Abstract
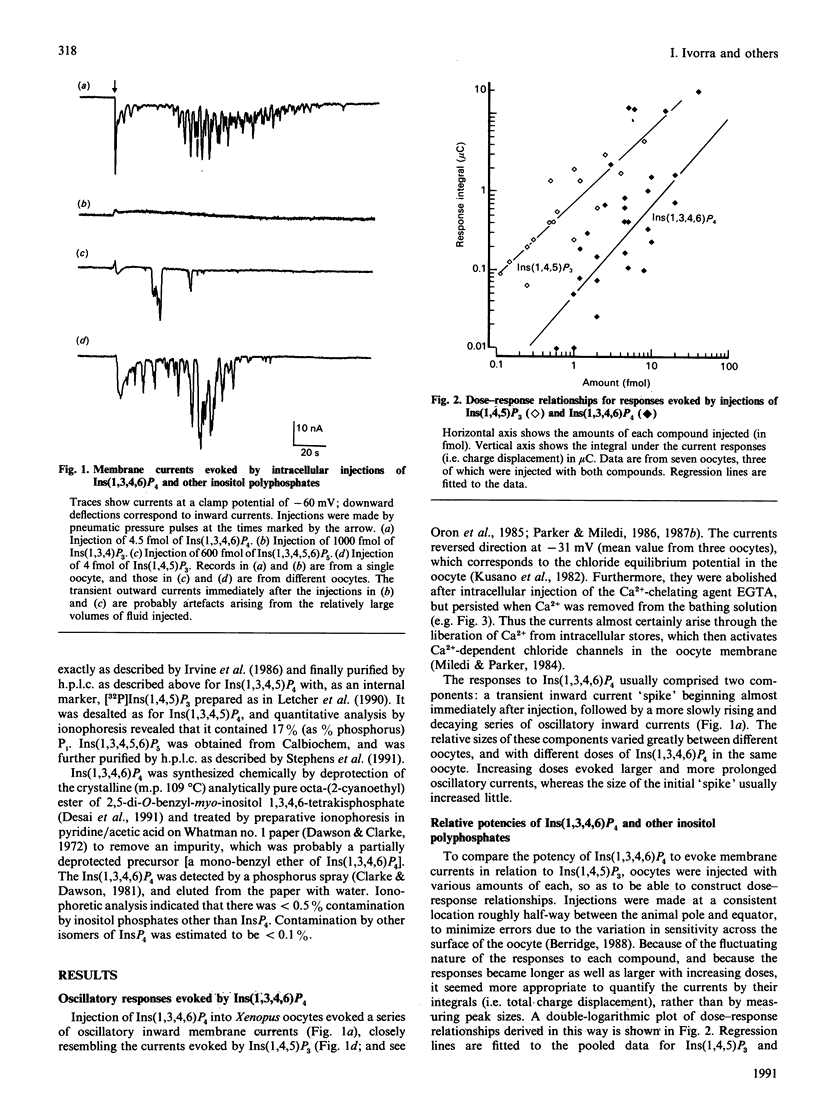
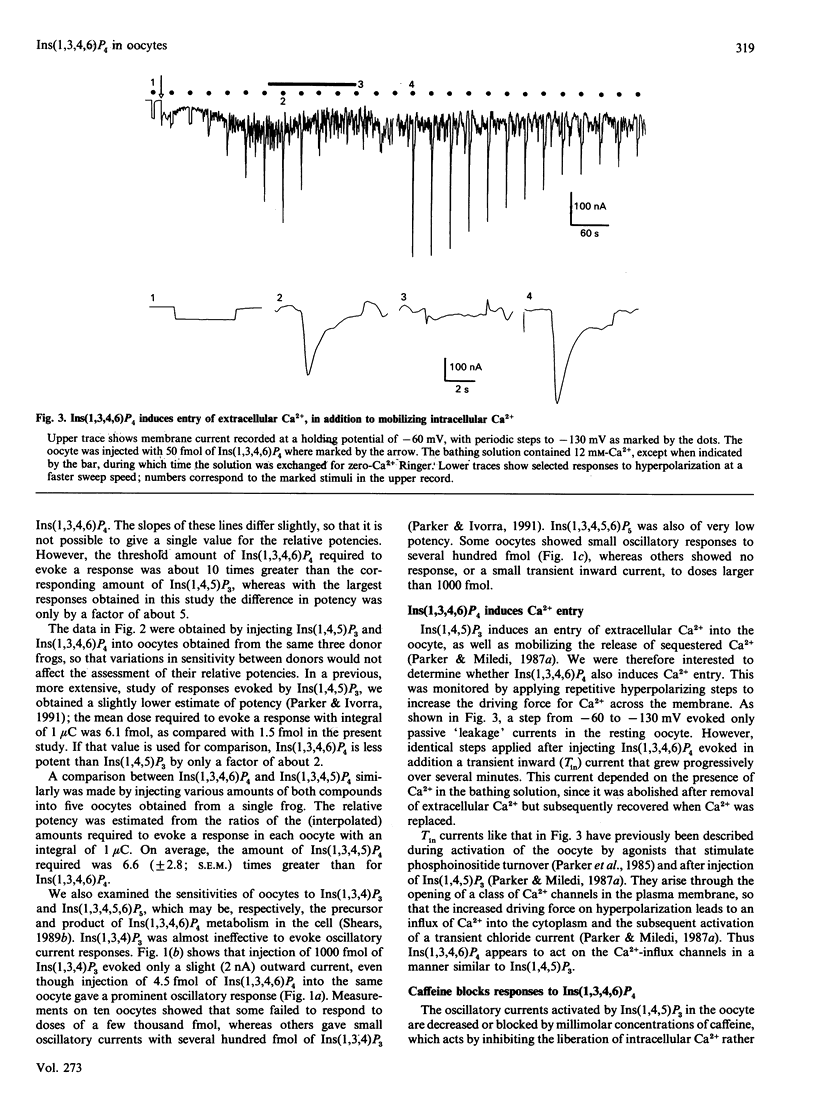
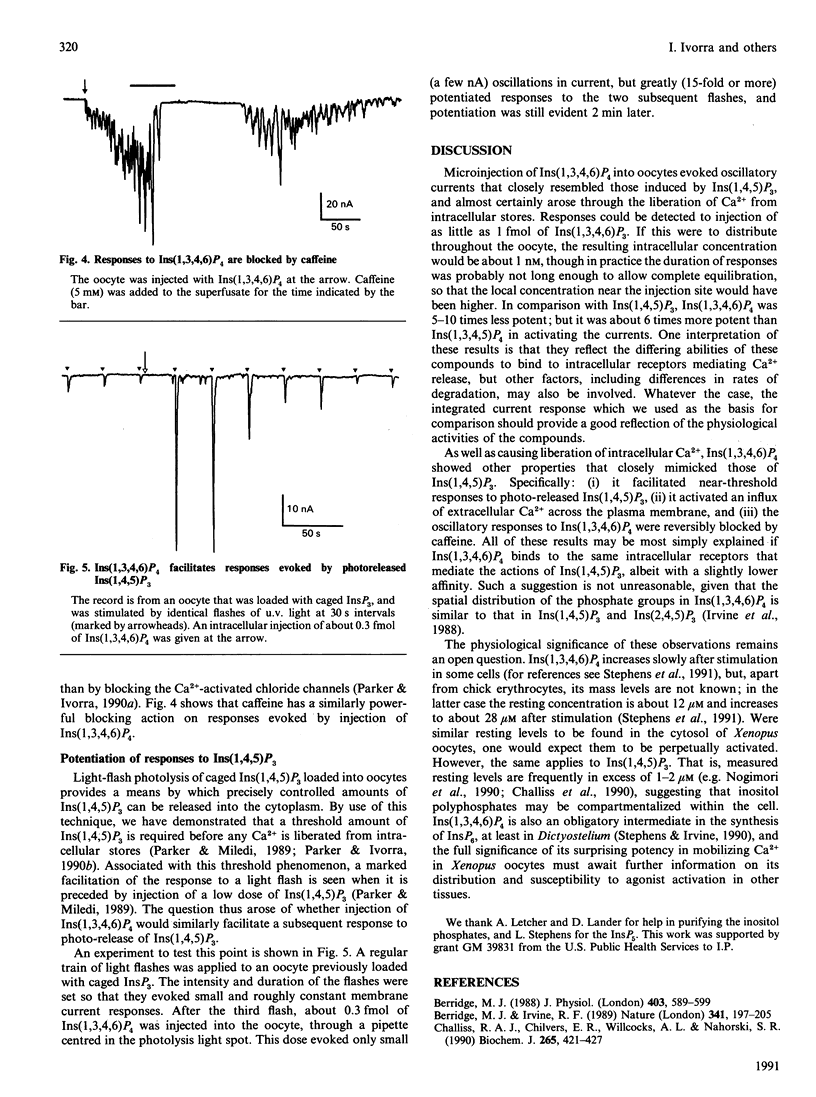
Injection of Ins(1,3,4,6)P4 into Xenopus oocytes evoked Ca2(+)-dependent membrane currents with a potency 5-10 times less than Ins(1,4,5)P3, whereas Ins(1,3,4)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5 were almost ineffective. Responses to Ins(1,3,4,6)P4 arose through liberation of intracellular Ca2+ and through entry of extracellular Ca2+. These results, together with the observation that Ins(1,3,4,6)P4 facilitated responses to Ins(1,4,5)P3, suggests that both of these compounds may act on the same intracellular receptors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate-induced membrane potential oscillations in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:589–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Chilvers E. R., Willcocks A. L., Nahorski S. R. Heterogeneity of [3H]inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate binding sites in adrenal-cortical membranes. Characterization and validation of a radioreceptor assay. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):421–427. doi: 10.1042/bj2650421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke N. G., Dawson R. M. Alkaline O leads to N-transacylation. A new method for the quantitative deacylation of phospholipids. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):301–306. doi: 10.1042/bj1950301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Clarke N. D-myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate 2-phosphohydrolase. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):113–118. doi: 10.1042/bj1270113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Berridge M. J. Specificity of inositol phosphate-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization from Swiss-mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):301–304. doi: 10.1042/bj2400301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M., Pollock W. K., Smith P. M., Wreggett K. A. Inositol phosphates: proliferation, metabolism and function. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):281–298. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Miledi R., Stinnakre J. Cholinergic and catecholaminergic receptors in the Xenopus oocyte membrane. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:143–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I. Chloride current induced by injection of calcium into Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:173–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogimori K., Menniti F. S., Putney J. W., Jr Identification in extracts from AR4-2J cells of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate by its susceptibility to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase and 5-phosphatase. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):195–200. doi: 10.1042/bj2690195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oron Y., Dascal N., Nadler E., Lupu M. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mimics muscarinic response in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):141–143. doi: 10.1038/313141a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Gundersen C. B., Miledi R. A transient inward current elicited by hyperpolarization during serotonin activation in Xenopus oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jan 22;223(1232):279–292. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Miledi R. Changes in intracellular calcium and in membrane currents evoked by injection of inositol trisphosphate into Xenopus oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Aug 22;228(1252):307–315. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1986.0057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Miledi R. Injection of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate into Xenopus oocytes generates a chloride current dependent upon intracellular calcium. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Oct 22;232(1266):59–70. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1987.0061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Miledi R. Nonlinearity and facilitation in phosphoinositide signaling studied by the use of caged inositol trisphosphate in Xenopus oocytes. J Neurosci. 1989 Nov;9(11):4068–4077. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-11-04068.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rana R. S., Hokin L. E. Role of phosphoinositides in transmembrane signaling. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jan;70(1):115–164. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert U. B., Agranoff B. W. Isolation and separation of inositol phosphates from hydrolysates of rat tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 1;98(3):574–581. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B. Inositol phosphate metabolism: further problems and some solutions. Cell Signal. 1989;1(2):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B. The pathway of myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate phosphorylation in liver. Identification of myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 6-kinase, myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5-kinase, and myo-inositol 1,3,4,6-tetrakisphosphate 5-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19879–19886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder P. M., Krause K. H., Welsh M. J. Inositol trisphosphate isomers, but not inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate, induce calcium influx in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11048–11051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Downes C. P. Product-precursor relationships amongst inositol polyphosphates. Incorporation of [32P]Pi into myo-inositol 1,3,4,6-tetrakisphosphate, myo-inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate, myo-inositol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate and myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate in intact avian erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):435–452. doi: 10.1042/bj2650435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Irvine R. F. Stepwise phosphorylation of myo-inositol leading to myo-inositol hexakisphosphate in Dictyostelium. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):580–583. doi: 10.1038/346580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stith B. J., Proctor W. R. Microinjection of inositol 1,2-(cyclic)-4,5-trisphosphate, inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate, and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate into intact Xenopus oocytes can induce membrane currents independent of extracellular calcium. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Jul;40(3):321–330. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240400308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


