Abstract
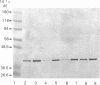
1. Rats (4 weeks old) were made hypothyroid by treatment with propylthiouracil together with a low-iodine diet for a further period of 4 weeks. Synaptosomal membranes were obtained from six anatomical regions of the brain. 2. The abundances in these membranes of the G-protein alpha-subunits Gi1 alpha, Gi2 alpha and Go alpha were measured by quantitative immunoblotting. 3. Hypothyroidism significantly increased the abundances of all three G-protein subunits in membranes from the cerebral cortex and the striatum. In the medulla oblongata and the hippocampus the abundances of Gi2 alpha and Go alpha were increased significantly. By contrast, in the cerebellum only Go alpha was increased, and in the hypothalamus only Gi2 alpha was increased. 4. It is suggested that this up-regulation of G-protein abundances may modify signalling pathways and may contribute to the functional changes that are observed in the central nervous system in hypothyroidism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L. G proteins in signal transduction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:675–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth R. F., Clark J. B. A rapid method for the preparation of relatively pure metabolically competent synaptosomes from rat brain. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):365–370. doi: 10.1042/bj1760365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Ionic channels and their regulation by G protein subunits. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:197–213. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A. G-proteins and potassium currents in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:215–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégin-Heick N. Quantification of the alpha and beta subunits of the transducing elements (Gs and Gi) of adenylate cyclase in adipocyte membranes from lean and obese (ob/ob) mice. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):83–89. doi: 10.1042/bj2680083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carty D. J., Padrell E., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Hildebrandt J. D., Iyengar R. Distinct guanine nucleotide binding and release properties of the three Gi proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6268–6273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chohan P., Carpenter C., Saggerson E. D. Changes in the anti-lipolytic action and binding to plasma membranes of N6-L-phenylisopropyladenosine in adipocytes from starved and hypothyroid rats. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):53–59. doi: 10.1042/bj2230053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Forda S. R., Scott R. H. Calcium-dependent currents in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurones are inhibited by an adenosine analogue. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:47–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C. G protein modulation of calcium currents in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:243–255. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dussault J. H., Ruel J. Thyroid hormones and brain development. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:321–334. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Dunwiddie T. V. How does adenosine inhibit transmitter release? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Apr;9(4):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler D., Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Houslay M. D. Abolition of the expression of inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi activity in diabetes. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):229–232. doi: 10.1038/327229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. S., Pottash A. L., Extein I. Hypothyroidism and depression. Evidence from complete thyroid function evaluation. JAMA. 1981 May 15;245(19):1919–1922. doi: 10.1001/jama.245.19.1919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Johnson J. L., Milligan G. Down-regulation of Gi sub-types by prolonged incubation of adipocytes with an A1 adenosine receptor agonist. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5206–5210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemon P. Malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (NADP) and alpha-glycerophosphate oxidase in the developing rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 25;151(3):681–683. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heninger R. W., Albright E. C. Alteration in tissue and serum concentrations of TSH, iodide, T4 and T3 induced by various dietary iodide levels. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Oct;150(1):137–141. doi: 10.3181/00379727-150-38990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W. H., Rudolph U., Sanford J., Bertrand P., Olate J., Nelson C., Moss L. G., Boyd A. E., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Molecular cloning of a novel splice variant of the alpha subunit of the mammalian Go protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11220–11226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail-Beigi F., Edelman I. S. The mechanism of the calorigenic action of thyroid hormone. Stimulation of Na plus + K plus-activated adenosinetriphosphatase activity. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jun;57(6):710–722. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.6.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby J. H., Mueller G., Wurtman R. J. Thyroid state and brain monoamine metabolism. Endocrinology. 1975 Nov;97(5):1332–1335. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-5-1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Goumaz M. O., Burger A. G. In vivo inhibition of the 5'-deiodinase type II in brain cortex and pituitary by reverse triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1986 Aug;119(2):762–770. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-2-762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. Y., Ang S. L., Bloch D. B., Bloch K. D., Kawahara Y., Tolman C., Lee R., Seidman J. G., Neer E. J. Identification of cDNA encoding an additional alpha subunit of a human GTP-binding protein: expression of three alpha i subtypes in human tissues and cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4153–4157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodny J. M., Larsen P. R., Silva J. E. In vitro 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine binding to rat cerebrocortical neuronal and glial nuclei suggests the presence of binding sites unavailable in vivo. Endocrinology. 1985 May;116(5):2019–2028. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-5-2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE Y. P., LARDY H. A. INFLUENCE OF THYROID HORMONES ON L-ALPHA-GLYCEROPHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASES AND OTHER DEHYDROGENASES IN VARIOUS ORGANS OF THE RAT. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1427–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. L., Kaplan M. M., Visser T. J., Silva J. E., Larsen P. R. Cerebral cortex responds rapidly to thyroid hormones. Science. 1981 Oct 30;214(4520):571–573. doi: 10.1126/science.7291997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. A., Feldman A. M., Robishaw J. D., Ladenson P. W., Ahn T. G., Moroney J. F., Smallwood P. M. Influence of thyroid hormone status on expression of genes encoding G protein subunits in the rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3553–3560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder M. E., Ewald D. A., Miller R. J., Gilman A. G. Purification and characterization of Go alpha and three types of Gi alpha after expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8243–8251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Rapiejko P. J., Mangano T. J. Fat cell adenylate cyclase system. Enhanced inhibition by adenosine and GTP in the hypothyroid rat. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2558–2564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurkiewicz D., Saggerson D. Changes in the activities of adenosine-metabolizing enzymes in six regions of the rat brain on chemical induction of hypothyroidism. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 15;261(2):667–672. doi: 10.1042/bj2610667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurkiewicz D., Saggerson E. D. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase in rat brain synaptosomal membranes by GTP and phenylisopropyladenosine is enhanced in hypothyroidism. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 1;263(3):829–835. doi: 10.1042/bj2630829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Delta-opioid-receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase is transduced specifically by the guanine-nucleotide-binding protein Gi2. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):391–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2670391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Saggerson E. D. Concurrent up-regulation of guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins Gi1 alpha, Gi2 alpha and Gi3 alpha in adipocytes of hypothyroid rats. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 15;270(3):765–769. doi: 10.1042/bj2700765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Saggerson E. D. Chemically induced hypothyroidism produces elevated amounts of the alpha subunit of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide binding protein (Gi) and the beta subunit common to all G-proteins. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):223–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2470223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Techniques used in the identification and analysis of function of pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2550001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell F. M., Griffiths S. L., Saggerson E. D., Houslay M. D., Knowler J. T., Milligan G. Guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins expressed in rat white adipose tissue. Identification of both mRNAs and proteins corresponding to Gi1, Gi2 and Gi3. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):403–408. doi: 10.1042/bj2620403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obregon M. J., Morreale de Escobar G., Escobar del Rey F. Concentrations of triiodo-L-thyronine in the plasma and tissues of normal rats, as determined by radioimmunoassay: comparison with results obtained by an isotopic equilibrium technique. Endocrinology. 1978 Dec;103(6):2145–2153. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-6-2145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohisalo J. J., Stouffer J. E. Adenosine, thyroid status and regulation of lipolysis. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):249–251. doi: 10.1042/bj1780249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Tissue differences in the concentration of triiodothyronine nuclear binding sites in the rat: liver, kidney, pituitary, heart, brain, spleen, and testis. Endocrinology. 1974 Sep;95(3):897–903. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-3-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor W. R., Dunwiddie T. V. Adenosine inhibits calcium spikes in hippocampal pyramidal neurons in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Feb 21;35(2):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90550-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapiejko P. J., Watkins D. C., Ros M., Malbon C. C. Thyroid hormones regulate G-protein beta-subunit mRNA expression in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16183–16189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reus V. I. Behavioral disturbances associated with endocrine disorders. Annu Rev Med. 1986;37:205–214. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.37.020186.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ros M., Northup J. K., Malbon C. C. Steady-state levels of G-proteins and beta-adrenergic receptors in rat fat cells. Permissive effects of thyroid hormones. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4362–4368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Carpenter C. A. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase in liver and five extrahepatic tissues in the rat. Inhibition by DL-2-bromopalmitoyl-CoA and effect of hypothyroidism. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):137–141. doi: 10.1042/bj2360137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D. Sensitivity of adipocyte lipolysis to stimulatory and inhibitory agonists in hypothyroidism and starvation. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):387–394. doi: 10.1042/bj2380387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito N., Guitart X., Hayward M., Tallman J. F., Duman R. S., Nestler E. J. Corticosterone differentially regulates the expression of Gs alpha and Gi alpha messenger RNA and protein in rat cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3906–3910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz G., Rosenthal W., Hescheler J., Trautwein W. Role of G proteins in calcium channel modulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. L., Oppenheimer J. H. Ontogenesis of 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine receptors in neonatal rat brain: dissociation between receptor concentration and stimulation of oxygen consumption by 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1978 Sep;103(3):943–948. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-3-943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegrist-Kaiser C. A., Juge-Aubry C., Tranter M. P., Ekenbarger D. M., Leonard J. L. Thyroxine-dependent modulation of actin polymerization in cultured astrocytes. A novel, extranuclear action of thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5296–5302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. E., Leonard J. L. Regulation of rat cerebrocortical and adenohypophyseal type II 5'-deiodinase by thyroxine, triiodothyronine, and reverse triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1627–1635. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Goldsmith P. K., Codina J., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. Gi2 mediates alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in platelet membranes: in situ identification with G alpha C-terminal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Jackson M. B. Adenosine-activated potassium conductance in cultured striatal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4857–4861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Jackson M. B. Dependence of an adenosine-activated potassium current on a GTP-binding protein in mammalian central neurons. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3306–3316. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03306.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valcana T., Timiras P. S. Nuclear triiodothyronine receptors in the developing rat brain. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1978 Jun;11(1):31–41. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(78)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]