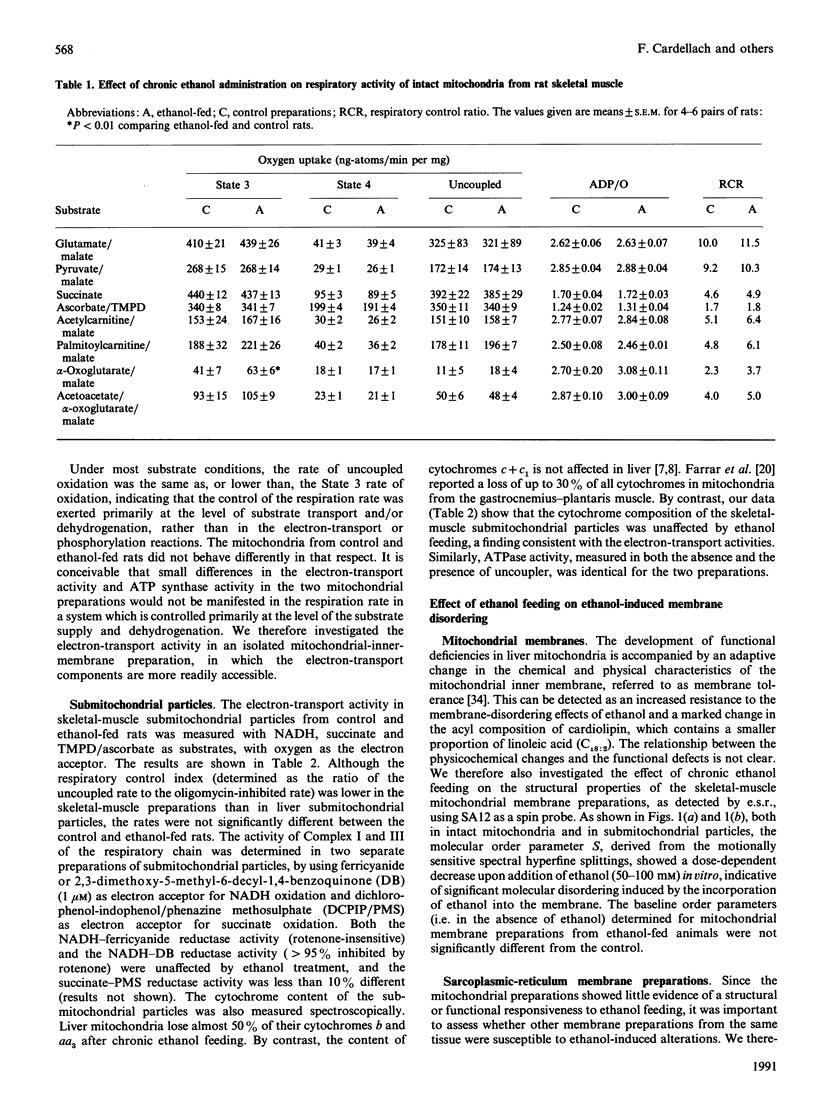
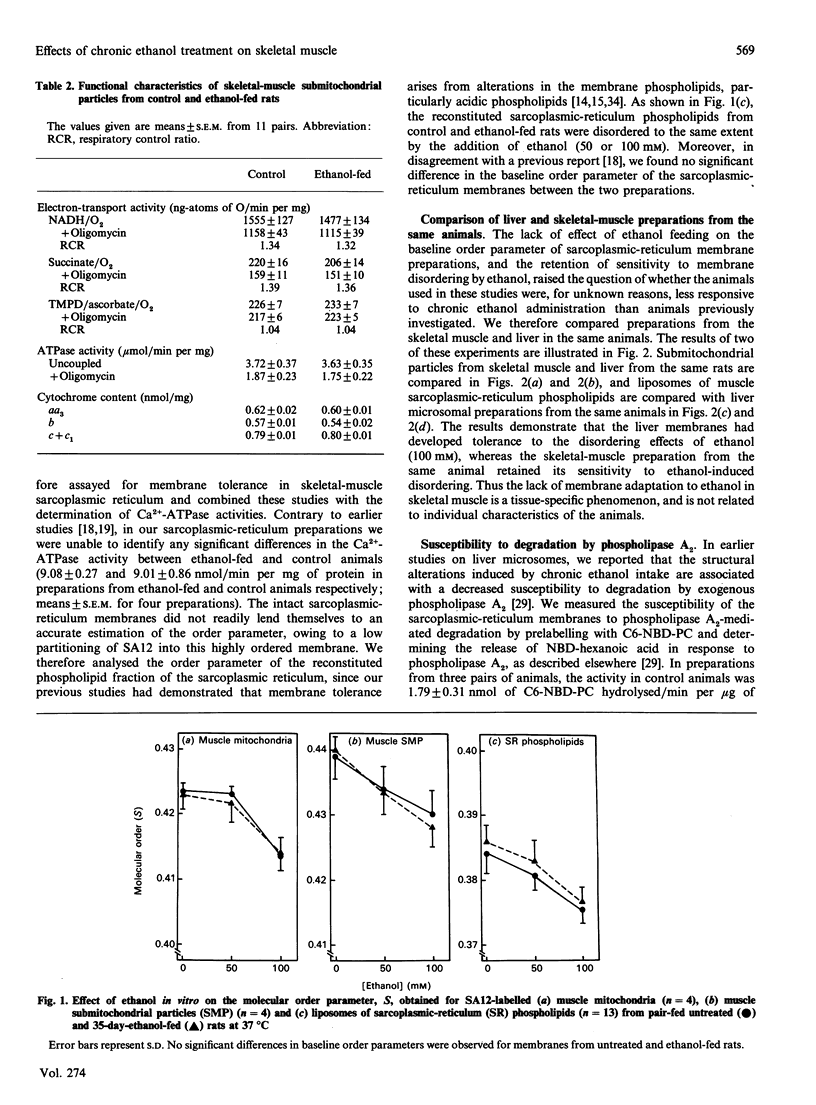
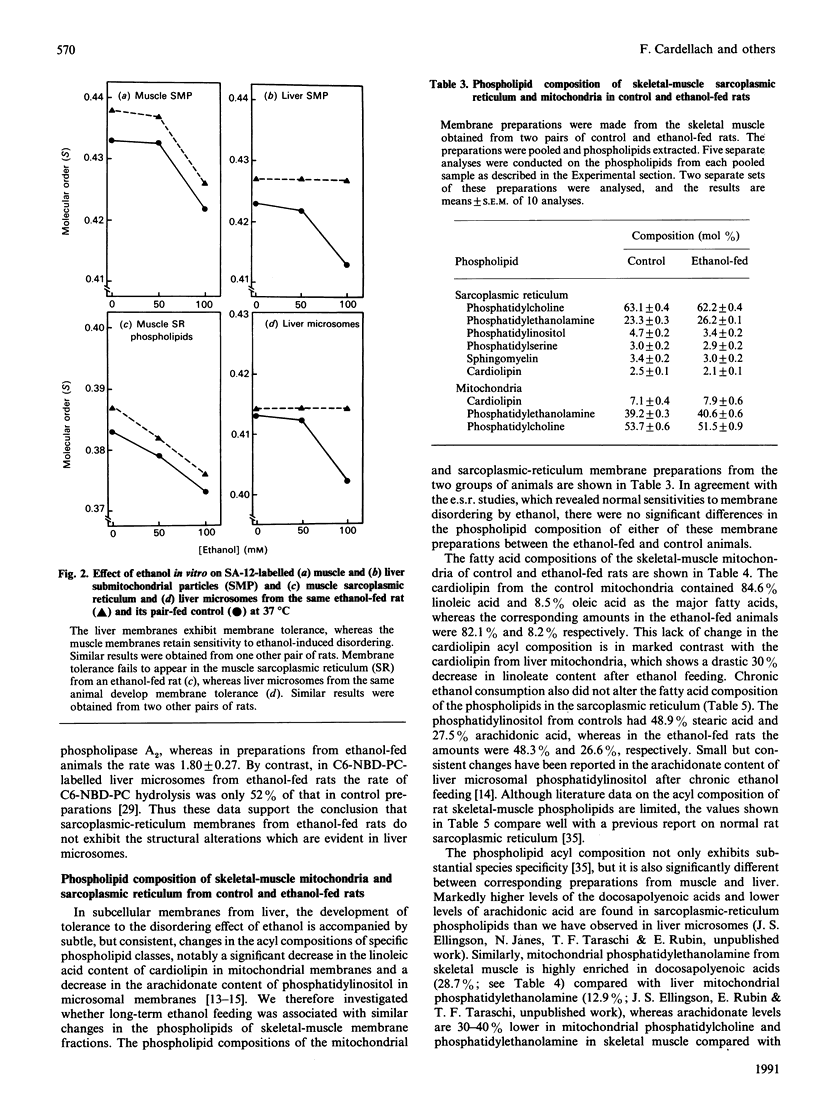
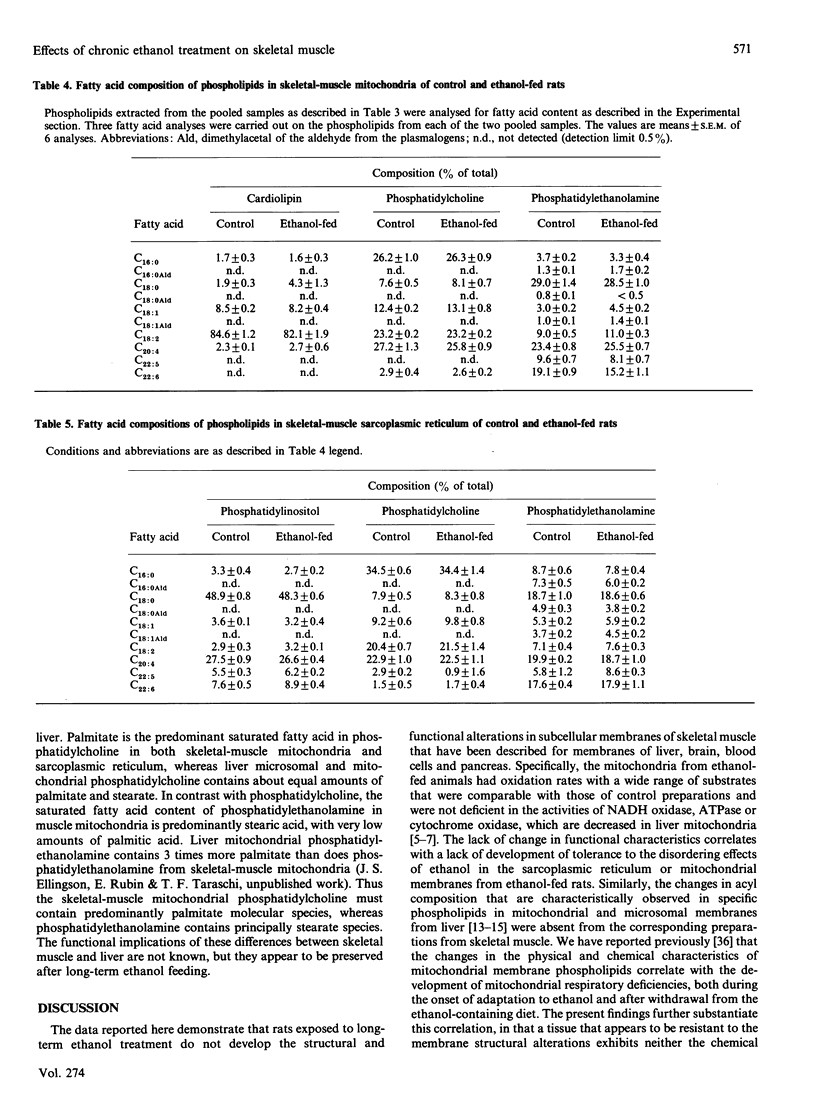
Abstract
The effect of long-term ethanol intake on the structural and functional characteristics of rat skeletal-muscle mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum was investigated. Functionally, skeletal-muscle mitochondria were characterized by a high respiratory control index and ADP/O ratio and a high State-3 respiration rate with different substrates. These parameters were not significantly different in preparations from control and ethanol-fed rats, except for a small increase in the rate of oxidation of alpha-oxoglutarate/malate in the latter. In submitochondrial particles from the two groups of animals there was no significant difference in cytochrome content, ATPase activity or the activity of respiratory-chain complexes. Mitochondrial membranes from untreated and ethanol-fed rats showed no difference in the baseline e.s.r. order parameter, and both preparations were equally sensitive to disordering by ethanol in vitro. Similarly, sarcoplasmic-reticulum preparations were not significantly affected by long-term ethanol feeding with respect to Ca2(+)-ATPase activity or in baseline order parameter and susceptibility to membrane disordering by ethanol in vitro. These membranes were also equally sensitive to degradation by exogenous phospholipase A2. Ethanol feeding did not alter the class composition of mitochondrial or sarcoplasmic-reticulum membrane phospholipids, nor the acyl composition of individual phospholipid classes. Specifically, the changes in acyl composition that characteristically occur in liver microsomal phosphatidylinositol and liver mitochondrial cardiolipin were not observed in the corresponding phospholipids from skeletal-muscle membranes. In experiments where membrane preparations from liver and skeletal muscle from the same ethanol-fed animals were compared, the liver membranes developed membrane tolerance, with the muscle membranes retaining normal sensitivity to disordering effects by ethanol. It is concluded that: (a) different tissues from the same animals differ in their susceptibility to ethanol; (b) the tissue-specific lack of development of membrane tolerance correlates with a lack of chemical changes in the phospholipids and with a retention of normal function of mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum; (c) effects of chronic ethanol intake on muscle function are not due to a defect in the mitochondrial energy supply.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allshire A. P., Heffron J. J. Uptake, retention, and efflux of Ca2+ by mitochondrial preparations from skeletal muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jan;228(1):353–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashour B., Hansford R. G. Effect of fatty acids and ketones on the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase in skeletal-muscle mitochondria. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 15;214(3):725–736. doi: 10.1042/bj2140725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederbaum A. I., Lieber C. S., Toth A., Beattie D. S., Rubin E. Effects of ethanol and fat on the transport of reducing equivalents into rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4977–4986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. H., Goldstein D. B. Drug tolerance in biomembranes: a spin label study of the effects of ethanol. Science. 1977 May 6;196(4290):684–685. doi: 10.1126/science.193186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. J., Packer L., Brooks G. A. Biochemical adaptation of mitochondria, muscle, and whole-animal respiration to endurance training. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jul;209(2):539–554. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCarli L. M., Lieber C. S. Fatty liver in the rat after prolonged intake of ethanol with a nutritionally adequate new liquid diet. J Nutr. 1967 Mar;91(3):331–336. doi: 10.1093/jn/91.3_Suppl.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Villar Negro A., Merino Angulo J., Rivera-Pomar J. M. Skeletal muscle changes in chronic alcoholic patients. A conventional, histochemical, ultrastructural and morphometric study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1984 Sep;70(3):185–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1984.tb00818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellingson J. S. Changes in the phospholipid composition in the differentiating cellular slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jan 23;337(1):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellingson J. S., Taraschi T. F., Wu A., Zimmerman R., Rubin E. Cardiolipin from ethanol-fed rats confers tolerance to ethanol in liver mitochondrial membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3353–3357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar R. P., Martin T. P., Abraham L. D., Erickson C. K. The interaction of endurance running and ethanol on skeletal muscle mitochondria. Life Sci. 1982 Jan 4;30(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90637-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar R. P., Seibert C., Gnau K., Leslie S. W. Development of tolerance in brain mitochondria for calcium uptake following chronic ethanol ingestion. Brain Res. 1989 Oct 23;500(1-2):374–378. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90334-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson S. M. Branched chain alpha-keto acid oxidative decarboxylation in skeletal muscle mitochondria. Effect of isolation procedure and mitochondrial delta pH. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4420–4425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. M., Freston J. W., Messineo F. C., Herbette L. G. Membrane damage and the pathogenesis of cardiomyopathies. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1985 Jul;17 (Suppl 2):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(85)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger D. A., Tate C. A., McMillin-Wood J., Booth F. W. Populations of rat skeletal muscle mitochondria after exercise and immobilization. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Jan;48(1):23–28. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laposata E. A., Lange L. G. Presence of nonoxidative ethanol metabolism in human organs commonly damaged by ethanol abuse. Science. 1986 Jan 31;231(4737):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.3941913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON W. R., SMITH L. M. PREPARATION OF FATTY ACID METHYL ESTERS AND DIMETHYLACETALS FROM LIPIDS WITH BORON FLUORIDE--METHANOL. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:600–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marai L., Kuksis A. Comparative study of molecular species of glycerolipids in sarcotubular membranes of skeletal muscle of rabbit, rat, chicken, and man. Can J Biochem. 1973 Oct;51(10):1365–1379. doi: 10.1139/o73-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. C., Slavin G., Levi A. J., Peters T. J. Investigation of the organelle pathology of skeletal muscle in chronic alcoholism. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Apr;37(4):448–454. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.4.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi S. T. Chronic alcohol ingestion alters the calcium permeability of sarcoplasmic reticulum of rat skeletal muscle. Membr Biochem. 1985;6(1):33–47. doi: 10.3109/09687688509065441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi S. T., Waring A. J., Fang S. R., Horiuchi K., Ohnishi T. Sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane of rat skeletal muscle is disordered with chronic alcohol ingestion. Membr Biochem. 1985;6(1):49–63. doi: 10.3109/09687688509065442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pande S. V., Blanchaer M. C. Carbohydrate and fat in energy metabolism of red and white muscle. Am J Physiol. 1971 Feb;220(2):549–553. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.2.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponnappa B. C., Hoek J. B., Waring A. J., Rubin E. Effect of ethanol on amylase secretion and cellular calcium homeostasis in pancreatic acini from normal and ethanol-fed rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 1;36(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponnappa B. C., Waring A. J., Hoek J. B., Rottenberg H., Rubin E. Chronic ethanol ingestion increases calcium uptake and resistance to molecular disordering by ethanol in liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10141–10146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H., Waring A., Rubin E. Tolerance and cross-tolerance in chronic alcoholics: reduced membrane binding of ethanol and other drugs. Science. 1981 Jul 31;213(4507):583–585. doi: 10.1126/science.6264608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E., Katz A. M., Lieber C. S., Stein E. P., Puszkin S. Muscle damage produced by chronic alcohol consumption. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jun;83(3):499–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E., Lieber C. S. Alcohol-induced hepatic injury in nonalcoholic volunteers. N Engl J Med. 1968 Apr 18;278(16):869–876. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196804182781602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E., Lieber C. S. Experimental alcoholic hepatitis: a new primate model. Science. 1973 Nov 16;182(4113):712–713. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4113.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E., Lieber C. S. Fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis produced by alcohol in primates. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 17;290(3):128–135. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401172900303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segel L. D., Rendig S. V., Choquet Y., Chacko K., Amsterdam E. A., Mason D. T. Effects of chronic graded ethanol consumption on the metabolism, ultrastructure, and mechanical function of the rat heart. Cardiovasc Res. 1975 Sep;9(5):649–663. doi: 10.1093/cvr/9.5.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Leo M. A., Jayatilleke E., Lieber C. S. Depressed oxidative metabolism in skeletal muscle after chronic alcohol consumption. Biochem Med. 1982 Oct;28(2):210–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(82)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song S. K., Rubin E. Ethanol produces muscle damage in human volunteers. Science. 1972 Jan 21;175(4019):327–328. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4019.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs C. D., Williams B. W., Pryor C. L., Rubin E. Ethanol-induced modifications to membrane lipid structure: effect on phospholipase A2-membrane interactions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 May 1;262(2):560–573. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90407-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraschi T. F., Ellingson J. S., Wu A., Zimmerman R., Rubin E. Phosphatidylinositol from ethanol-fed rats confers membrane tolerance to ethanol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9398–9402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraschi T. F., Rubin E. Effects of ethanol on the chemical and structural properties of biologic membranes. Lab Invest. 1985 Feb;52(2):120–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraschi T. F., Thayer W. S., Ellingson J. S., Rubin E. Effects of ethanol on the structure and function of rat liver mitochondrial and microsomal membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;488:127–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb46553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraschi T. F., Wu A., Rubin E. Phospholipid spin probes measure the effects of ethanol on the molecular order of liver microsomes. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7096–7101. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer W. S., Rubin E. Effects of chronic ethanol intoxication on oxidative phosphorylation in rat liver submitochondrial particles. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7717–7723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer W. S., Rubin E. Molecular alterations in the respiratory chain of rat liver after chronic ethanol consumption. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6090–6097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbano-Marquez A., Estruch R., Navarro-Lopez F., Grau J. M., Mont L., Rubin E. The effects of alcoholism on skeletal and cardiac muscle. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 16;320(7):409–415. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902163200701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Toon P. A., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. Reconstitution of a calcium pump using defined membrane components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):622–626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


