Abstract
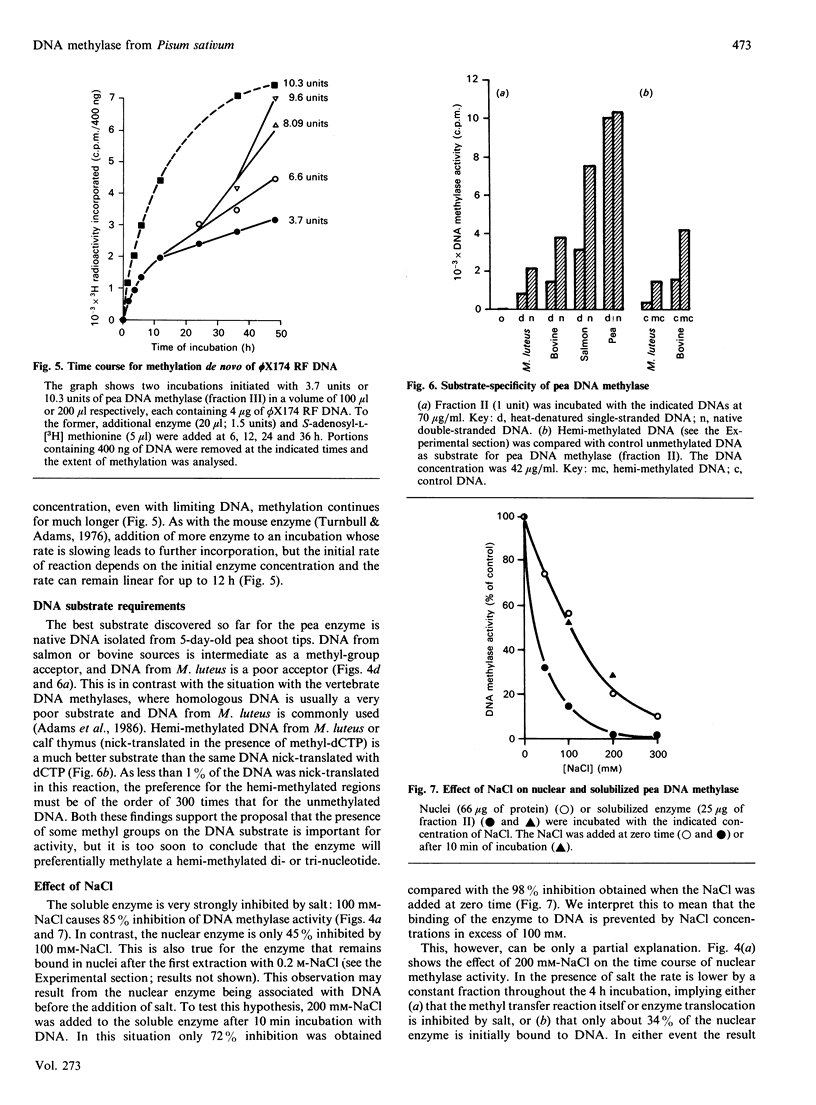
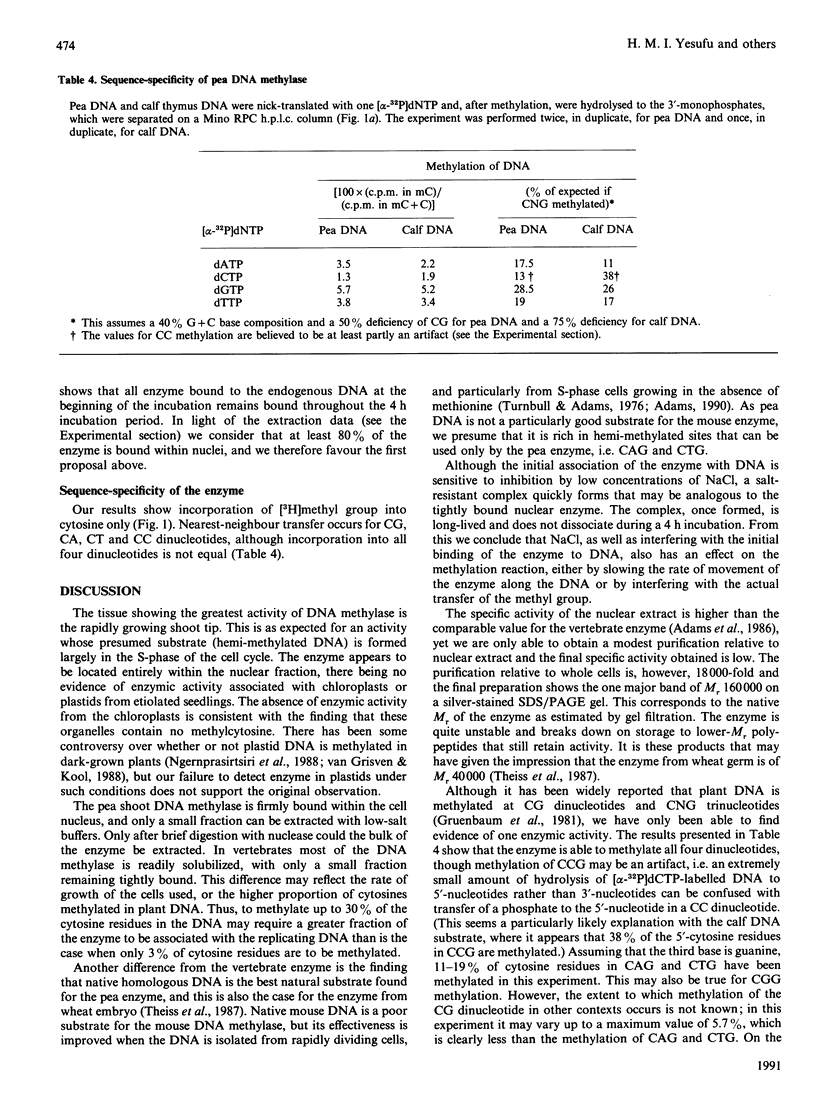
DNA methylase activity was detected in nuclei from pea shoots. The enzyme can only be extracted by low-salt treatment if the nuclei are pretreated with micrococcal nuclease. Only a single enzyme was detected, and it was purified to a specific activity of 1620 units/mg of protein. It has an Mr of 160,000 on gel filtration and SDS/PAGE. Pea DNA methylase methylates cytosine in all four dinucleotides, and this is interpreted to show that it acts on CNG trinucleotides. Although it shows a strong preference for hemi-methylated double-stranded DNA, it is also capable of methylation de novo. Homologous DNA is the best natural substrate. In vitro the enzyme interacts with DNA to form a salt-resistant complex with DNA that is stable for at least 4 h.
Full text
PDF
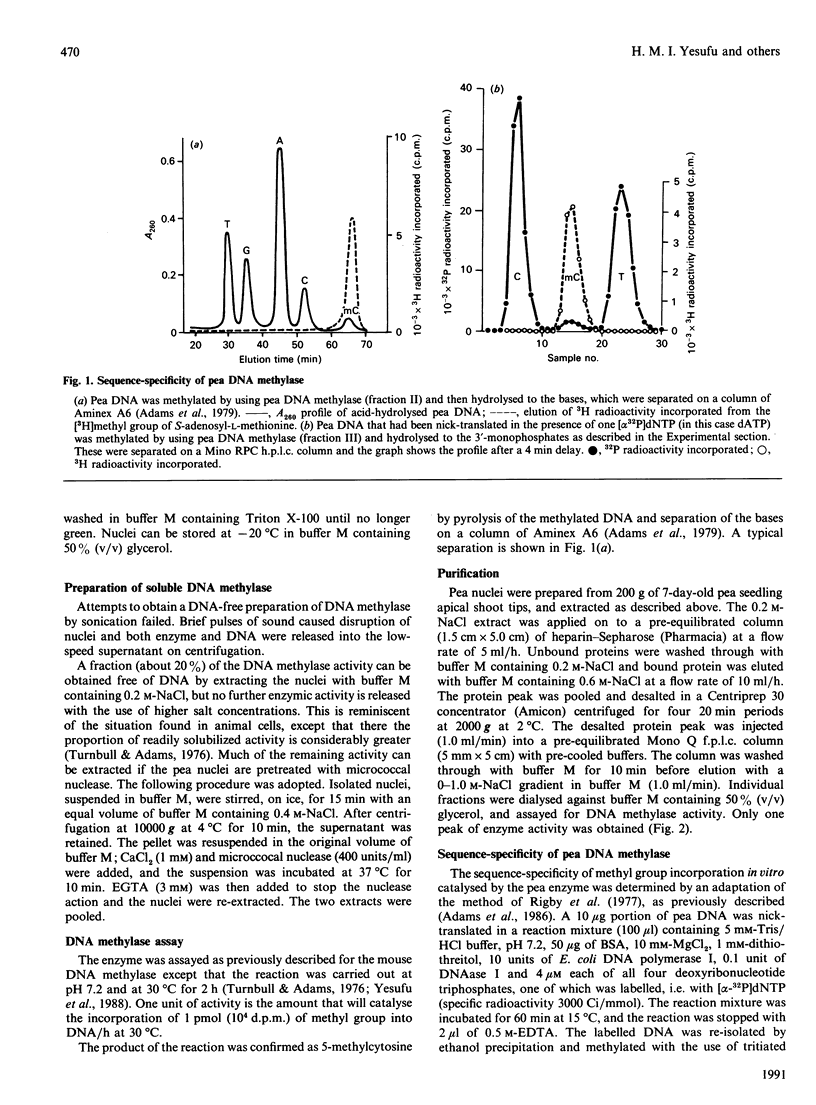
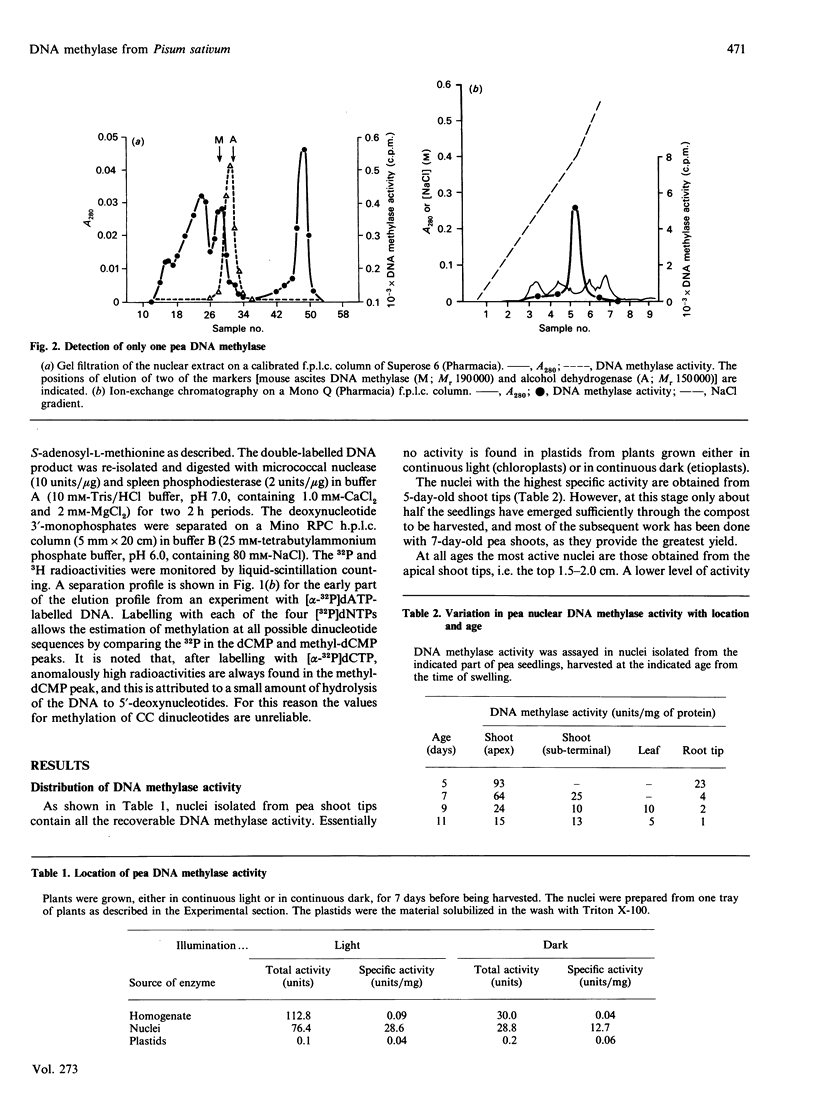
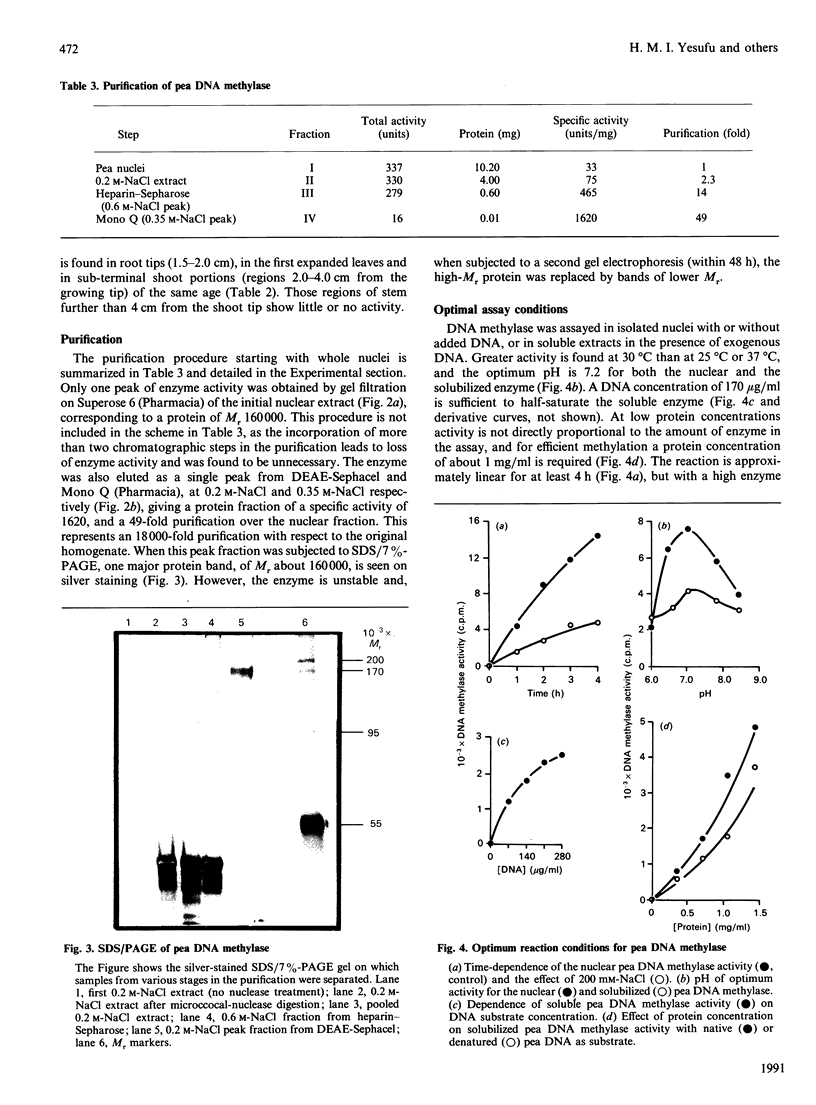

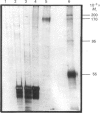
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. L. DNA methylation. The effect of minor bases on DNA-protein interactions. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):309–320. doi: 10.1042/bj2650309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams R. L., Davis T., Rinaldi A., Eason R. CpG deficiency, dinucleotide distributions and nucleosome positioning. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 15;165(1):107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams R. L., Gardiner K., Rinaldi A., Bryans M., McGarvey M., Burdon R. H. Mouse ascites DNA methylase: characterisation of size, proteolytic breakdown and nucleotide recognition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 16;868(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(86)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams R. L., McKay E. L., Craig L. M., Burdon R. H. Methylation of mosquito DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 20;563(1):72–81. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antequera F., Bird A. P. Unmethylated CpG islands associated with genes in higher plant DNA. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2295–2299. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03072.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestor T., Laudano A., Mattaliano R., Ingram V. Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding DNA methyltransferase of mouse cells. The carboxyl-terminal domain of the mammalian enzymes is related to bacterial restriction methyltransferases. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):971–983. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1499–1504. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen P. L., Grant D. M., Swinton D., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Extensive methylation of chloroplast DNA by a nuclear gene mutation does not affect chloroplast gene transmission in chlamydomonas. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudraa M., Perrin P. CpG and TpA frequencies in the plant system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5729–5737. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng T. Y., Chiang K. S. The persistence of maternal inheritance in Chlamydomonas despite hypomethylation of chloroplast DNA induced by inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3438–3442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenbaum Y., Naveh-Many T., Cedar H., Razin A. Sequence specificity of methylation in higher plant DNA. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):860–862. doi: 10.1038/292860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalousek F., Morris N. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid methylase activity in pea seedlings. Science. 1969 May 9;164(3880):721–722. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3880.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp J. D., Sutton D. W. A chemical and physical method for determining the complete base composition of plant DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 4;425(2):148–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naveh-Many T., Cedar H. Topographical distribution of 5-methylcytosine in animal and plant DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):758–762. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngernprasirtsiri J., Kobayashi H., Akazawa T. DNA methylation as a mechanism of transcriptional regulation in nonphotosynthetic plastids in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4750–4754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Grünwald S., Palitti F., Kaul S., Boehm T. L., Hirth H. P., Drahovsky D. Purification and characterization of mammalian DNA methyltransferases by use of monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13787–13793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer H. D., Sager R. Methylation of chloroplast DNAs in the life cycle of Chlamydomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santi D. V., Garrett C. E., Barr P. J. On the mechanism of inhibition of DNA-cytosine methyltransferases by cytosine analogs. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theiss G., Schleicher R., Schimpff-Weiland G., Follmann H. DNA methylation in wheat. Purification and properties of DNA methyltransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 17;167(1):89–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull J. F., Adams R. L. DNA methylase: purification from ascites cells and the effect of various DNA substrates on its activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Mar;3(3):677–695. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner I., Capesius I. Determination of 5-methylcytosine from plant DNA by high-performance liquid chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 26;654(1):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]