Abstract
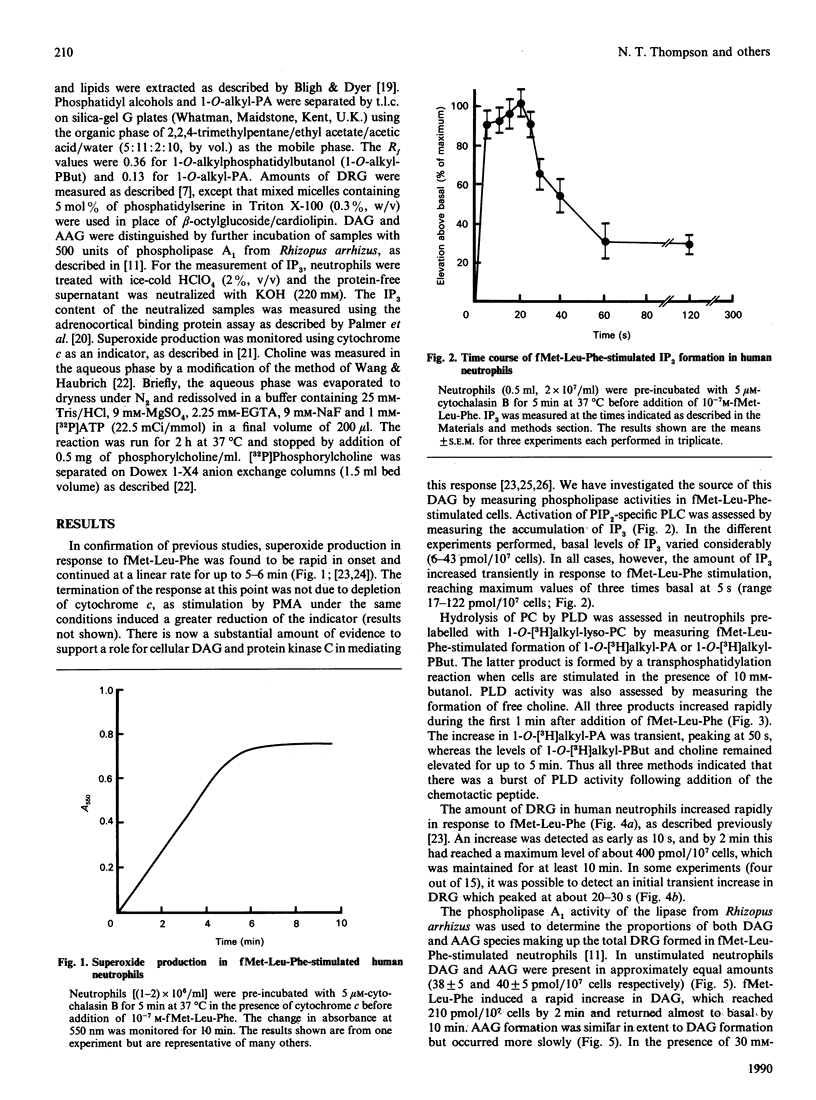
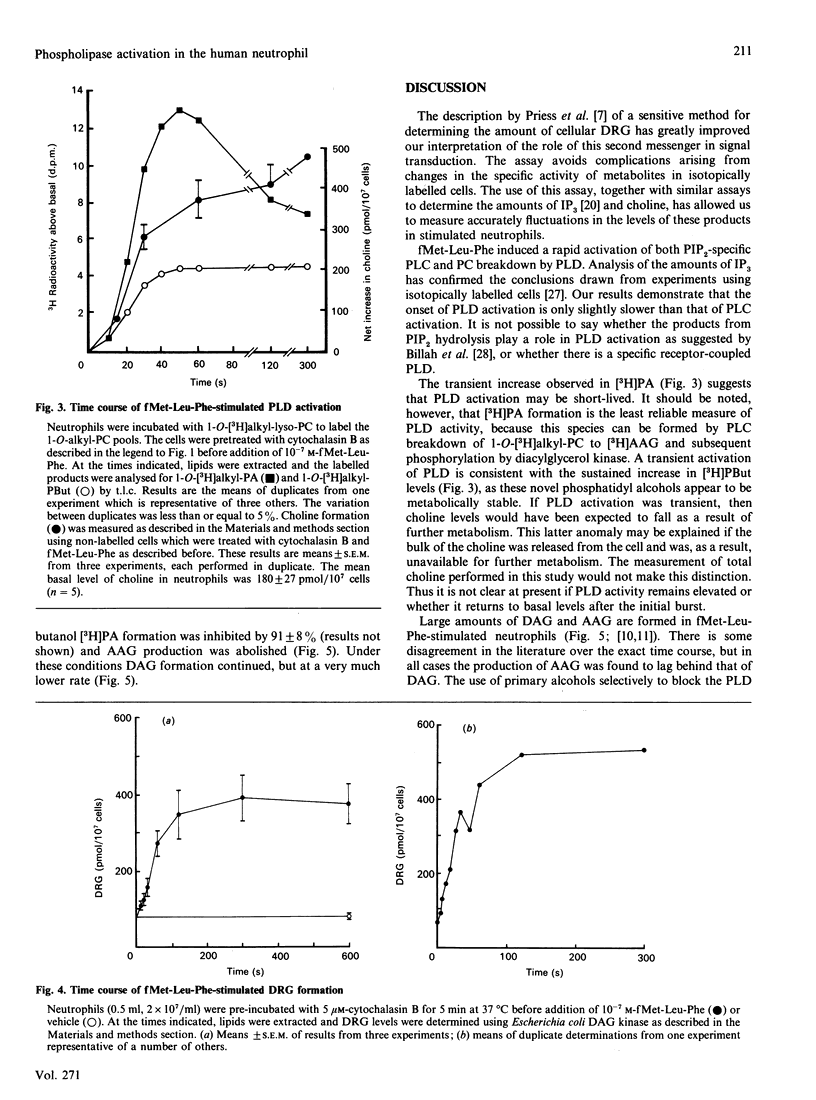
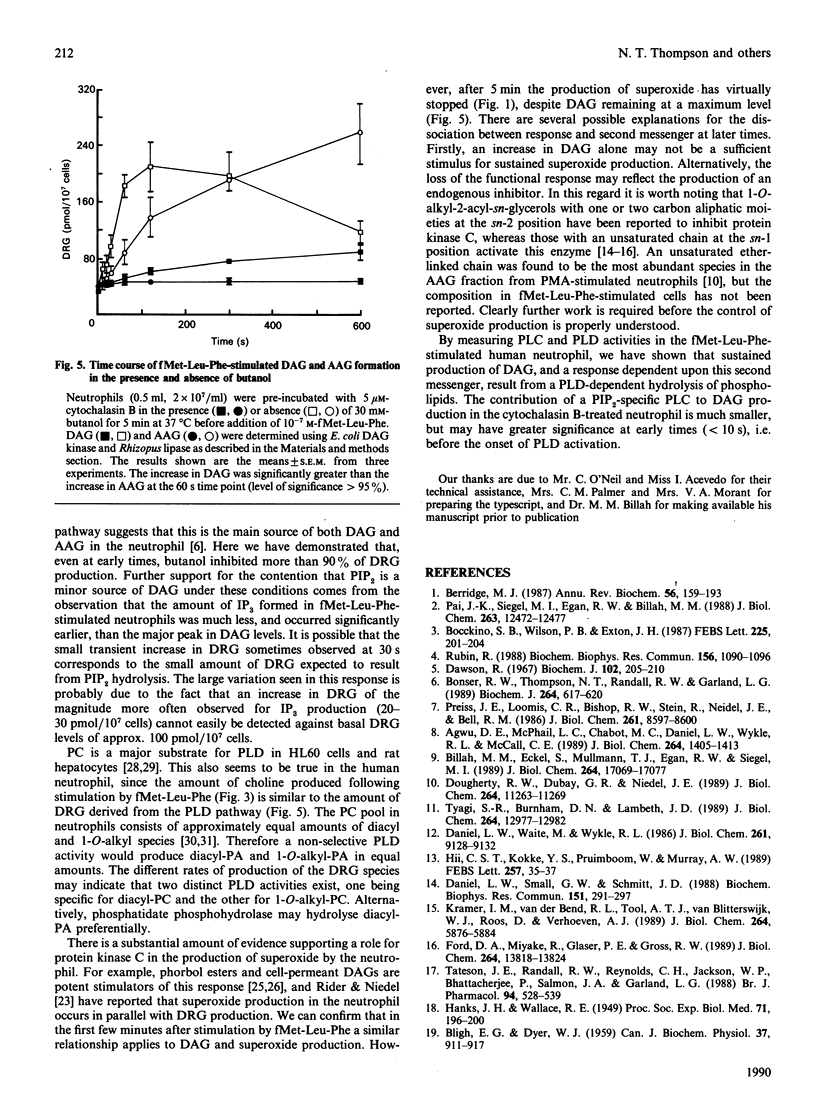
Fluctuations in the amounts of choline, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diradylglycerol have been used to monitor phospholipase activation in the human neutrophil. Stimulation of human neutrophils by formylmethionyl-leucylphenylalanine (fMet-Leu-Phe) resulted in a rapid activation of both phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate breakdown by phospholipase C and phosphatidylcholine breakdown by phospholipase D. Diradylglycerol accumulation occurred more slowly than that of either choline or IP3 and was inhibited by 30 mM-butanol, suggesting that the bulk was derived from the phospholipase D pathway via phosphatidate phosphohydrolase. Consistent with this is the observation that choline and diradylglycerol are produced in similar amounts. 1,2-Diacylglycerol (DAG) and 1-O-alkyl-2-acyl-sn-glycerol species accumulated with different time courses, indicating that one or more steps in the phospholipase D pathway was selective for the diacyl species. Superoxide production by fMet-Leu-Phe-stimulated neutrophils paralleled DAG accumulation over the first 5 min, but thereafter this production stopped, despite the fact that DAG remained elevated. We conclude that DAG derived from the phospholipase D pathway is only one of the second messengers important in controlling this functional response.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agwu D. E., McPhail L. C., Chabot M. C., Daniel L. W., Wykle R. L., McCall C. E. Choline-linked phosphoglycerides. A source of phosphatidic acid and diglycerides in stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1405–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Eckel S., Mullmann T. J., Egan R. W., Siegel M. I. Phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by phospholipase D determines phosphatidate and diglyceride levels in chemotactic peptide-stimulated human neutrophils. Involvement of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17069–17077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Phosphatidate accumulation in hormone-treated hepatocytes via a phospholipase D mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15309–15315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Ca2+-mobilizing hormones elicit phosphatidylethanol accumulation via phospholipase D activation. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonser R. W., Thompson N. T., Randall R. W., Garland L. G. Phospholipase D activation is functionally linked to superoxide generation in the human neutrophil. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):617–620. doi: 10.1042/bj2640617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham D. N., Tyagi S. R., Uhlinger D. J., Lambeth J. D. Diacylglycerol generation and phosphoinositide turnover in human neutrophils: effects of particulate versus soluble stimuli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Feb 15;269(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H. J., Chovaniec M. E. Superoxide generation by digitonin-stimulated guinea pig granulocytes. A basis for a continuous assay for monitoring superoxide production and for the study of the activation of the generating system. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1081–1087. doi: 10.1172/JCI109007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel L. W., Small G. W., Schmitt J. D., Marasco C. J., Ishaq K., Piantadosi C. Alkyl-linked diglycerides inhibit protein kinase C activation by diacylglycerols. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90592-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel L. W., Waite M., Wykle R. L. A novel mechanism of diglyceride formation. 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate stimulates the cyclic breakdown and resynthesis of phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9128–9132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M. The formation of phosphatidylglycerol and other phospholipids by the transferase activity of phospholipase D. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):205–210. doi: 10.1042/bj1020205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Lew D. P., Pozzan T. Protein kinase C activation of physiological processes in human neutrophils at vanishingly small cytosolic Ca2+ levels. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):691–693. doi: 10.1038/310691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty R. W., Dubay G. R., Niedel J. E. Dynamics of the diradylglycerol responses of stimulated phagocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11263–11269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford D. A., Miyake R., Glaser P. E., Gross R. W. Activation of protein kinase C by naturally occurring ether-linked diglycerides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13818–13824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hii C. S., Kokke Y. S., Pruimboom W., Murray A. W. Phorbol esters stimulate a phospholipase D-catalysed reaction with both ester- and ether-linked phospholipids in HeLa cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 23;257(1):35–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81779-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Vosshall L. B., Haines K. A., Wilkenfeld C., Lundquist K. F., Weissmann G. Activation of the human neutrophil by calcium-mobilizing ligands. II. Correlation of calcium, diacyl glycerol, and phosphatidic acid generation with superoxide anion generation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11098–11105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer I. M., van der Bend R. L., Tool A. T., van Blitterswijk W. J., Roos D., Verhoeven A. J. 1-O-hexadecyl-2-Q-methylglycerol, a novel inhibitor of protein kinase C, inhibits the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5876–5884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller H. W., O'Flaherty J. T., Greene D. G., Samuel M. P., Wykle R. L. 1-O-alkyl-linked glycerophospholipids of human neutrophils: distribution of arachidonate and other acyl residues in the ether-linked and diacyl species. J Lipid Res. 1984 Apr;25(4):383–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Phospholipase D catalyzes phospholipid metabolism in chemotactic peptide-stimulated HL-60 granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12472–12477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S., Hughes K. T., Lee D. Y., Wakelam M. J. Development of a novel, Ins(1,4,5)P3-specific binding assay. Its use to determine the intracellular concentration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 in unstimulated and vasopressin-stimulated rat hepatocytes. Cell Signal. 1989;1(2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penfield A., Dale M. M. Synergism between A23187 and 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-glycerol in superoxide production by human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 30;125(1):332–336. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80372-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider L. G., Niedel J. E. Diacylglycerol accumulation and superoxide anion production in stimulated human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5603–5608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. Phosphatidylethanol formation in human platelets: evidence for thrombin-induced activation of phospholipase D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 15;156(3):1090–1096. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80744-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateson J. E., Randall R. W., Reynolds C. H., Jackson W. P., Bhattacherjee P., Salmon J. A., Garland L. G. Selective inhibition of arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase by novel acetohydroxamic acids: biochemical assessment in vitro and ex vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):528–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tencé M., Jouvin-Marche E., Bessou G., Record M., Benveniste J. Ether-phospholipid composition in neutrophils and platelets. Thromb Res. 1985 May 1;38(3):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi S. R., Burnham D. N., Lambeth J. D. On the biological occurrence and regulation of 1-acyl and 1-O-alkyl-diradylglycerols in human neutrophils. Selective destruction of diacyl species using Rhizopus lipase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12977–12982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F. L., Haubrich D. R. A simple, sensitive, and specific assay for free choline in plasma. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jan;63(1):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90204-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


