Abstract
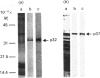
Aggregation of cells of the marine sponge Geodia cydonium is mediated by an aggregation factor (AF) particle of Mr 1.3 X 10(8). It is now reported that the AF particle is associated with calpactin, which was ascribed a role in the cell-adhesion process. In order to identify the sequence similarity to other members of the lipocortin family, the cDNA of sponge calpactin was cloned and found to display an 80% sequence similarity to vertebrate calpactin II but only a 47% similarity to calpactin I. The calpactin gene, which contains the consensus sequence coding for the amino acids G-T-D-E, was expressed in Escherichia coli and subsequently purified to a 37000-Mr polypeptide. Both the p32 and the p37 are provided with approximately two Ca2+ ions/molecule and the property to bind to phospholipids. The dissociation constant (calpactin-Ca2+) was in the absence of phospholipids in the range 500-700 microM-Ca2+ but in their presence about 20-30 microM-Ca2+. On the basis of (i) inhibition studies with antibodies to calelectrin and (ii) competition experiments with soluble phospholipids (both chemically defined as well as total homologous membrane lipids) we conclude that the AF-associated calpactin and plasma-membrane-bound phospholipid(s) are involved in cell-cell aggregation in sponges.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann E., Brosius J. "ATG vectors' for regulated high-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M., Mayet W. J., Schröder H. C., Pfeifer K., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Müller W. E. Association of La and Ro antigens with intracellular structures in HEp-2 carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7770–7774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck C. A., Horwitz A. F. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M. R., Owens R. J., Totty N. F., Moss S. E., Waterfield M. D., Crumpton M. J. Primary structure of the human, membrane-associated Ca2+-binding protein p68 a novel member of a protein family. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):21–27. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl-Seifert B., Uhlenbruck G., Geisert M., Zahn R. K., Müller W. E. Physicochemical and functional characterization of the polymerization process of the Geodia cydonium lectin. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 15;147(3):517–523. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-2956.1985.00517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsche U., von Kieckebusch A., Potschka M., Whittaker V. P., Witzemann V. The separation and characterization of two forms of Torpedo electric organ calelectrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 2;957(1):122–130. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J., Fritsche U., Hexham J. M., Dash B., Johnson T. A consensus amino-acid sequence repeat in Torpedo and mammalian Ca2+-dependent membrane-binding proteins. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):636–638. doi: 10.1038/320636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J., Zokas L. Antibodies to the N-terminus of calpactin II (p35) affect Ca2+ binding and phosphorylation by the epidermal growth factor receptor in vitro. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2069–2076. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramzow M., Bachmann M., Uhlenbruck G., Dorn A., Müller W. E. Identification and further characterization of the specific cell binding fragment from sponge aggregation factor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1344–1349. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramzow M., Schröder H. C., Fritsche U., Kurelec B., Robitzki A., Zimmermann H., Friese K., Kreuter M. H., Müller W. E. Role of phospholipase A2 in the stimulation of sponge cell proliferation by homologous lectin. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):939–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90616-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramzow M., Schröder H. C., Uhlenbruck G., Batel R., Müller W. E. Sponge aggregation factor: identification of the specific collagen-binding site by means of a monoclonal antibody. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Feb;36(2):205–212. doi: 10.1177/36.2.3335775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramzow M., Zimmermann H., Janetzko A., Dorn A., Kurelec B., Schröder H. C., Müller W. E. Control of the aggregation factor-aggregation receptor interaction in sponges by protein kinase C. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Nov;179(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL J. P., DREYER W. J. Measurement of protein-binding phenomena by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;63:530–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREYS T. CHEMICAL DISSOLUTION AND IN VITRO RECONSTRUCTION OF SPONGE CELL ADHESIONS. I. ISOLATION AND FUNCTIONAL DEMONSTRATION OF THE COMPONENTS INVOLVED. Dev Biol. 1963 Aug;8:27–47. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(63)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H., Creutz C. E. Cell biology. Consensus in exocytosis. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):573–573. doi: 10.1038/320573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Rottmann M., Diehl-Seifert B., Kurelec B., Uhlenbruck G., Schröder H. C. Role of the aggregation factor in the regulation of phosphoinositide metabolism in sponges. Possible consequences on calcium efflux and on mitogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9850–9858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Zahn R. K., Arendes J., Kurelec B., Steffen R., Müller I. Aggregation of sponge cells. XX. Self-aggregation of the circular proteid particle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 8;551(2):363–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Zahn R. K., Kurelec B., Müller I., Uhlenbruck G., Vaith P. Aggregation of sponge cells. A novel mechanism of controlled intercellular adhesion, basing on the interrelation between glycosyltransferases and glycosidases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1280–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Zahn R. K., Müller I., Kurelec B., Uhlenbruck G., Vaith P. Cell aggregation of the marine sponge Geodia cydonium. Identification of lectin-producing cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;24(1):28–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Zahn R. K. Purification and characterization of a species-specific aggregation factor in sponges. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jul;80(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90279-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Sinclair L. K., Browning J. L., Mattaliano R. J., Smart J. E., Chow E. P., Falbel T., Ribolini A., Garwin J. L., Wallner B. P. Purification and partial sequence analysis of a 37-kDa protein that inhibits phospholipase A2 activity from rat peritoneal exudates. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4239–4246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice D. J., Humphreys T. Two Ca2+ functions are demonstrated by the substitution of specific divalent and lanthanide cations for the Ca2+ required by the aggregation factor complex from the marine sponge, Microciona prolifera. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6394–6399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robitzki A., Schröder H. C., Ugarkovic D., Pfeifer K., Uhlenbruck G., Müller W. E. Demonstration of an endocrine signaling circuit for insulin in the sponge Geodia cydonium. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2905–2909. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottmann M., Schröder H. C., Gramzow M., Renneisen K., Kurelec B., Dorn A., Friese U., Müller W. E. Specific phosphorylation of proteins in pore complex-laminae from the sponge Geodia cydonium by the homologous aggregation factor and phorbol ester. Role of protein kinase C in the phosphorylation of DNA topoisomerase II. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3939–3944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02735.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Tack B. F., Kristensen T., Glenney J. R., Jr, Hunter T. The cDNA sequence for the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I heavy chain) reveals a multidomain protein with internal repeats. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Kuchino Y., Gramzow M., Kurelec B., Friese U., Uhlenbruck G., Müller W. E. Induction of ras gene expression by homologous aggregation factor in cells from the sponge Geodia cydonium. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16334–16340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Takabayashi E., Yano S. Y., Shimizu N., Yamada K., Gushima H. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the cDNA coding for rat lipocortin I (calpactin II). Gene. 1988 May 15;65(1):141–147. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90427-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll G., Fritsche U., Witzemann V., Müller H. W. Antibodies to calcium/phospholipid binding protein (calelectrin) recognize neurons, astrocytes and Schwann cells in the nervous system of rat. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Mar 21;86(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi S. Stepwise cleavage of rabbit immunoglobulin G by papain and isolation of four types of biologically active Fc fragments. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(3):343–355. doi: 10.1042/bj1120343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Johnsson N. Repeating sequence homologies in the p36 target protein of retroviral protein kinases and lipocortin, the p37 inhibitor of phospholipase A2. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 14;203(1):95–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81444-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum G., Burger M. M. Two component system for surface guided reassociation of animal cells. Nature. 1973 Aug 24;244(5417):510–512. doi: 10.1038/244510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kieckebusch A., Fritsche U., Vogel V., Witzemann V., Whittaker V. P. Ca2+- and phospholipid-binding properties of Torpedo electric organ calelectrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 2;957(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]