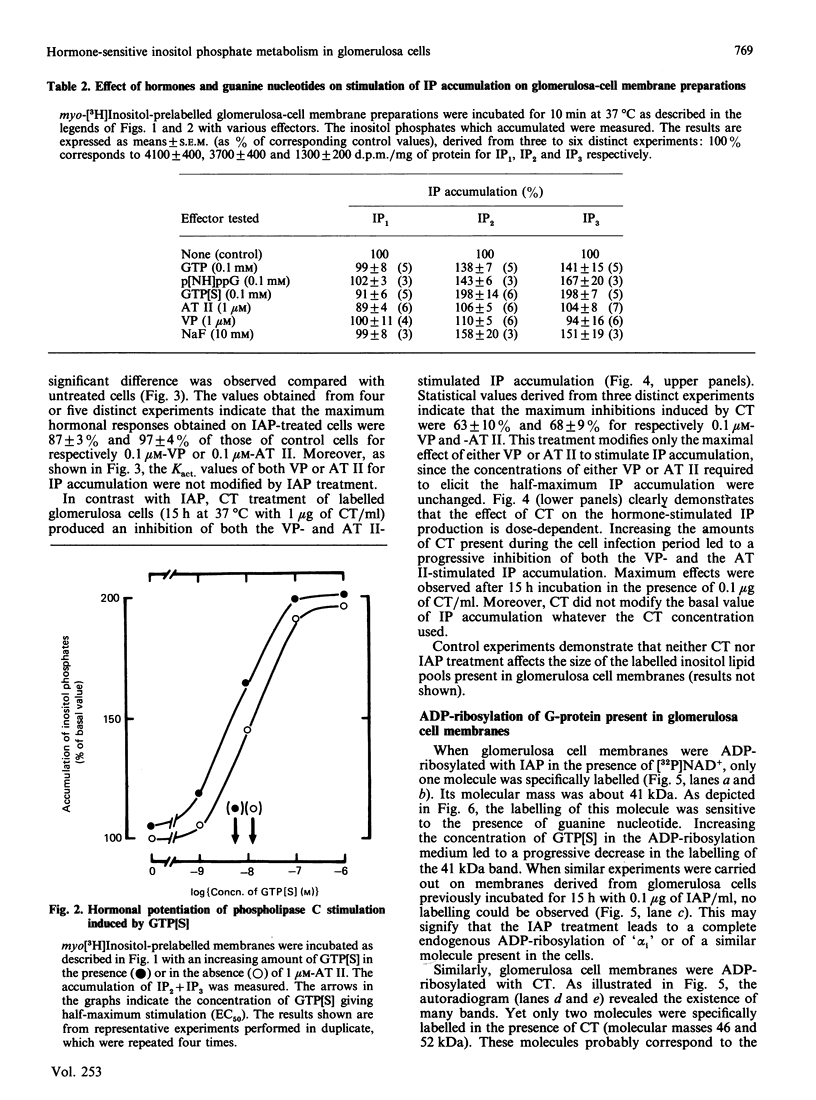
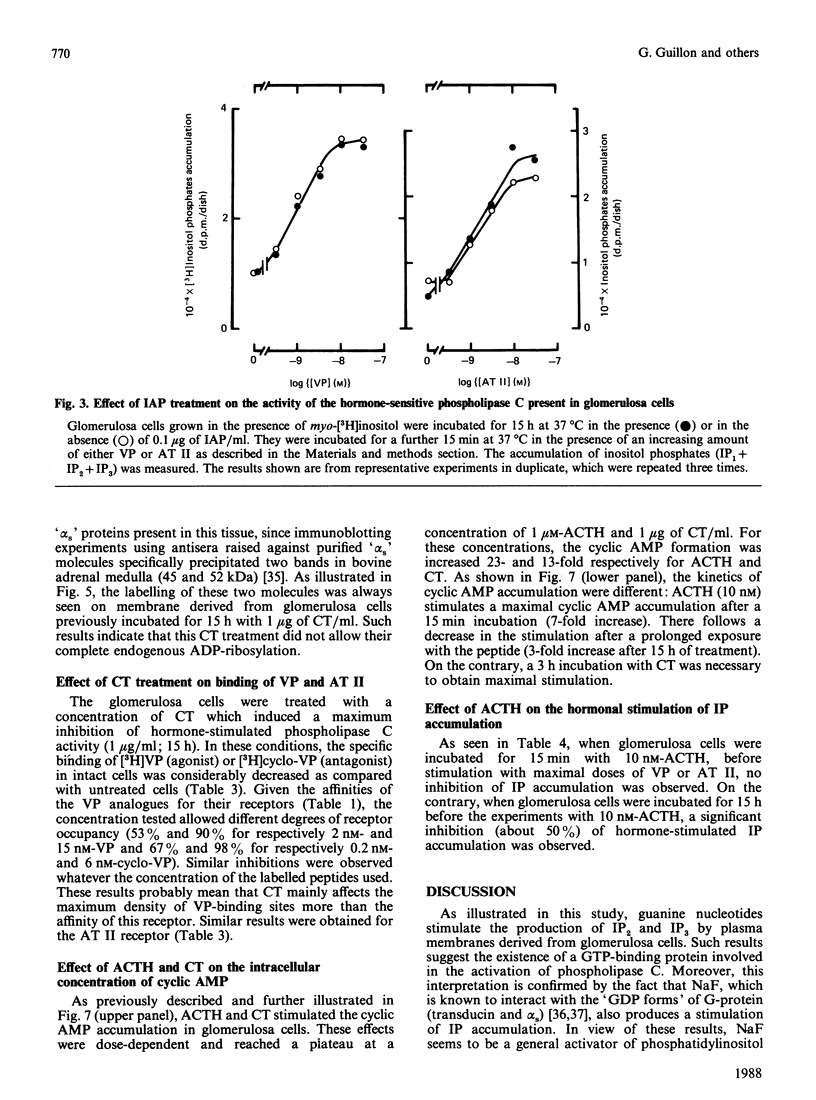
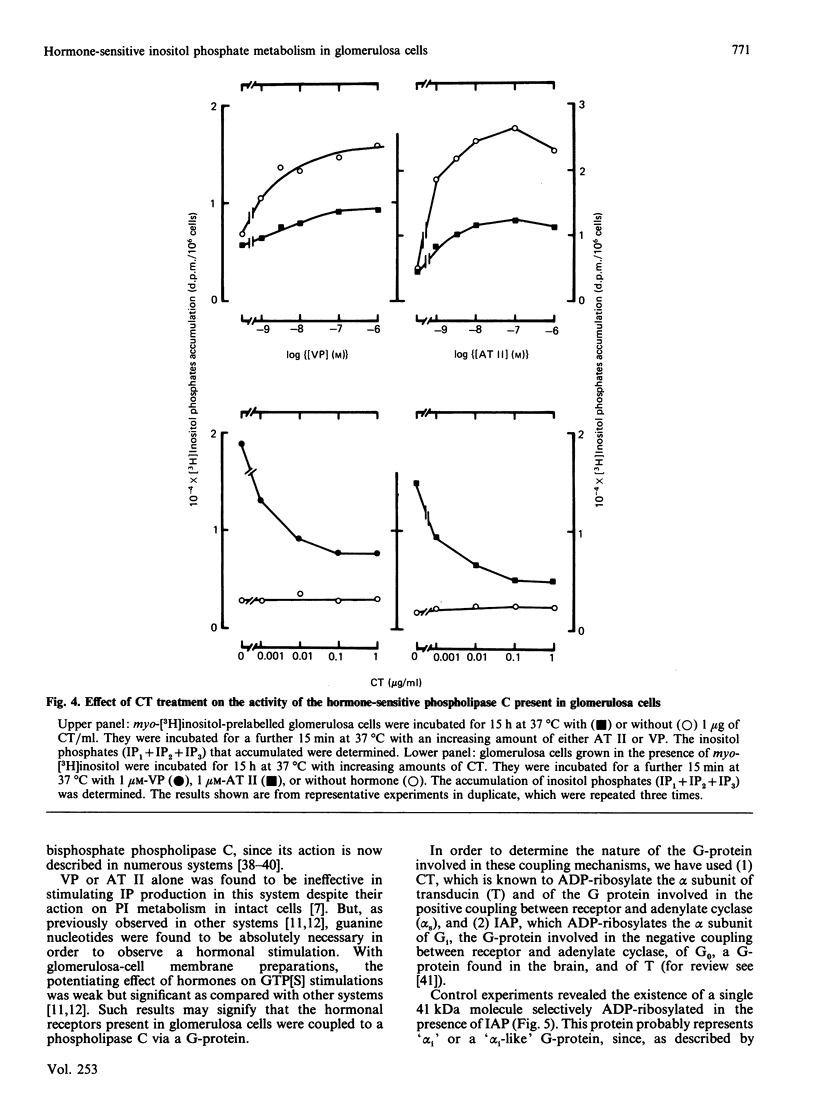
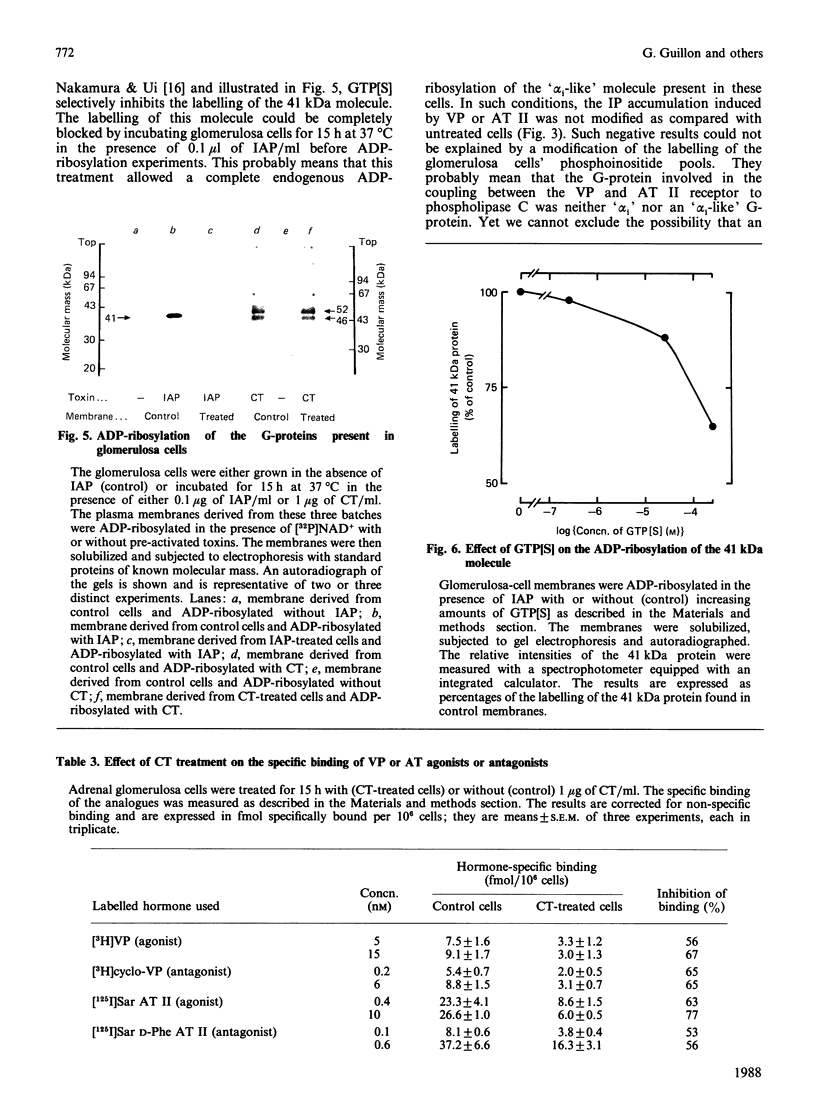
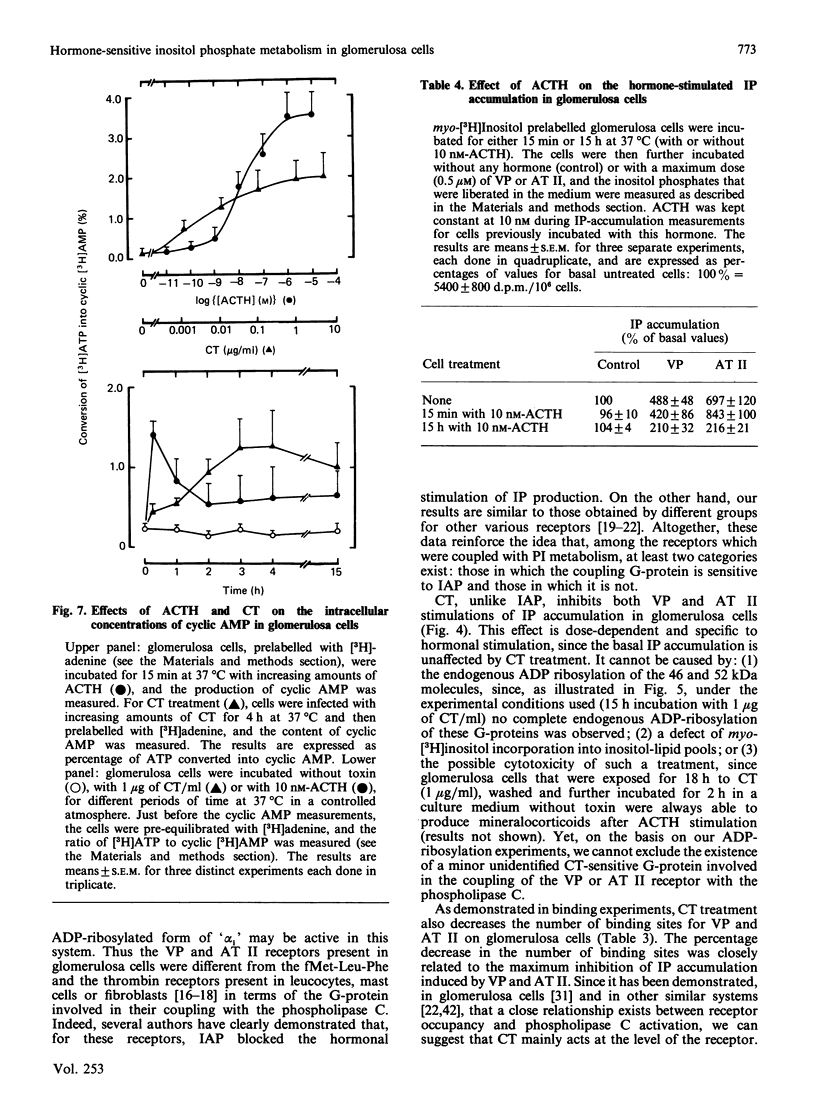
Vasopressin (VP) and angiotensin II (AT II) stimulate the production of inositol phosphates (IP) in rat glomerulosa cells. Guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]), but not VP or AT II, stimulates IP production in a myo-[3H]inositol-prelabelled glomerulosa-cell membrane preparation. In combination with GTP[S], these hormones potentiate the response to GTP[S], indicating the existence of a G-protein involved in the coupling of the VP and AT II receptor with the phospholipase C. ADP-ribosylation with pertussis toxin (IAP) revealed the specific labelling of a single molecule of 41 kDa. No significant inhibition of VP- or AT II-stimulated IP accumulation was detected in intact cells when the whole 41 kDa molecule was endogenously ADP-ribosylated by IAP treatment. On the contrary, when glomerulosa cells were infected with cholera toxin (CT), both the VP- and AT II-stimulated IP accumulations were inhibited in a dose-dependent manner. Yet these effects were partial even at high concentrations of CT, and could not be related to the ADP-ribosylation of 'alpha s' molecules. Similarly, when the cells were infected with 1 microgram of CT/ml, the specific binding of VP and AT II decreased by 50-60%. Such results may signify that the treatment primarily affects the densities of the hormone receptors. When glomerulosa cells were incubated for 15 h in the presence of 10 nM-corticotropin (ACTH), a condition in which the intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP was increased 3-fold, the maximum IP response to 0.1 microM-VP or -AT II was decreased by 50%. When similar experiments were carried out only after a 15 min incubation period with the same concentration of ACTH, the increase in cyclic AMP was more pronounced, but no inhibition of hormone-induced IP accumulation was observed. Altogether, these results may suggest that CT exerts its action on the VP- or AT II-sensitive phospholipase C systems via a prolonged increase in intracellular cyclic AMP.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aranda A., Samuels H. H. Modulation of thyroid hormone nuclear receptors by cholera toxin in cultured GH1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6110–6116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balla T., Baukal A. J., Guillemette G., Morgan R. O., Catt K. J. Angiotensin-stimulated production of inositol trisphosphate isomers and rapid metabolism through inositol 4-monophosphate in adrenal glomerulosa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9323–9327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balla T., Enyedi P., Spät A., Antoni F. A. Pressor-type vasopressin receptors in the adrenal cortex: properties of binding, effects on phosphoinositide metabolism and aldosterone secretion. Endocrinology. 1985 Jul;117(1):421–423. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-1-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoroaluminates activate transducin-GDP by mimicking the gamma-phosphate of GTP in its binding site. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Studies on the hepatic calcium-mobilizing activity of aluminum fluoride and glucagon. Modulation by cAMP and phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11056–11063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert J., Homburger V., Rouot B. GTP binding proteins: a key role in cellular communication. Biochimie. 1987 Apr;69(4):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of adrenergic receptor function by phosphorylation. II. Effects of agonist occupancy on phosphorylation of alpha 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors by protein kinase C and the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3106–3113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabre M. Trigger and amplification mechanisms in visual phototransduction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:331–360. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Taylor J. A. Fluoroaluminates mimic guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate in activating the polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of hepatocyte membranes. Role for the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gp in signal transduction. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):409–414. doi: 10.1042/bj2410409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J., Aguilera G., Kondo T., Catt K. Angiotensin II receptors and aldosterone production in rat adrenal glomerulosa cells. Endocrinology. 1978 Mar;102(3):685–696. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-3-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyedi P., Büki B., Muscsi I., Spät A. Polyphosphoinositide metabolism in adrenal glomerulosa cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Jun;41(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyedi P., Mucsi I., Hunyady L., Catt K. J., Spät A. The role of guanyl nucleotide binding proteins in the formation of inositol phosphates in adrenal glomerulosa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 14;140(3):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90726-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Larson R. E., Davis J. S. Rapid effects of angiotensin-II on polyphosphoinositide metabolism in the rat adrenal glomerulosa. Endocrinology. 1984 Jan;114(1):302–304. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-1-302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita K., Aguilera G., Catt K. J. The role of cyclic AMP in aldosterone production by isolated zona glomerulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8567–8574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo-Payet N., Guillon G., Balestre M. N., Jard S. Vasopressin induces breakdown of membrane phosphoinositides in adrenal glomerulosa and fasciculata cells. Endocrinology. 1986 Sep;119(3):1042–1047. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-3-1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Escher E. Analysis of the adrenal angiotensin II receptor with the photoaffinity labeling method. Biochemistry. 1983 Nov 22;22(24):5591–5596. doi: 10.1021/bi00293a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon G., Balestre M. N., Mouillac B., Berrada R., Kirk C. J. Mechanisms of phospholipase C activation: a comparison with the adenylate cyclase system. Biochimie. 1987 Apr;69(4):351–363. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon G., Balestre M. N., Mouillac B., Devilliers G. Activation of membrane phospholipase C by vasopressin. A requirement for guanyl nucleotides. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 3;196(1):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon G., Gallo-Payet N. Specific vasopressin binding to rat adrenal glomerulosa cells. Relationship to inositol lipid breakdown. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):209–214. doi: 10.1042/bj2350209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon G., Mouillac B., Balestre M. N. Activation of polyphosphoinositide phospholipase C by fluoride in WRK1 cell membranes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80808-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai A., Gershengorn M. C. Evidence for tight coupling of thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptors to stimulated inositol trisphosphate formation in rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10536–10540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Shoback D. M., Pattison G., Stobo J. D. Cholera toxin inhibits the T-cell antigen receptor-mediated increases in inositol trisphosphate and cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5673–5677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Kozawa O., Kaibuchi K., Katada T., Ui M., Takai Y. Direct evidence for involvement of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein in chemotactic peptide-stimulated formation of inositol bisphosphate and trisphosphate in differentiated human leukemic (HL-60) cells. Reconstitution with Gi or Go of the plasma membranes ADP-ribosylated by pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11558–11562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Guillon G., Balestre M. N., Jard S. Stimulation, by vasopressin and other agonists, of inositol-lipid breakdown and inositol phosphate accumulation in WRK 1 cells. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):197–204. doi: 10.1042/bj2400197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch D., Kemmler W., Häring H. U. Cyclic AMP modulates insulin binding and induces post-receptor insulin resistance of glucose transport in isolated rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):398–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima I., Kojima K., Kreutter D., Rasmussen H. The temporal integration of the aldosterone secretory response to angiotensin occurs via two intracellular pathways. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14448–14457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima I., Lippes H., Kojima K., Rasmussen H. Aldosterone secretion: effect of phorbol ester and A23187. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):555–562. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima I., Shibata H., Ogata E. Pertussis toxin blocks angiotensin II-induced calcium influx but not inositol trisphosphate production in adrenal glomerulosa cell. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):347–351. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80841-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. H., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B., Andersson T., Waldvogel F. A., Lew P. D. Chemotactic peptide activation of human neutrophils and HL-60 cells. Pertussis toxin reveals correlation between inositol trisphosphate generation, calcium ion transients, and cellular activation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1348–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Cotecchia S., DeBlasi A., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of adrenergic receptor function by phosphorylation. I. Agonist-promoted desensitization and phosphorylation of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors coupled to inositol phospholipid metabolism in DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3098–3105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone activates a Ca2+-dependent polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in permeable GH3 cells. GTP gamma S potentiation by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2918–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Martin M. W., Harden T. K., Brown J. H. Pertussis toxin does not inhibit muscarinic-receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis or calcium mobilization. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):933–937. doi: 10.1042/bj2270933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Kahn R. A., Manning D. R., Gilman A. G. Antisera of designed specificity for subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):265–269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase and stimulation of arachidonic acid release in 3T3 fibroblasts. Selective susceptibility to islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7226–7233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Katada T., Ui M. Coupling of the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein to chemotactic peptide receptors in neutrophil membranes and its uncoupling by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible role of the toxin substrate in Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6761–6768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Pouysségur J. Pertussis toxin inhibits thrombin-induced activation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis and Na+/H+ exchange in hamster fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):55–60. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payet N., Lehoux J. G. A comparative study of the role of vasopressin and ACTH in the regulation of growth and function of rat adrenal glands. J Steroid Biochem. 1980 Jan;12:461–467. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(80)90307-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Neto F. A., Mattera R., Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Field J. B., Birnbaumer L., Sekura R. D. ADP-ribosylation of membrane components by pertussis and cholera toxin. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:566–572. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Strasser R. H., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Homologous desensitization of adenylate cyclase is associated with phosphorylation of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):3883–3886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Aluminum: a requirement for activation of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by fluoride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4888–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser R. H., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-agonist- and prostaglandin E1-induced translocation of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: evidence that the kinase may act on multiple adenylate cyclase-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6362–6366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing R. J., Prpic V., Jiang H., Exton J. H. Hormone-stimulated polyphosphoinositide breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Murphy G. J., Hruby V. J., Houslay M. D. Activation of two signal-transduction systems in hepatocytes by glucagon. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):68–71. doi: 10.1038/323068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. A., Fain J. N. Guanosine 5'-O-thiotriphosphate stimulates phospholipase C activity in plasma membranes of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9527–9530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. The rapid formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets by thrombin is inhibited by prostacyclin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13199–13203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S., Sebben M., Bockaert J. Corticotropin-peptide regulation of intracellular cyclic AMP production in cortical neurons in primary culture. J Neurochem. 1985 Sep;45(3):869–874. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb04074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock E. A., Johnston C. I. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase in rat adrenal glomerulosa cells by angiotensin II. Endocrinology. 1984 Jul;115(1):337–341. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-1-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock E. A., Mcleod J. K., Johnston C. I. Vasopressin stimulates phosphatidylinositol turnover and aldosterone synthesis in rat adrenal glomerulosa cells: comparison with angiotensin II. Endocrinology. 1986 Jun;118(6):2432–2436. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-6-2432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



