Abstract
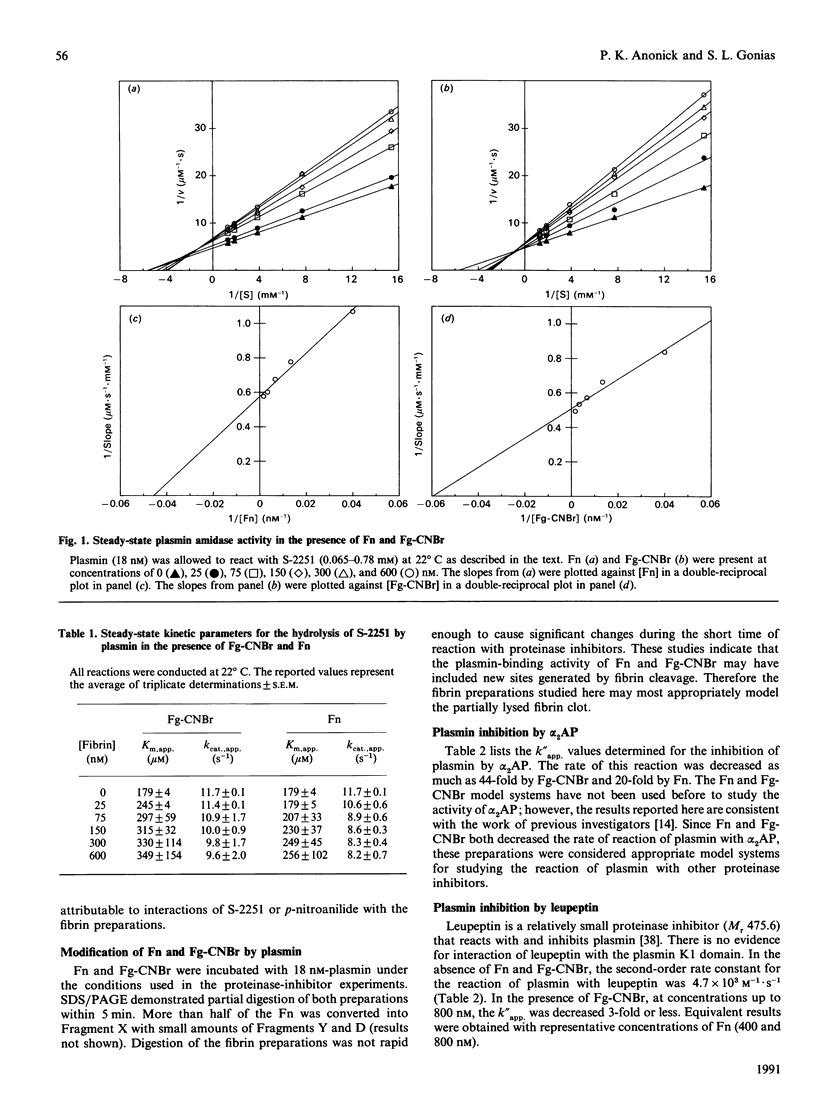
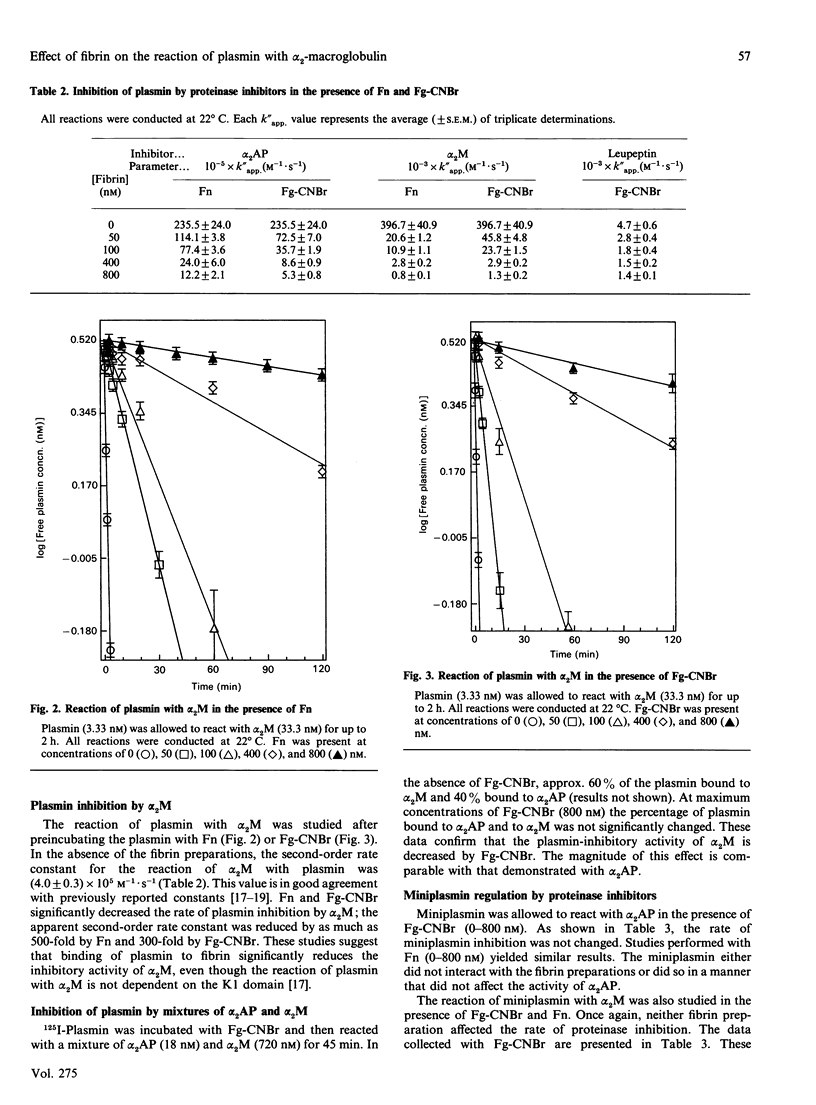
The kinetics of plasmin inhibition by alpha 2-antiplasmin (alpha 2AP), alpha 2-macroglobulin (alpha 2M) and leupeptin were studied in the presence of fibrin monomer (Fn) and CNBr fragments of fibrinogen (Fg-CNBr). Active plasmin was detected in continuous and discontinuous assays using the chromogenic substrate D-Val-L-Leu-L-Lys p-nitroanilide hydrochloride (S-2251). The two 'fibrin-like' preparations functioned as hyperbolic mixed-type inhibitors of S-2251 hydrolysis. The dissociation constants (KF) for the binding of plasmin to Fn and Fg-CNBr were 22 nM and 17 nM respectively. Fn and Fg-CNBr inhibited the reaction of plasmin with alpha 2AP: the extent of inhibition depended on the fibrin concentration. In the presence of 800 nM-Fn or 800 nM-Fg-CNBr, the experimental second-order rate constant (K"app.) was decreased from 2.4 x 10(7) M-1.s-1 to 1.2 x 10(6) and 5.3 x 10(5) M-1.s-1 respectively. The effect of Fn and Fg-CNBr on the rate of plasmin inhibition by alpha 2M was even greater. The k"app. value was decreased from 4.0 x 10(5) M-1.s-1 to 8.0 x 10(2) and 1.3 x 10(3) M-1.s-1 in the presence of 800 nM-Fn and -Fg-CNBr respectively. By contrast, the fibrin preparations caused only a small change in the rate of plasmin inhibition by leupeptin. The maximum change in k"app. was 3-fold. All plasmin inhibition curves were linear, suggesting that free and fibrin-bound forms of plasmin remained in equilibrium during the course of reaction with proteinase inhibitors. Fn and Fg-CNBr had no effect on the reaction of miniplasmin with S-2251, alpha 2AP or alpha 2M. When 125I-plasmin was incubated with Fg-CNBr and then allowed to react with a premixed solution of alpha 2AP and alpha 2M, the Fg-CNBr did not significantly change the percentage of plasmin bound to alpha 2AP. These experiments demonstrate that the reaction of plasmin with alpha 2M is inhibited by the non-covalent binding of plasmin to fibrin. We propose that plasmin bound to the surface of a clot is protected from inhibition by alpha 2M as well as by alpha 2AP.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anonick P. K., Wolf B., Gonias S. L. Regulation of plasmin, miniplasmin, and streptokinase-plasmin complex by alpha 2-antiplasmin, alpha 2-macroglobulin, and antithrombin III in the presence of heparin. Thromb Res. 1990 Aug 1;59(3):449–462. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90406-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Harpel P. C. Inhibitors of the fibrinolytic enzyme system. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Jan;10(1):24–41. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Moroi M., Tachiya K. Effects of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor on fibrin clot lysis. Its comparison with alpha2-macroglobulin. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Feb 28;39(1):22–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi T., Miyata S., Nanbo M., Kojima F., Matsuzaki M. Biological activities of leupeptins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Nov;22(11):558–568. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.22.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Blombäck M., Henschen A., Hessel B., Iwanaga S., Woods K. R. N-terminal disulphide knot of human fibrinogen. Nature. 1968 Apr 13;218(5137):130–134. doi: 10.1038/218130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho M., Fondaneche M. C., Burtin P. Limited proteolysis of tumor cells increases their plasmin-binding ability. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassels R., Fears R., Smith R. A. The interaction of streptokinase.plasminogen activator complex, tissue-type plasminogen activator, urokinase and their acylated derivatives with fibrin and cyanogen bromide digest of fibrinogen. Relationship to fibrinolytic potency in vitro. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):395–400. doi: 10.1042/bj2470395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen U. C-terminal lysine residues of fibrinogen fragments essential for binding to plasminogen. FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 11;182(1):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81150-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen U., Sottrup-Jensen L. Mechanism of alpha 2-macroglobulin-proteinase interactions. Studies with trypsin and plasmin. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6619–6626. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen U. The AH-site of plasminogen and two C-terminal fragments. A weak lysine-binding site preferring ligands not carrying a free carboxylate function. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):413–421. doi: 10.1042/bj2230413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen U. pH effects in plasmin-catalysed hydrolysis of alpha-N-benzoyl-L-arginine compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 26;397(2):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fears R. Binding of plasminogen activators to fibrin: characterization and pharmacological consequences. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 15;261(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2610313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fears R. Kinetic studies on the effect of heparin and fibrin on plasminogen activators. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):77–81. doi: 10.1042/bj2490077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Braud L. L., Geary W. A., VandenBerg S. R. Plasminogen binding to rat hepatocytes in primary culture and to thin slices of rat liver. Blood. 1989 Aug 1;74(2):729–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Figler N. L. Alpha 2-macroglobulin is the primary inhibitor of miniplasmin in vitro and in vivo in the mouse. Comparison with alpha 2-antiplasmin in simultaneous reaction experiments. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 15;255(2):725–730. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Figler N. L., Braud L. L. Regulation of streptokinase-human plasmin complex by the plasma proteinase inhibitors alpha 2-antiplasmin and alpha 2-macroglobulin is species specific and temperature dependent. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1658–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Pasqua J. J., Greenberg C., Pizzo S. V. Precipitation of fibrinogen, fibrinogen degradation products and fibrin monomer by histone H3. Thromb Res. 1985 Jul 1;39(1):97–116. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Pizzo S. V. Reaction of human alpha 2-macroglobulin half-molecules with plasmin as a probe of protease binding site structure. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 11;22(21):4933–4940. doi: 10.1021/bi00290a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Hamel N. M. Identification and characterization of human endothelial cell membrane binding sites for tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2908–2916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Harpel P. C., Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L. Binding of plasminogen to cultured human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11656–11662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Sullivan R., Chang T. S. Binding and activation of plasminogen on immobilized immunoglobulin G. Identification of the plasmin-derived Fab as the plasminogen-binding fragment. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):616–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoylaerts M., Rijken D. C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2912–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imber M. J., Pizzo S. V. Clearance and binding of two electrophoretic "fast" forms of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8134–8139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen B. S., Silverstein R. L., Leung L. L., Harpel P. C., Nachman R. L. Binding of plasminogen to extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10765–10771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent P., Bieth J. G. Kinetics of the inhibition of free and elastin-bound human pancreatic elastase by alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor and alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 23;994(3):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Interaction of plasminogen activators and inhibitors with plasminogen and fibrin. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1982 Jan;8(1):2–10. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan T. Electrophoresis buffers for polyacrylamide gels at various pH. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):94–99. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Dahlberg C. M., Levin E. G., Plow E. F. Gangliosides interact directly with plasminogen and urokinase and may mediate binding of these fibrinolytic components to cells. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9337–9343. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannell R., Black J., Gurewich V. Complementary modes of action of tissue-type plasminogen activator and pro-urokinase by which their synergistic effect on clot lysis may be explained. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):853–859. doi: 10.1172/JCI113394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Saksela O., Vartio T., Vaheri A., Nielsen L. S., Zeuthen J. Plasminogen and tissue-type plasminogen activator bind to immobilized fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12302–12307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Morita T., Iwanaga S. Identification of the plasminogen-binding site of human alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor. J Biochem. 1986 Jun;99(6):1699–1705. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The effect of fibrin-stabilizing factor on the subunit structure of human fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1506–1513. doi: 10.1172/JCI106636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R. L., Leung L. L., Harpel P. C., Nachman R. L. Complex formation of platelet thrombospondin with plasminogen. Modulation of activation by tissue activator. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1625–1633. doi: 10.1172/JCI111578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R. L., Leung L. L., Harpel P. C., Nachman R. L. Platelet thrombospondin forms a trimolecular complex with plasminogen and histidine-rich glycoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):2065–2073. doi: 10.1172/JCI111926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner J. P., Migliorini M., Strickland D. K. Characterization of the reaction of plasmin with alpha 2-macroglobulin: effect of antifibrinolytic agents. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8487–8495. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsen S., Clemmensen I., Sottrup-Jensen L., Magnusson S. Adsorption to fibrin of native fragments of known primary structure from human plasminogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 29;668(3):377–387. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B. Affinity-chromatographic purification of human alpha 2-antiplasmin. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):229–232. doi: 10.1042/bj1910229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Boman L., Collen D. On the kinetics of the reaction between human antiplasmin and a low-molecular-weight form of plasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 1;87(1):143–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. On the kinetics of the reaction between human antiplasmin and plasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):573–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. On the specific interaction between the lysine-binding sites in plasmin and complementary sites in alpha2-antiplasmin and in fibrinogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 25;579(1):142–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Serrano V. S., Urano T., Gaffney P. J., Castellino F. J. Influence of various structural domains of fibrinogen and fibrin on the potentiation of plasminogen activation by recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. J Protein Chem. 1989 Feb;8(1):61–77. doi: 10.1007/BF01025079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


