Abstract
The rate of leucine C-2 incorporation into glutamine was compared in control and septic rats. Female Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 46, 210-260 g) were fed parenterally for 3 days and then randomized into two groups (control and septic). Sepsis was induced by the injection of 10(10) live Escherichia coli/kg on day 4 into the septic group. Rats in each group were given a continuous (8 h) infusion of one of three different isotopes. The isotopes were given 24 h after inoculation. Leucine oxidation and incorporation into protein were determined with [1-13C]leucine; glutamine flux and oxidation were determined with [5-13C]glutamine, and the fraction of leucine C-2 incorporated into glutamine was determined by giving [1,2-13C]leucine. Results were as follows: sepsis caused a significant increase in the rate of leucine C-2 incorporation into glutamine (66.0 +/- 3.7 as against 29.6 +/- 3.7 mumol/h per kg, P less than 0.01). This increase was due to both an increase in glutamine production (2331 +/- 76 as against 1959 +/- 94 mumol/h per kg, P less than 0.01) and an increase in the proportion of glutamine derived from leucine (2.83 +/- 0.27% as against 1.51 +/- 0.31%, P less than 0.01). The ratio of leucine C-2 incorporated into glutamine to leucine oxidized increased from 7.16 +/- 0.91% to 11.49 +/- 1.12% with sepsis (P less than 0.05).
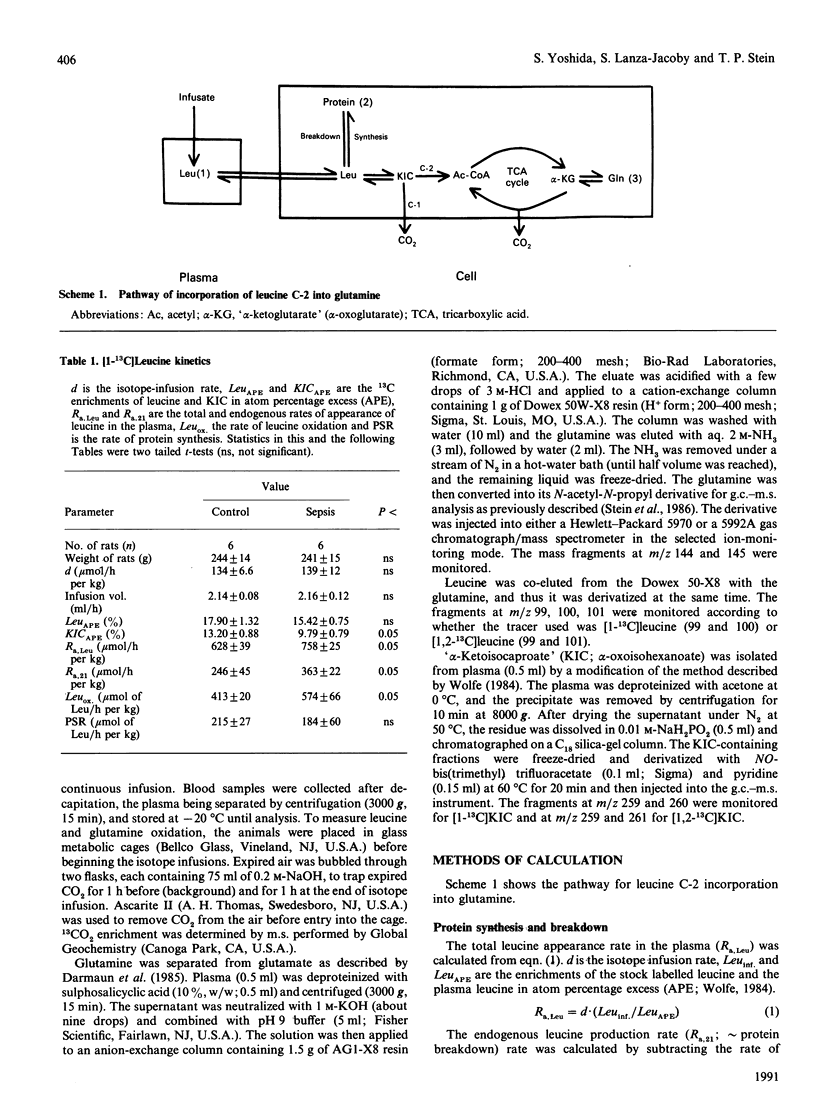
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki T. T., Brennan M. F., Fitzpatrick G. F., Knight D. C. Leucine meal increases glutamine and total nitrogen release from forearm muscle. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1522–1528. doi: 10.1172/JCI110406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askanazi J., Carpentier Y. A., Michelsen C. B., Elwyn D. H., Furst P., Kantrowitz L. R., Gump F. E., Kinney J. M. Muscle and plasma amino acids following injury. Influence of intercurrent infection. Ann Surg. 1980 Jul;192(1):78–85. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198007000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. R., Brooks D. C., Bessey P. Q., Wolfe R. R., Wilmore D. W. Mechanisms of insulin resistance following injury. Ann Surg. 1982 Oct;196(4):420–435. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198210000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn G. L., Moldawer L. L., Usui S., Bothe A., Jr, O'Keefe S. J., Bistrian B. R. Branched chain amino acid administration and metabolism during starvation, injury, and infection. Surgery. 1979 Aug;86(2):307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darmaun D., Manary M. J., Matthews D. E. A method for measuring both glutamine and glutamate levels and stable isotopic enrichments. Anal Biochem. 1985 May 15;147(1):92–102. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durkot M. J., Wolfe R. R. Hyper and hypodynamic models of sepsis in guinea pigs. J Surg Res. 1989 Feb;46(2):118–122. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(89)90213-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elia M., Neale G., Livesey G. Alanine and glutamine release from the human forearm: effects of glucose administration. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Aug;69(2):123–133. doi: 10.1042/cs0690123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. Glutamine metabolism in the rat. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 25;117 (Suppl):K86–K92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80573-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P., Williamson D. H. Inter-tissue nitrogen fluxes. Br Med Bull. 1985 Jul;41(3):251–256. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon M. M., Schwenk W. F., Haymond M. W., Rizza R. A. Underestimation of glucose turnover measured with [6-3H]- and [6,6-2H]- but not [6-14C]glucose during hyperinsulinemia in humans. Diabetes. 1989 Jan;38(1):97–107. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melville S., McNurlan M. A., McHardy K. C., Broom J., Milne E., Calder A. G., Garlick P. J. The role of degradation in the acute control of protein balance in adult man: failure of feeding to stimulate protein synthesis as assessed by L-[1-13C]leucin infusion. Metabolism. 1989 Mar;38(3):248–255. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pencharz P. B., Motil K. J., Parsons H. G., Duffy B. J. The effect of an energy-restricted diet on the protein metabolism of obese adolescents: nitrogen-balance and whole-body nitrogen turnover. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Jul;59(1):13–18. doi: 10.1042/cs0590013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie M. J., MacLennan P. A., Hundal H. S., Weryk B., Smith K., Taylor P. M., Egan C., Watt P. W. Skeletal muscle glutamine transport, intramuscular glutamine concentration, and muscle-protein turnover. Metabolism. 1989 Aug;38(8 Suppl 1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein T. P., Buzby G. P., Leskiw M. J., Giandomenico A. R., Mullen J. L. Protein and fat metabolism in rats during repletion with total parenteral nutrition (TPN). J Nutr. 1981 Jan;111(1):154–165. doi: 10.1093/jn/111.1.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein T. P., Leskiw M. J., Buzby G. P., Giandomenico A. L., Wallace H. W., Mullen J. L. Measurement of protein synthesis rates with [15N]glycine. Am J Physiol. 1980 Oct;239(4):E294–E300. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.4.E294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein T. P., Settle R. G., Albina J. A., Dempsey D. T., Melnick G. Metabolism of nonessential 15N-labeled amino acids and the measurement of human whole-body protein synthesis rates. J Nutr. 1986 Sep;116(9):1651–1659. doi: 10.1093/jn/116.9.1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez J. A., Paul H. S., Adibi S. A. Relation between plasma and tissue parameters of leucine metabolism in fed and starved rats. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):E615–E621. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.6.E615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. R., Jahoor F., Hartl W. H. Protein and amino acid metabolism after injury. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1989 Mar;5(2):149–164. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610050205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


