Abstract
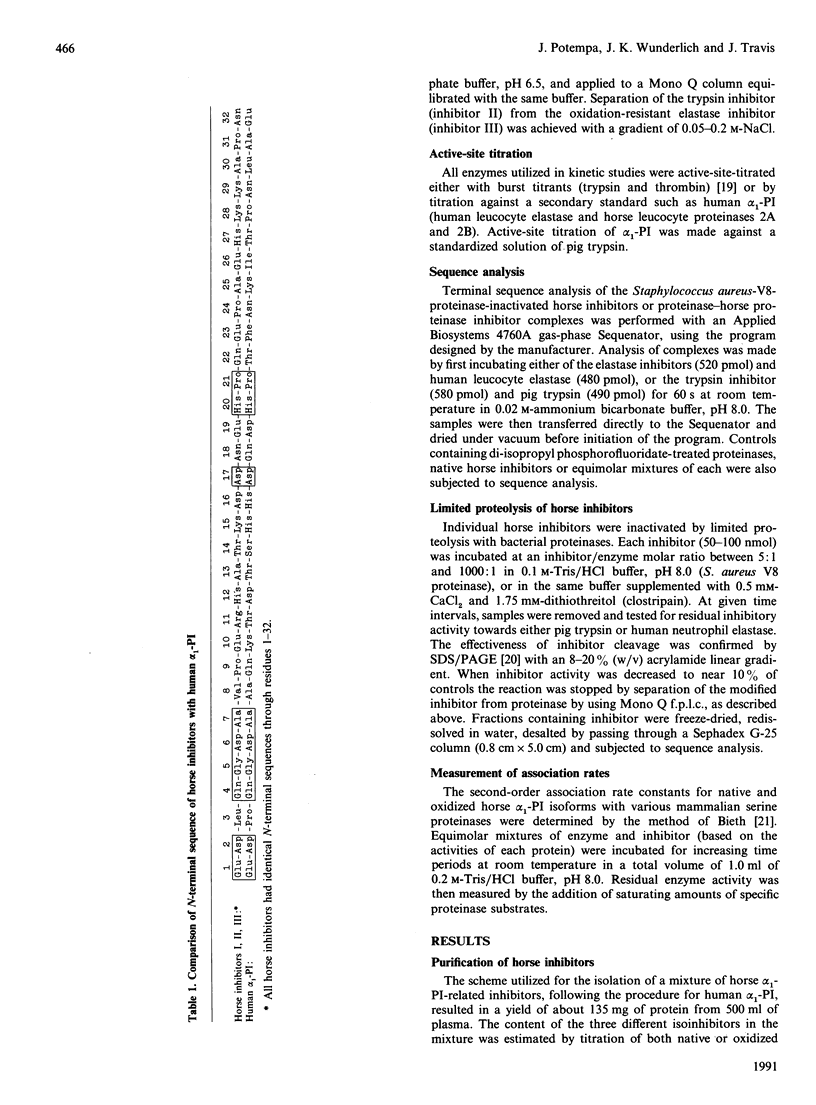
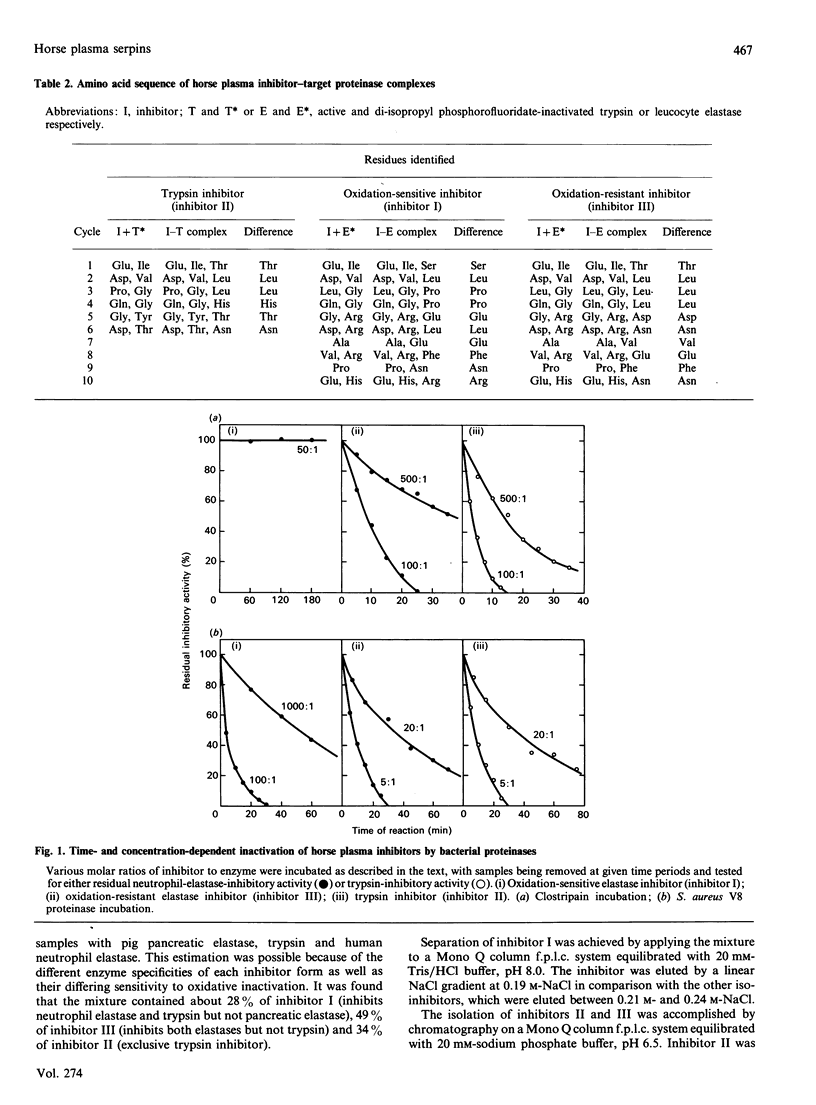
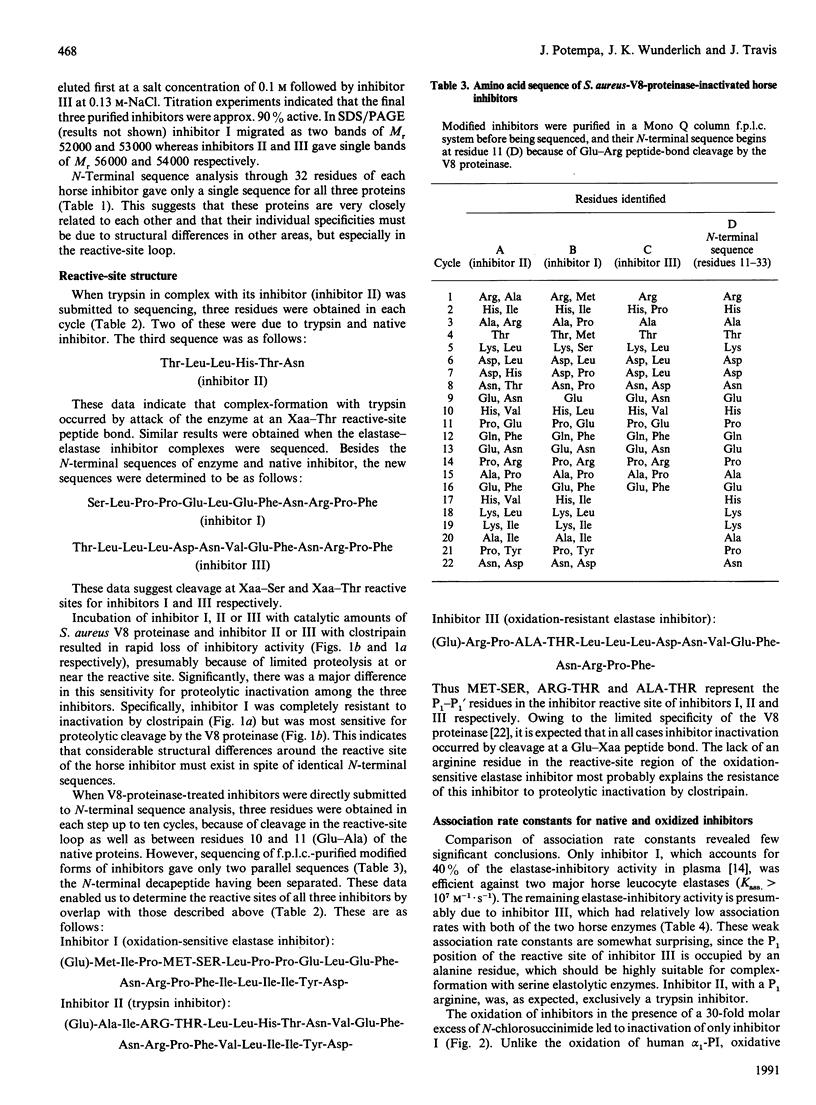
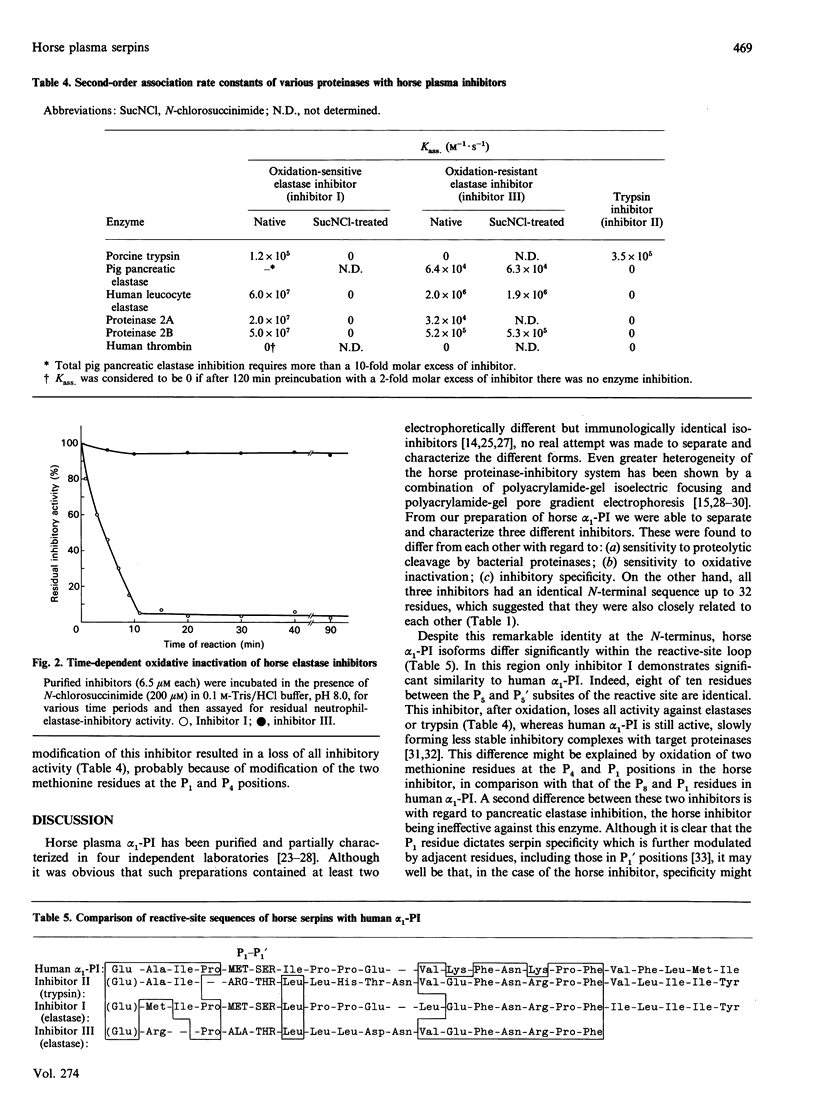
Three structurally related but functionally different serpins from horse plasma were isolated and characterized. In spite of their identical N-terminal sequences, which show some similarity to that of human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor, the reactive-centre loops of each of these proteins show extensive variation. Only inhibitor I, with a P1 methionine residue, resembles human alpha 1-PI with regard to (a) similarity of amino acid sequence in the vicinity of the reactive-site peptide bond, (b) broad inhibitory specificity, (c) sensitivity to oxidative inactivation and (d) high rate of reactivity with neutrophil elastase(s). Inhibitor II, with a P1 arginine residue, is an exclusive trypsin inhibitor, and inhibitor III is an oxidation-resistant slow-reacting elastase inhibitor with a P1 alanine residue. Comparison of association rate constants for the inhibition of horse neutrophil elastases by the three inhibitors indicates that only inhibitor I is likely to be physiologically important in the regulation of these enzymes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER A. F. Chronic alveolar emphysema in the horse. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Jul;80(1 Pt 2):141–146. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.1P2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach O., Hammond E. C., Garfinkel L., Benante C. Relation of smoking and age to emphysema. Whole-lung section study. N Engl J Med. 1972 Apr 20;286(16):853–857. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197204202861601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baugh R. J., Travis J. Human leukocyte granule elastase: rapid isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):836–841. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beatty K., Bieth J., Travis J. Kinetics of association of serine proteinases with native and oxidized alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor and alpha-1-antichymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3931–3934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell K., Patterson S., Pollitt C. C. The plasma protease inhibitor system (Pi) of Standardbred horses. Anim Blood Groups Biochem Genet. 1984;15(3):191–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1984.tb01116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieth J. G. Pathophysiological interpretation of kinetic constants of protease inhibitors. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1980;16 (Suppl):183–197. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-08-027379-2.50020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell D. R., Carrell R. W. Genetic engineering and the serpins. Bioessays. 1988 Feb-Mar;8(2):83–87. doi: 10.1002/bies.950080209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp H., Janoff A. In vitro suppression of serum elastase-inhibitory capacity by reactive oxygen species generated by phagocytosing polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):793–797. doi: 10.1172/JCI109364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp H., Janoff A. Potential mediator of inflammation. Phagocyte-derived oxidants suppress the elastase-inhibitory capacity of alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):987–995. doi: 10.1172/JCI109968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Pemberton P. A., Boswell D. R. The serpins: evolution and adaptation in a family of protease inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:527–535. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A. A polyvalent proteinase inhibitor from horse-blood-leucocyte cytosol. Isolation, purification and some molecular parameters. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 1;73(2):429–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Koj A., Chudzik J. Isolation and some molecular parameters of elastase-like normal proteinases from horse blood leucocytes. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):389–396. doi: 10.1042/bj1530389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Potempa J., Kurdowska A., Pajdak W., Koj A. Comparison of antiproteolytic activities of alpha-1-proteinase inhibitors from the plasma of some mammalian species. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1986;83(2):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(86)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Fells G. A., Crystal R. G. Cigarette smoking induces functional antiprotease deficiency in the lower respiratory tract of humans. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1315–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.316188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Hunninghake G. W., Fells G. A., Zimmerman R. L., Keogh B. A., Crystal R. G. Evaluation of the protease-antiprotease theory of human destructive lung disease. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1980;16 (Suppl):27–40. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-08-027379-2.50005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahne B., Juneja R. K. Extensive genetic polymorphism of four plasma alpha-protease inhibitors in pigs and evidence for tight linkage between the structural loci of these inhibitors. Anim Genet. 1986;17(2):135–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1986.tb00733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. R., Tyler W. S. Chronic alveolar emphysema in the horse. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1969;13:59–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Hastie N. D. Accelerated evolution in the reactive centre regions of serine protease inhibitors. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):96–99. doi: 10.1038/326096a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Shaw P. H., Barth R. K., Hastie N. D. A genetic locus closely linked to a protease inhibitor gene complex controls the level of multiple RNA transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2114–2122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmard J., Drapeau G. R. Staphylococcal protease: a proteolytic enzyme specific for glutamoyl bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3506–3509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jallat S., Carvallo D., Tessier L. H., Roecklin D., Roitsch C., Ogushi F., Crystal R. G., Courtney M. Altered specificities of genetically engineered alpha 1 antitrypsin variants. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):29–35. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. Elastases and emphysema. Current assessment of the protease-antiprotease hypothesis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):417–433. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Travis J. The oxidative inactivation of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor. Further evidence for methionine at the reactive center. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4022–4026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juneja R. K., Gahne B., Sandberg K. Genetic polymorphism and close linkage of two alpha 1-protease inhibitors in horse serum. Anim Blood Groups Biochem Genet. 1979;10(4):235–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1979.tb01031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurdowska A., Koj A., Jaśkowska M. Simultaneous isolation and partial characterization of antithrombin III and alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor from horse plasma. Acta Biochim Pol. 1982;29(1-2):95–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laegreid W. W., Breeze R. G., Counts D. F. Isolation and some properties of equine alpha 1-antitrypsin. Int J Biochem. 1982;14(4):327–334. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(82)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson N. R., Gibson H. L., Hallewell R. A., Barr P. J., Travis J. Recombinant DNA-derived forms of human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Studies on the alanine 358 and cysteine 358 substituted mutants. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10404–10409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson E. A., Lawson G. H., Murphy J. R., Nicholson J. M., Breeze R. G., Pirie H. M. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in horses: aetiological studies: responses to intradermal and inhalation antigenic challenge. Equine Vet J. 1979 Jul;11(3):159–166. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1979.tb01330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padrines M., Schneider-Pozzer M., Bieth J. G. Inhibition of neutrophil elastase by alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor oxidized by activated neutrophils. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):783–790. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannell R., Johnson D., Travis J. Isolation and properties of human plasma alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5439–5445. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S. D., Bell K. Application of an affinity electrophoretic and in situ oxidation method to the study of the equine protease inhibitory proteins. Electrophoresis. 1989 Jan;10(1):40–45. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S. D., Bell K. ISO-DALT characterization of 12 'new' equine plasma protease inhibitor (Pi) alleles. Anim Genet. 1987;18(2):167–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1987.tb00756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S. D., Bell K. The equine protease inhibitory system (Pi): abnormal expressions of PiF, PiL, and PiS1. Biochem Genet. 1986 Aug;24(7-8):529–543. doi: 10.1007/BF00504333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini A., Zweifel H. R., von Fellenberg R. Horse alpha-1 protease inhibitors: relationship between the slow (S) and fast (F) isoforms. Int J Biochem. 1985;17(4):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(85)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini A., von Fellenberg R. Fractionation and partial characterization of alpha-1-protease isoinhibitors of horse. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 4;616(2):351–361. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollitt C. C., Bell K. Characterisation of the alpha 1-protease inhibitor system in Thoroughbred horse plasma by horizontal two-dimensional (ISO-DALT) electrophoresis. 1. Protein staining. Anim Blood Groups Biochem Genet. 1983;14(2):83–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1983.tb01065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollitt C. C., Bell K. Characterisation of the alpha 1-protease inhibitor system in Thoroughbred horse plasma by horizontal two-dimensional (ISO-DALT) electrophoresis. 2. Protease inhibition. Anim Blood Groups Biochem Genet. 1983;14(2):107–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1983.tb01066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa J., Dubin A., Watorek W., Travis J. An elastase inhibitor from equine leukocyte cytosol belongs to the serpin superfamily. Further characterization and amino acid sequence of the reactive center. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7364–7369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa J., Korzus E., Dubin A., Silberring J. Elastinolytic activity of horse leukocyte proteinases. Comparison with elastases from human leukocytes and porcine pancreas. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 1986;24(2):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin M., Watson M., Kidd V., Woo S. L., Breg W. R., Ruddle F. H. Regional location of alpha 1-antichymotrypsin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes on human chromosome 14. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Mar;12(2):209–214. doi: 10.1007/BF01560668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff M., Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing buffers using multiphasic buffer systems: properties of the stack, valid Rf- measurement, and optimized procedure. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):459–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. B., Towle H. C., Seelig S. Growth hormone induces two mRNA species of the serine protease inhibitor gene family in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4284–4289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Fellenberg R., Kohler L., Grünig G., Pellegrini A. Comparison of neutrophil elastases and of neutrophil protease inhibitors in the horse and man. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Dec;46(12):2480–2484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


