Abstract
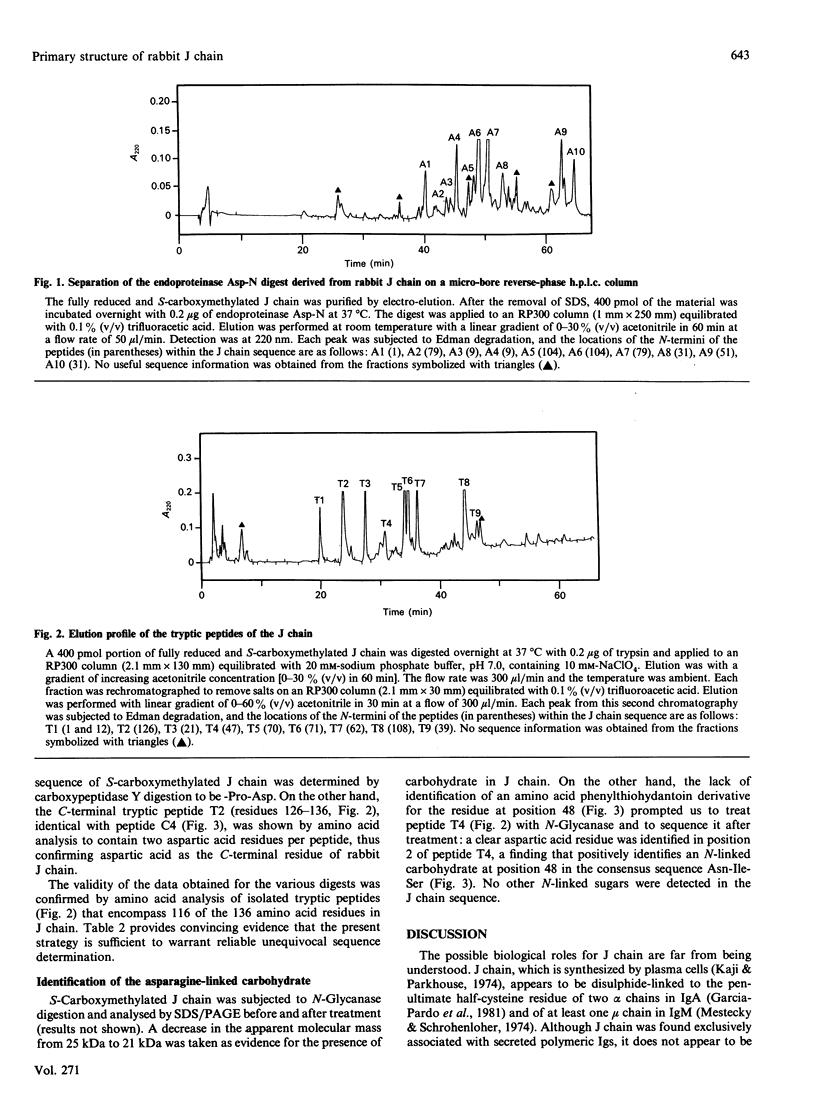
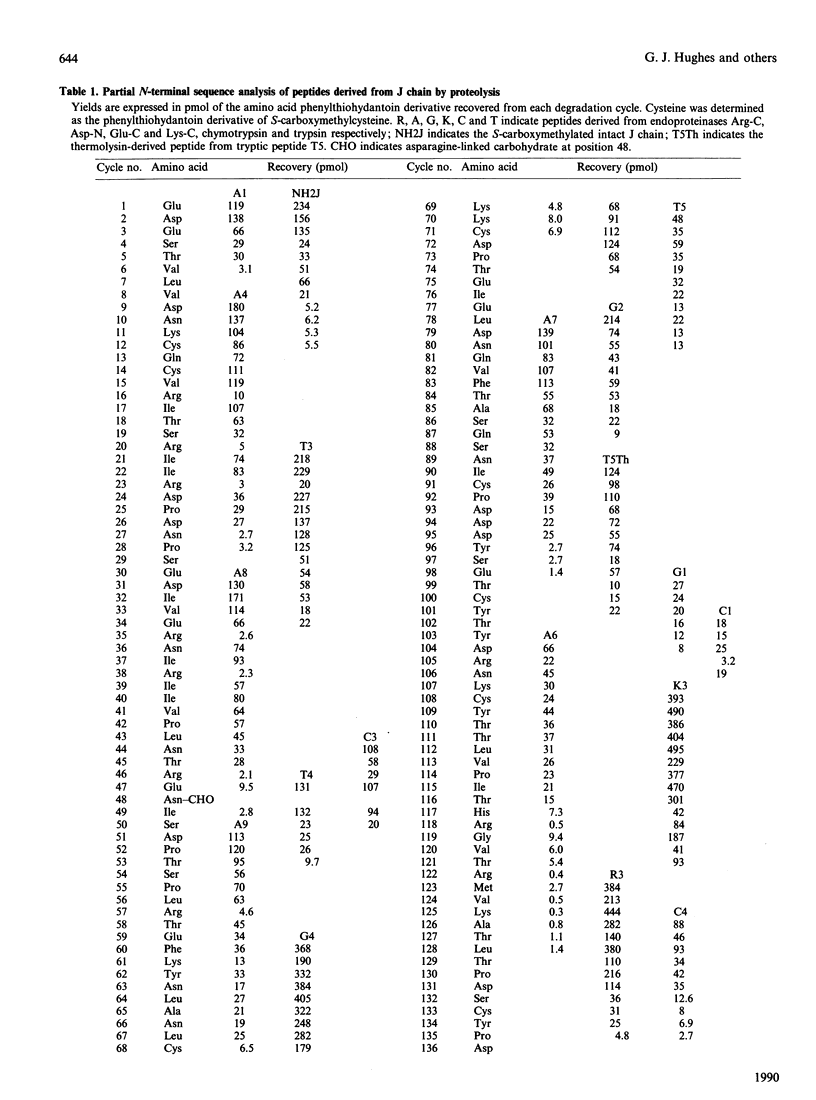
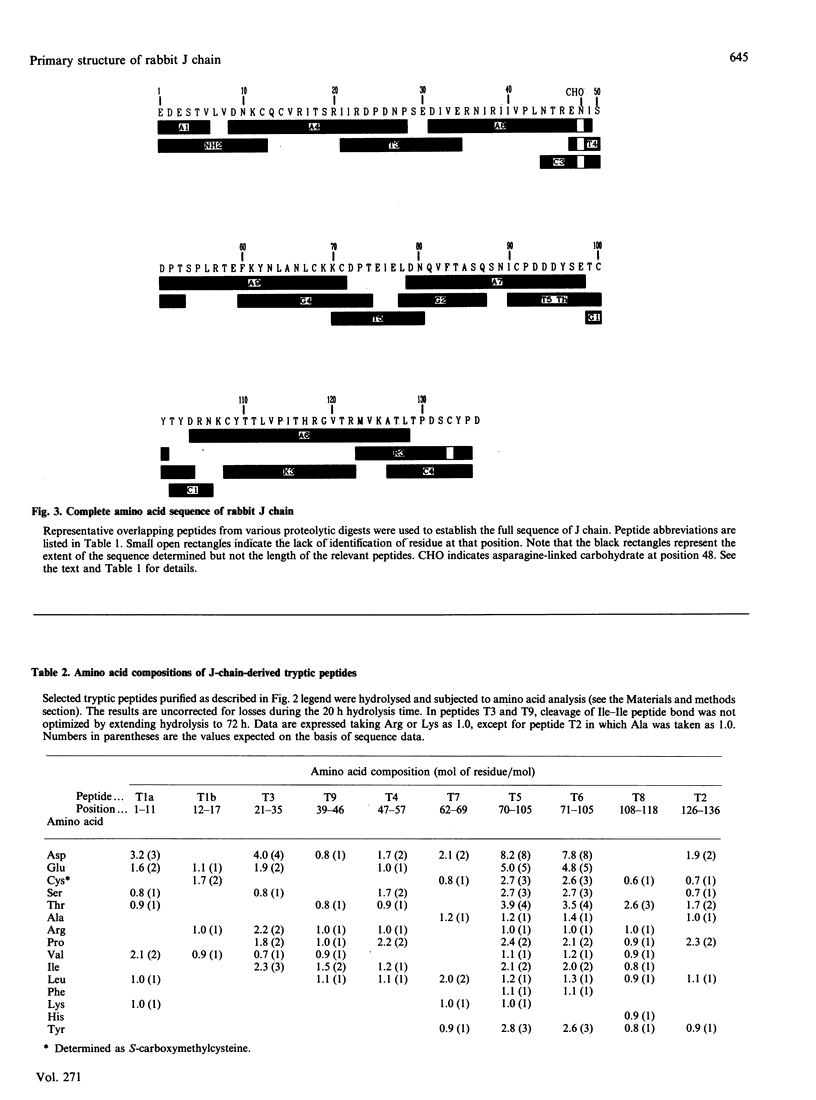
The primary structure of rabbit J chain, which occurs covalently bound to secretory IgA, was determined. J chain was isolated in its S-carboxymethylated form, in one step, by SDS/PAGE followed by electro-elution; 5 nmol of protein (approx. 75 micrograms), in all, was necessary for the determination of the complete sequence by the 'shot-gun' microsquencing technique; with the use of several site-specific endoproteinases, the various digests of S-carboxymethylated J chain were separated by micro-bore reverse-phase h.p.l.c. and the partial N-terminal sequences of all peptides were analysed. From the sequence alignment, gaps were filled by further extensive sequencing of the relevant overlapping fragments isolated from selected digests. Rabbit J chain comprises 136 amino acid residues, out of which eight are conserved cysteine residues, and is more closely similar to the human sequence (73.5% identify) than to the mouse sequence (68% identity). There is one unique glycosylation site at asparagine-48.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandtzaeg P. Blocking effect of J chain and J-chain antibody on the binding of secretory component to human IgA and IgM. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(8):837–842. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb03725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Prydz H. Direct evidence for an integrated function of J chain and secretory component in epithelial transport of immunoglobulins. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):71–73. doi: 10.1038/311071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Role of J chain and secretory component in receptor-mediated glandular and hepatic transport of immunoglobulins in man. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(2):111–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann G. M., Zaritsky A., Koshland M. E. Primary structure of the immunoglobulin J chain from the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6656–6660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo A., Neuberger M. S. Polymeric immunoglobulin M is secreted by transfectants of non-lymphoid cells in the absence of immunoglobulin J chain. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2753–2758. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02569.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. C., Roux K. H., Shulman M. J. On the structure of polymeric IgM. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jul;18(7):1001–1008. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. C., Shulman M. J. IgM--molecular requirements for its assembly and function. Immunol Today. 1989 Apr;10(4):118–128. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90244-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzandu J. K., Johnson J. F., Wise G. E. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel electrophoresis: staining of polypeptides using heavy metal salts. Anal Biochem. 1988 Oct;174(1):157–167. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiffert H., Quentin E., Decker J., Hillemeir S., Hufschmidt M., Klingmüller D., Weber M. H., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstruktur der menschlichen freien Sekretkomponente und die Anordnung der Disulfidbrücken. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1984 Dec;365(12):1489–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott B. W., Jr, Steiner L. A. Amino- and carboxy-terminal sequence of mouse J chain and analysis of tryptic peptides. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2968–2974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonck C., Frutiger S., Hughes G. J. Solvent system for the rapid identification of phenylthiohydantoin derivatives of amino acids by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1986 Dec 5;370(2):339–343. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)94705-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frutiger S., Hughes G. J., Hanly W. C., Kingzette M., Jaton J. C. The amino-terminal domain of rabbit secretory component is responsible for noncovalent binding to immunoglobulin A dimers. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16673–16681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pardo A., Lamm M. E., Plaut A. G., Frangione B. J chain is covalently bound to both monomer subunits in human secretory IgA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11734–11738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman J. J. Fluorescent labeling of cysteinyl residues to facilitate electrophoretic isolation of proteins suitable for amino-terminal sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1987 Feb 1;160(2):376–387. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G. J., Frutiger S., Fonck C. Quantitative high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of Dabsyl-amino acids within 14 min. J Chromatogr. 1987 Feb 27;389(1):327–333. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)94443-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hewick R. M., Dreyer W. J., Hood L. E. High-sensitivity sequencing with a gas-phase sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:399–413. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C., Frutiger S., Hughes G. J. Recent studies of the interaction of rabbit dimeric IgA with its polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1988 Jan-Feb;139(1):21–40. doi: 10.1016/0769-2625(88)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji H., Parkhouse R. M. Intracellular J chain in mouse plasmacytomas secreting IgA, IgM and IgG. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):45–47. doi: 10.1038/249045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konigsberg W. H., Henderson L. Removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate from proteins by ion-pair extraction. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:254–259. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland M. E. The coming of age of the immunoglobulin J chain. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:425–453. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kownatzki E., Drescher M. Antigen binding and complement fixing activity of IgM molecules reassociated in the presence and absence of J chains. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Dec;15(4):557–563. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuuchi L., Cann G. M., Koshland M. E. Immunoglobulin J chain gene from the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):456–460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Korsmeyer S. J. Human J chain gene. Structure and expression in B lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):832–849. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez E., Frangione B., Franklin E. C. Structure of immunoglobulin A. Amino acid sequence of cysteine-containing peptides from the J chain. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 13;12(6):1119–1124. doi: 10.1021/bi00730a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., McGhee J. R. Immunoglobulin A (IgA): molecular and cellular interactions involved in IgA biosynthesis and immune response. Adv Immunol. 1987;40:153–245. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., Schrohenloher R. E. Site of attachment of J chain to human immunoglobulin M. Nature. 1974 Jun 14;249(458):650–652. doi: 10.1038/249650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikoryak C. A., Margolies M. N., Steiner L. A. J chain in Rana catesbeiana high molecular weight Ig. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4279–4285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole J. E., Bhown A. S., Bennett J. C. Primary structure of human J chain: alignment of peptides from chemical and enzymatic hydrolyses. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 9;16(16):3507–3513. doi: 10.1021/bi00635a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., Friedlander M., Blobel G. The receptor for transepithelial transport of IgA and IgM contains multiple immunoglobulin-like domains. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):37–43. doi: 10.1038/308037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., Simister N. E. Transcytosis. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):389–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný J., Auffray C. A program for prediction of protein secondary structure from nucleotide sequence data: application to histocompatibility antigens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):243–255. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner L. A. Immunoglobulin disulfide bridges: theme and variations. Biosci Rep. 1985 Oct-Nov;5(10-11):973–989. doi: 10.1007/BF01119910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zikan J., Novotny J., Trapane T. L., Koshland M. E., Urry D. W., Bennett J. C., Mestecky J. Secondary structure of the immunoglobulin J chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5905–5909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


