Abstract
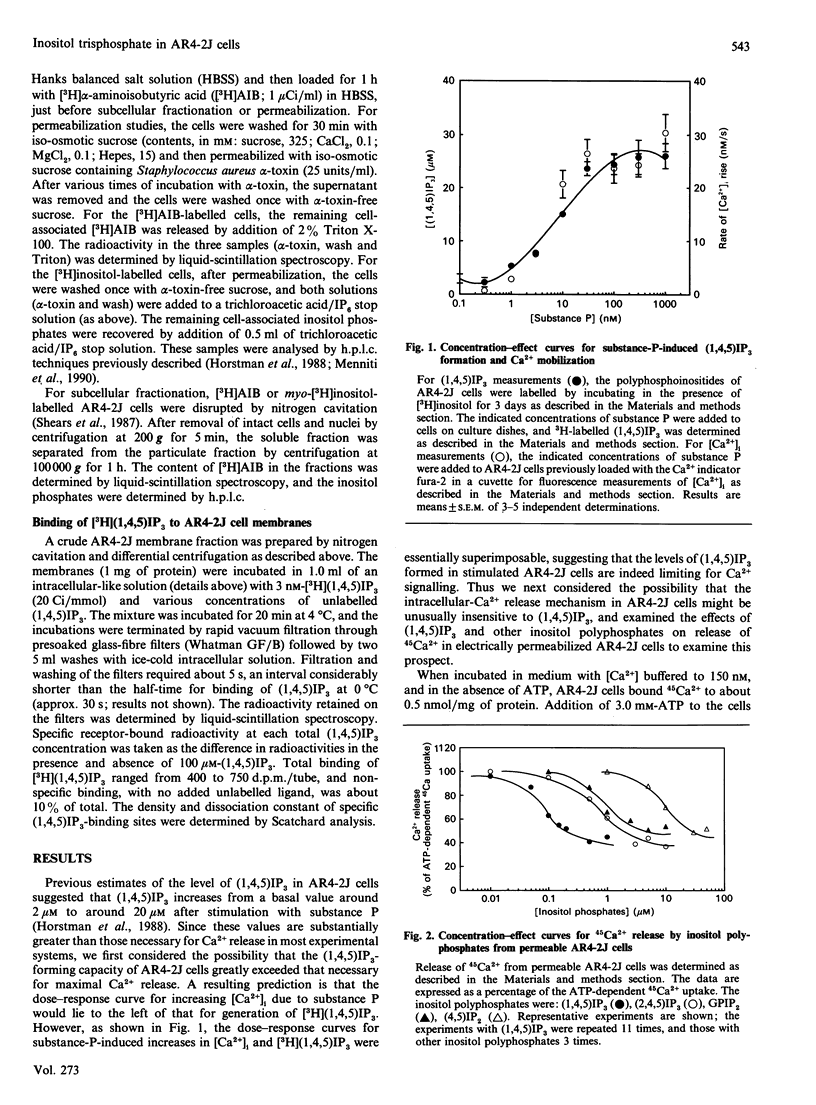
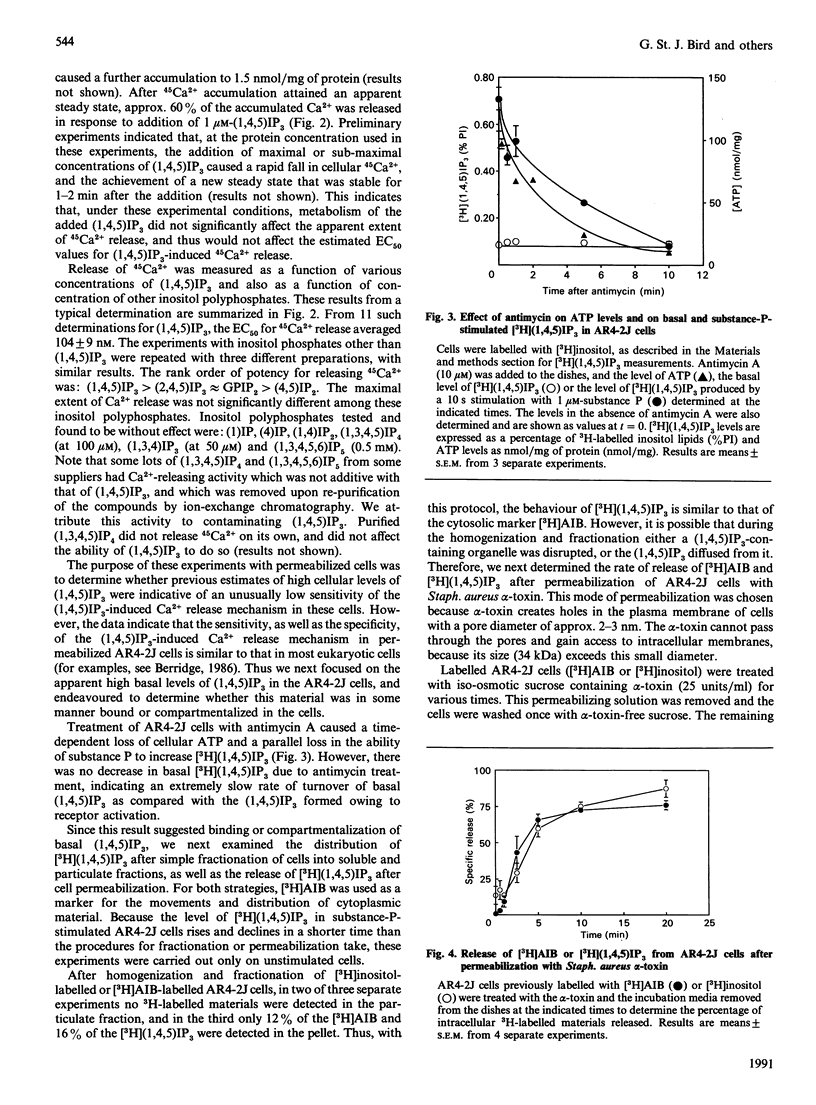
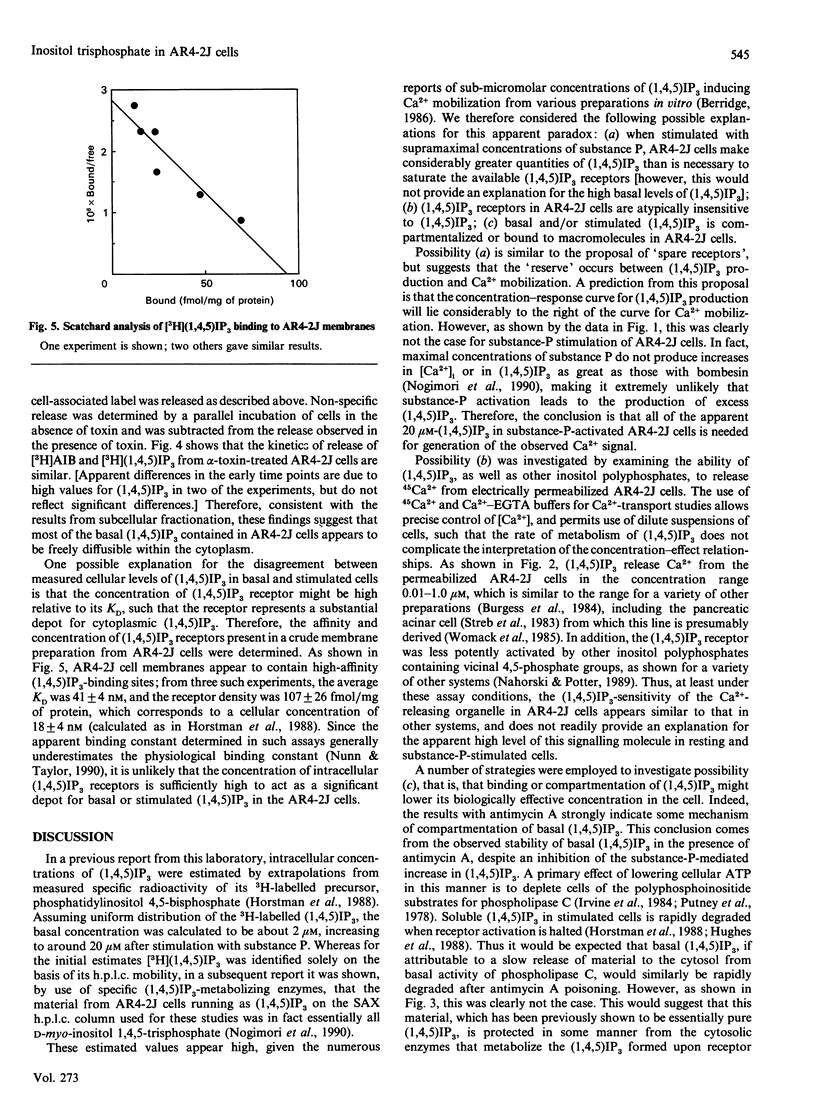
Various experimental strategies were employed in an effort to explain the previously reported [Horstman, Takemura & Putney (1988) J. Biol. Chem. 263, 15297-15303] paradoxically high levels of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate [(1,4,5)IP3] in resting and substance-P-stimulated AR4-2J cells. The concentration-effect curves for substance-P-induced [3H](1,4,5)IP3 formation in [3H]inositol-labelled cells and substance-P-induced increase in intracellular [Ca2+] were essentially superimposable, suggesting that formation of (1,4,5)IP3 is limiting for cellular Ca2+ mobilization. In electrically permeabilized AR4-2J cells, (1,4,5)IP3 and other inositol polyphosphates stimulated Ca2+ release with potencies similar to those reported for other cell types, including the parent pancreatic acinar cell. Compartmentalization of basal (1,4,5)IP3 was suggested by the fact that this material was stable in the presence of antimycin A, although this toxin completely blocked agonist stimulation of phospholipase C. However, subcellular fractionation as well as permeabilization of the cells with Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin failed to provide evidence for binding or sequestration of [3H](1,4,5)IP3 in AR4-2J cells. The density of (1,4,5)IP3 receptors in AR4-2J cells was not sufficiently large to impose non-linearity in the relationship between (1,4,5)IP3 concentration and (1,4,5)IP3-induced Ca2+ release. Thus the apparent high concentrations of (1,4,5)IP3 in resting and stimulated AR4-2J cells are not indicative of atypically low sensitivity or high concentration of (1,4,5)IP3 receptors, nor is there evidence for compartmentalization of (1,4,5)IP3 outside of the cytoplasm in these cells. It is possible that soluble factors in the cytoplasm of AR4-2J cells regulate the free concentration of (1,4,5)IP3 or the sensitivity of receptors to (1,4,5)IP3.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford P. G., Rubin R. P. Quantitative changes in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in chemoattractant-stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15644–15647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Mourey R. J., Snyder S. H. A simple, sensitive, and specific radioreceptor assay for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in biological tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):976–982. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92204-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Actions of inositol phosphates on Ca2+ pools in guinea-pig hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):741–746. doi: 10.1042/bj2240741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., McKinney J. S., Fabiato A., Leslie B. A., Putney J. W., Jr Calcium pools in saponin-permeabilized guinea pig hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15336–15345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Batty I. H., Nahorski S. R. Mass measurements of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in rat cerebral cortex slices using a radioreceptor assay: effects of neurotransmitters and depolarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):684–691. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Quantitative aspects of hormone-receptor interactions of high affinity. Effect of receptor concentration and measurement of dissociation constants of labeled and unlabeled hormones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 6;406(2):294–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstman D. A., Takemura H., Putney J. W., Jr Formation and metabolism of [3H]inositol phosphates in AR42J pancreatoma cells. Substance P-induced Ca2+ mobilization in the apparent absence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15297–15303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. R., Takemura H., Putney J. W., Jr Kinetics of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol cyclic 1:2,4,5-trisphosphate metabolism in intact rat parotid acinar cells. Relationship to calcium signalling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10314–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Kobayashi S., Horiuti K., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Receptor-coupled, permeabilized smooth muscle. Role of the phosphatidylinositol cascade, G-proteins, and modulation of the contractile response to Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5339–5342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. G., Nahorski S. R. Muscarinic-receptor-mediated changes in intracellular Ca2+ and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mass in a human neuroblastoma cell line, SH-SY5Y. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):555–562. doi: 10.1042/bj2650555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menniti F. S., Oliver K. G., Nogimori K., Obie J. F., Shears S. B., Putney J. W., Jr Origins of myo-inositol tetrakisphosphates in agonist-stimulated rat pancreatoma cells. Stimulation by bombesin of myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate breakdown to myo-inositol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11167–11176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahorski S. R., Potter B. V. Molecular recognition of inositol polyphosphates by intracellular receptors and metabolic enzymes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogimori K., Menniti F. S., Putney J. W., Jr Identification in extracts from AR4-2J cells of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate by its susceptibility to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase and 5-phosphatase. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):195–200. doi: 10.1042/bj2690195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn D. L., Taylor C. W. Liver inositol, 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding sites are the Ca2(+)-mobilizing receptors. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):227–232. doi: 10.1042/bj2700227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, VanDeWalle C. M., Leslie B. A. Receptor control of calcium influx in parotid acinar cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;14(6):1046–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shayman J. A., Kirkwood M. T. Bradykinin-stimulated changes in inositol phosphate mass in renal papillary collecting tubule cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 30;145(3):1119–1125. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B. Metabolism of the inositol phosphates produced upon receptor activation. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2600313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B., Parry J. B., Tang E. K., Irvine R. F., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Metabolism of D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate by rat liver, including the synthesis of a novel isomer of myo-inositol tetrakisphosphate. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 15;246(1):139–147. doi: 10.1042/bj2460139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spät A., Bradford P. G., McKinney J. S., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr A saturable receptor for 32P-inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate in hepatocytes and neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):514–516. doi: 10.1038/319514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Schulz I., Berridge M. J. Relationship between secretagogue-induced Ca2+ release and inositol polyphosphate production in permeabilized pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7309–7315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiya H., Putney J. W., Jr Substance P receptor desensitization requires receptor activation but not phospholipase C. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 1):C149–C154. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.2.C149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiya H., Tennes K. A., Putney J. W., Jr Homologous desensitization of substance-P-induced inositol polyphosphate formation in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):647–653. doi: 10.1042/bj2440647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarver A. P., King W. G., Rittenhouse S. E. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,2-cyclic 4,5-trisphosphate are minor components of total mass of inositol trisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17268–17271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood R. H., Greeley R., Glennon E. T., Menachery A. I., Braley L. M., Williams G. H. Mass determination of polyphosphoinositides and inositol triphosphate in rat adrenal glomerulosa cells with a microspectrophotometric method. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):211–219. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womack M. D., Hanley M. R., Jessell T. M. Functional substance P receptors on a rat pancreatic acinar cell line. J Neurosci. 1985 Dec;5(12):3370–3378. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-12-03370.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


