Abstract
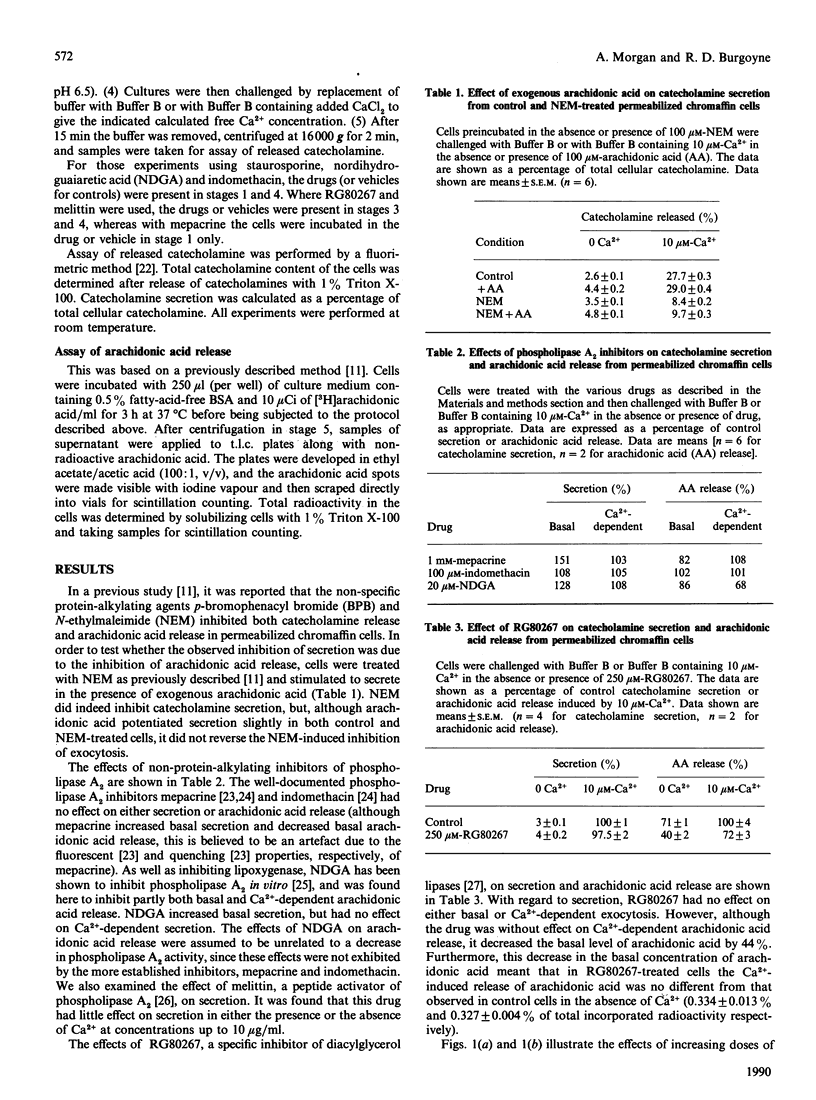
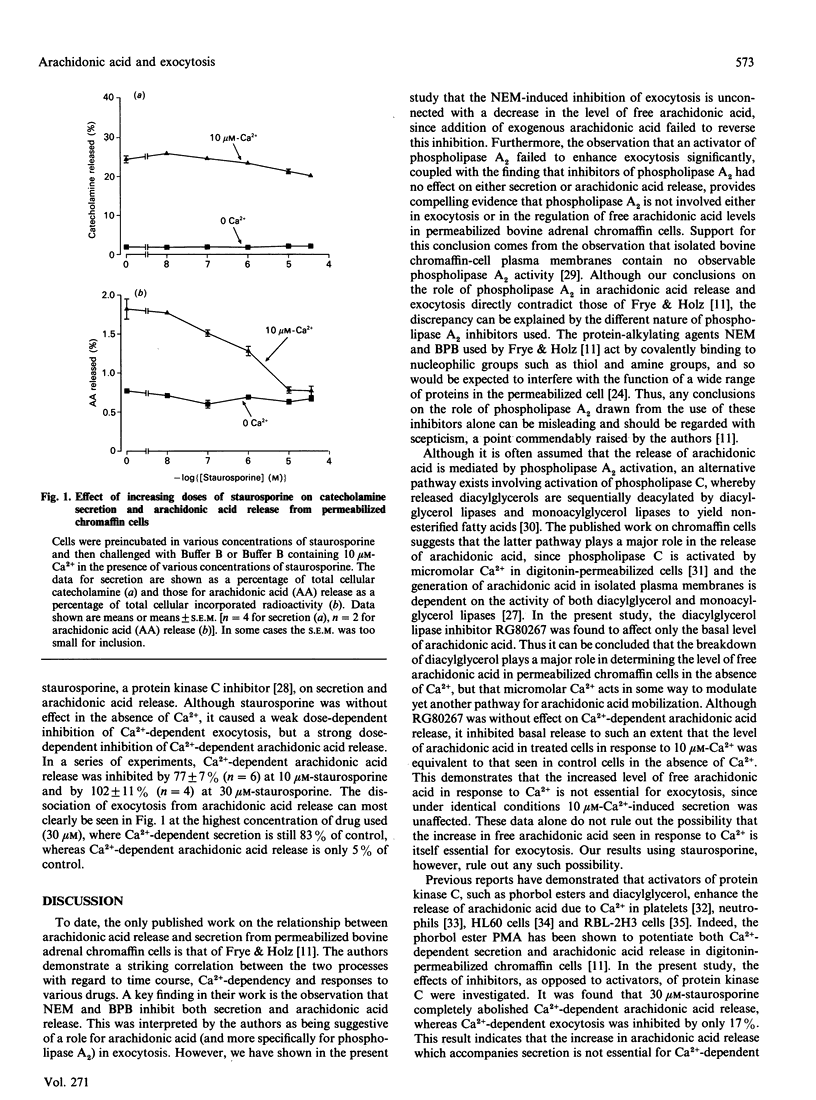
The relationship between Ca2(+)-dependent arachidonic acid release and exocytosis from digitonin-permeabilized bovine adrenal chromaffin cells was investigated. The phospholipase A2 inhibitors mepacrine, nordihydroguaiaretic acid and indomethacin had no effect on either arachidonic acid release or secretion. The phospholipase A2 activator melittin had no effect on secretion. The specific diacylglycerol lipase inhibitor RG80267 had no effect on secretion, but decreased basal arachidonic acid release to such an extent that the level of arachidonic acid in treated cells in response to 10 microM-Ca2+ was equivalent to that of control cells in the absence of Ca2+. Staurosporine, a protein kinase C inhibitor, was found to abolish Ca2(+)-dependent arachidonic acid release completely, but had only a slight inhibitory effect on Ca2(+)-dependent secretion. It is concluded that arachidonic acid is not essential for Ca2(+)-dependent exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S. M., Geisow M. J., Burgoyne R. D. A role for calpactin in calcium-dependent exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):313–315. doi: 10.1038/340313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aunis D., Bader M. F. The cytoskeleton as a barrier to exocytosis in secretory cells. J Exp Biol. 1988 Sep;139:253–266. doi: 10.1242/jeb.139.1.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Knight D. E. Calcium control of exocytosis and endocytosis in bovine adrenal medullary cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Dec 18;296(1080):83–103. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Siegel M. I. Phospholipase A2 activation in chemotactic peptide-stimulated HL60 granulocytes: synergism between diacylglycerol and Ca2+ in a protein kinase C-independent mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):683–691. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Morgan A., O'Sullivan A. J. A major role for protein kinase C in calcium-activated exocytosis in permeabilised adrenal chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 26;238(1):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80246-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Morgan A., O'Sullivan A. J. The control of cytoskeletal actin and exocytosis in intact and permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells: role of calcium and protein kinase C. Cell Signal. 1989;1(4):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. P., Graeter J., Catt K. J. Coordinate actions of arachidonic acid and protein kinase C in gonadotropin-releasing hormone-stimulated secretion of luteinizing hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):134–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90537-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J., Musser J. H., McGregor H. Phospholipase A2: function and pharmacological regulation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Aug 1;36(15):2429–2436. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90512-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E. cis-Unsaturated fatty acids induce the fusion of chromaffin granules aggregated by synexin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):247–256. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn L. A., Holz R. W. Catecholamine secretion from digitonin-treated adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4989–4993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard D. A., Holz R. W. Cholinergic stimulation of inositol phosphate formation in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: distinct nicotinic and muscarinic mechanisms. J Neurochem. 1987 Nov;49(5):1634–1643. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb01037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froissart P., Unligil P., Aubry H., Proulx P. Modulation by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate of arachidonic acid release from rat basophilic leukemia cells stimulated with A23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Apr 26;1002(3):376–381. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90352-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frye R. A., Holz R. W. Arachidonic acid release and catecholamine secretion from digitonin-treated chromaffin cells: effects of micromolar calcium, phorbol ester, and protein alkylating agents. J Neurochem. 1985 Jan;44(1):265–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frye R. A., Holz R. W. Phospholipase A2 inhibitors block catecholamine secretion and calcium uptake in cultured bovine adrenal medullary cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 May;23(3):547–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frye R. A., Holz R. W. The relationship between arachidonic acid release and catecholamine secretion from cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1984 Jul;43(1):146–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuse I., Iwanaga T., Tai H. H. Phorbol ester, 1,2-diacylglycerol, and collagen induce inhibition of arachidonic acid incorporation into phospholipids in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3890–3895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., Frey W., 2nd, Carr D. W., Goldberg N. D. Stimulation of human platelet guanylate cyclase by fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1279–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A., Zinder O. Alpha- and beta-receptor control of catecholamine secretion from isolated adrenal medulla cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;226(3):655–665. doi: 10.1007/BF00214792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halenda S. P., Banga H. S., Zavoico G. B., Lau L. F., Feinstein M. B. Synergistic release of arachidonic acid from platelets by activators of protein kinase C and Ca2+ ionophores. Evidence for the role of protein phosphorylation in the activation of phospholipase A2 and independence from the Na+/H+ exchanger. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7356–7363. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W., Senter R. A., Frye R. A. Relationship between Ca2+ uptake and catecholamine secretion in primary dissociated cultures of adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1982 Sep;39(3):635–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Dawson R. M. Fatty acid stimulation of membrane phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis by brain phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):497–500. doi: 10.1042/bj1780497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenigsberg R. L., Trifaró J. M. Microinjection of calmodulin antibodies into cultured chromaffin cells blocks catecholamine release in response to stimulation. Neuroscience. 1985 Jan;14(1):335–347. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnick R. N., Musacchio I., Thaw C., Gershengorn M. C. Arachidonic acid mobilizes calcium and stimulates prolactin secretion from GH3 cells. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):E458–E462. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.246.5.E458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl S. R., Hurst N. P., Cleland L. G. Modulation by phorbol myristate acetate of arachidonic acid release and leukotriene synthesis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes stimulated with A23187. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):399–404. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., Clayton C. C., Snyderman R. A potential second messenger role for unsaturated fatty acids: activation of Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):622–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6231726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Burgoyne R. D. Stimulation of Ca2(+)-independent catecholamine secretion from digitonin-permeabilized bovine adrenal chromaffin cells by guanine nucleotide analogues. Relationship to arachidonate release. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):521–526. doi: 10.1042/bj2690521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Kajiyama Y., Takahashi A., Nomura Y. Modes of inhibitory action of 4 beta-phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate in thrombin-stimulated arachidonic acid release in intact and permeabilized platelets. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Jan;276(1):146–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A. J., Cheek T. R., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Burgoyne R. D. Localization and heterogeneity of agonist-induced changes in cytosolic calcium concentration in single bovine adrenal chromaffin cells from video imaging of fura-2. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):401–411. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03391.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindlisbacher B., Reist M., Zahler P. Diacylglycerol breakdown in plasma membranes of bovine chromaffin cells is a two-step mechanism mediated by a diacylglycerol lipase and a monoacylglycerol lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 11;905(2):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindlisbacher B., Sidler M. A., Galatioto L. E., Zahler P. Arachidonic acid liberated by diacylglycerol lipase is essential for the release mechanism in chromaffin cells from bovine adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1990 Apr;54(4):1247–1252. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler P., Reist M., Pilarska M., Rosenheck K. Phospholipase C and diacylglycerol lipase activities associated with plasma membranes of chromaffin cells isolated from bovine adrenal medulla. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 18;877(3):372–379. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H. Phosphoglyceride metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):243–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


