Abstract
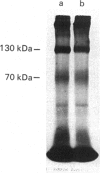
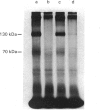
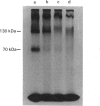
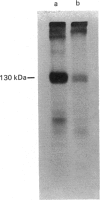
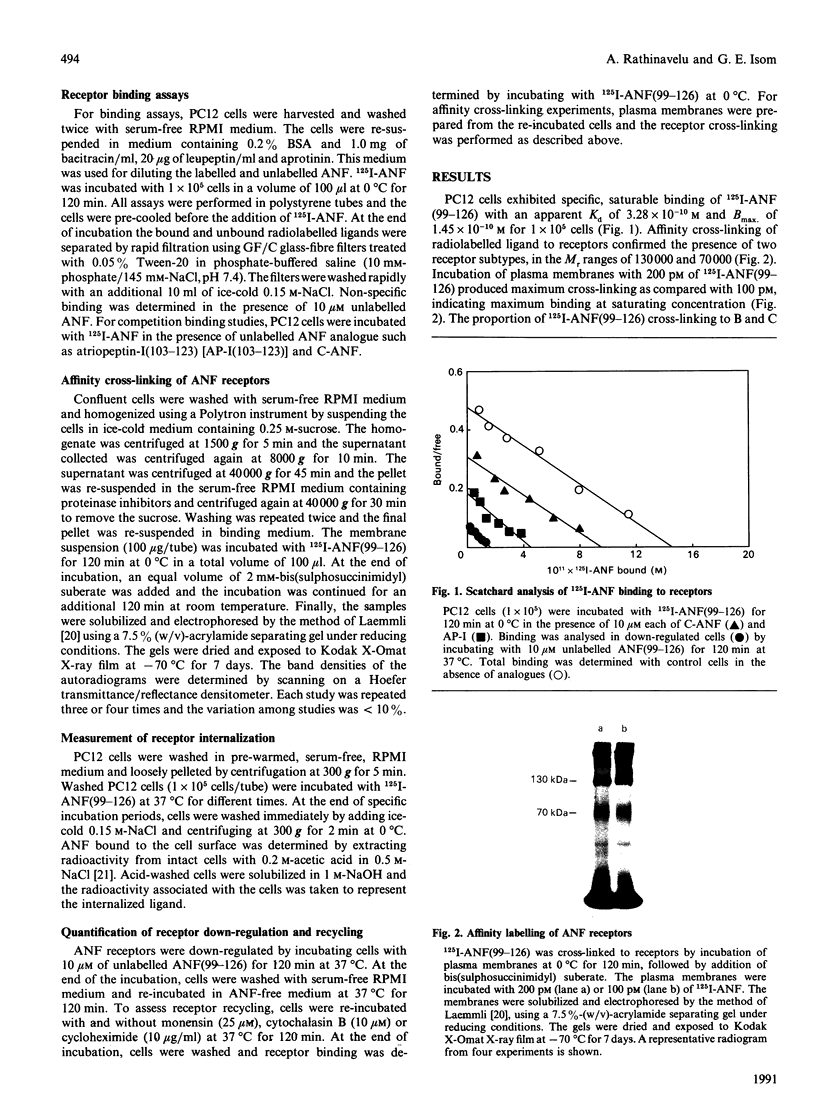
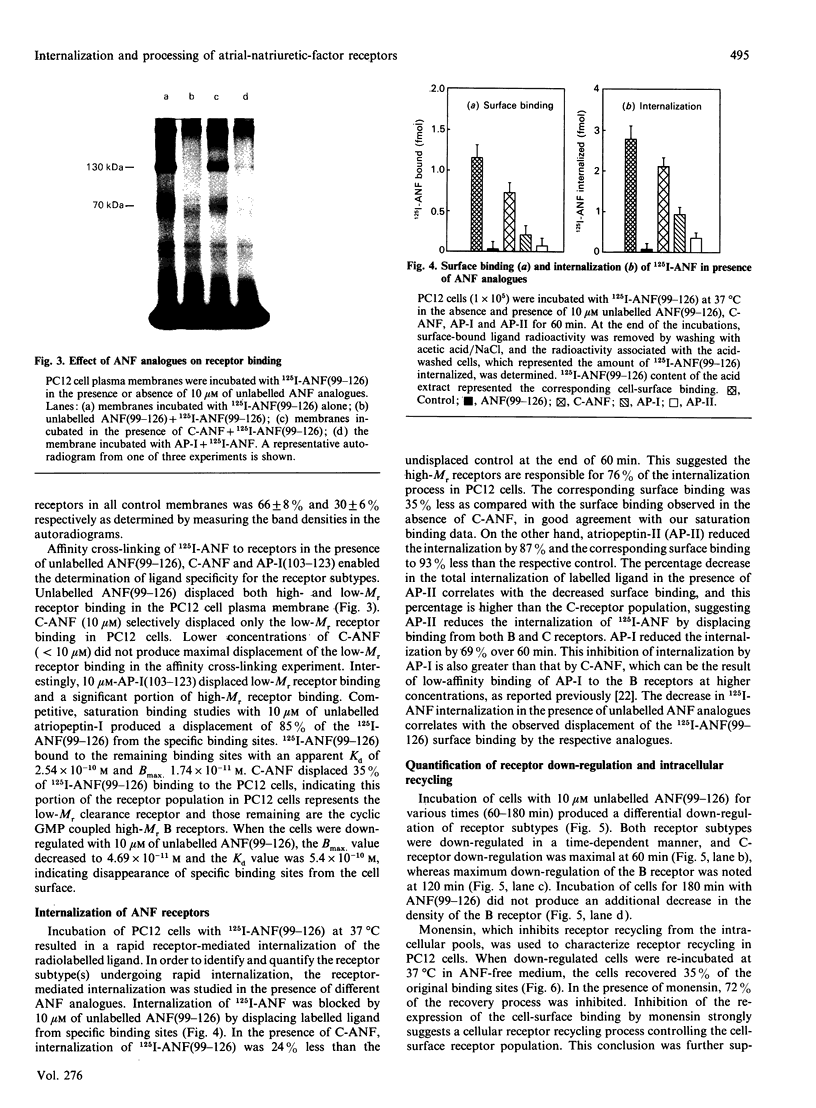
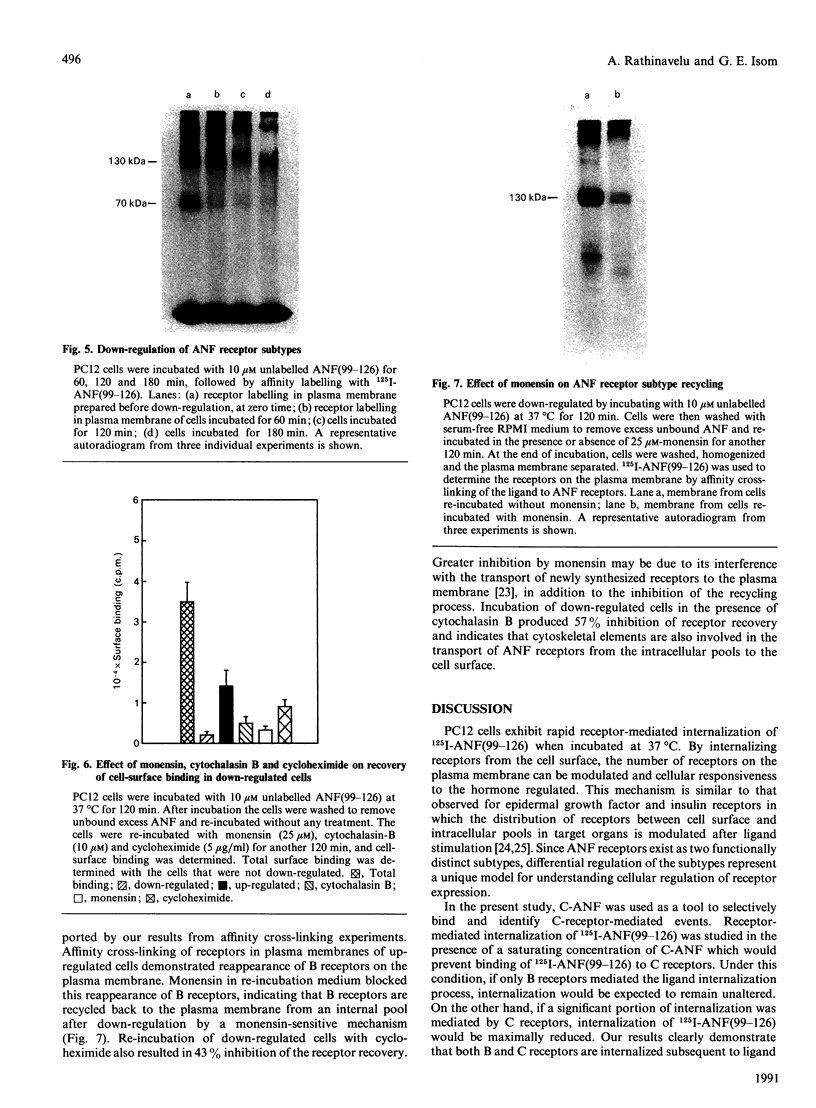
PC12 cells express two atrial-natriuretic-factor-(ANF)-receptor subtypes with molecular masses of 130,000 (B receptor) and 70,000 (C receptor). The B-receptor subtype constitutes 65% of the cell-surface receptor population, and the remaining 35% are C receptors as determined by saturation binding studies in the presence of C-ANF, a C-receptor-selective analogue. ANF-(99-126)-peptide [ANF(99-126)], which can bind to both B- and C-receptor subtypes, was rapidly internalized into the cells after incubation at 37 degrees C. Internalization of 125I-ANF(99-126) was used as an index of the receptor-mediated endocytosis and to quantify receptor internalization. In the presence of a saturating concentration of C-ANF, receptor-mediated internalization of 125I-ANF(99-126) was reduced by 24%, indicating B receptor mediate 76% of ligand internalization. Incubation of cells with 10 microM-ANF at 37 degrees C down-regulated both receptor subtypes as reflected by decreased surface binding. Time-dependent studies suggest that B- and C-receptor subtypes undergo differential down-regulation. Incubation of down-regulated cells for 120 min in ANF-free medium produced a recovery of 35% of the original cell-surface binding. Affinity cross-linking of 125I-ANF to the receptors on the plasma membrane in re-incubated (up-regulated) cells demonstrated expression of predominantly the B-receptor subtype. Monensin blocked 72% of receptor up-regulation, whereas cycloheximide inhibited 43%, suggesting an active recycling mechanism involved in mediating up-regulation of the B receptors. The present study demonstrates a rapid internalization and intracellular recycling mechanism for B receptors in PC12 cells. C receptors also undergo internalization and down-regulation, but recycling of this receptor subtype into the plasma membrane occurs at a lower rate and to a lesser extent than is the case for the B receptor.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Monensin interrupts the recycling of low density lipoprotein receptors in human fibroblasts. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro D. P., Bonner-Weir S., King G. L. Insulin receptor recycling in vascular endothelial cells. Regulation by insulin and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5916–5923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot J. G., Morel G., Kopelman H., Belles-Isles M., Heisler S. Atrial natriuretic factor and exocrine pancreas: autoradiographic localization of binding sites and ultrastructural evidence for internalization of endogenous ANF. Pancreas. 1987;2(4):404–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Garbers D. L., Chang M. S., Lowe D. G., Chin H. M., Goeddel D. V., Schulz S. A membrane form of guanylate cyclase is an atrial natriuretic peptide receptor. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):78–83. doi: 10.1038/338078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genest J., Cantin M. The atrial natriuretic factor: its physiology and biochemistry. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1988;110:1–145. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladhaug I. P., Christoffersen T. Rapid constitutive internalization and externalization of epidermal growth factor receptors in isolated rat hepatocytes. Monensin inhibits receptor externalization and reduces the capacity for continued endocytosis of epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12199–12203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Dansylcadaverine inhibits internalization of 125I-epidermal growth factor in BALB 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1239–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Hirose S., Takata S., Takagi Y., Matsubara H. Down-regulation of atrial natriuretic peptide receptor and cyclic GMP response in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 31;135(3):439–442. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90697-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Takata S., Takagi Y., Matsubara H., Omae T. Regulation of atrial natriuretic peptide receptors in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells of rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 16;138(1):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R. K., Toews M. L. Activation of protein kinase C inhibits internalization and downregulation of muscarinic receptors in 1321N1 human astrocytoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Apr;253(1):185–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. J., Struthers R. S., Fong A. M., Insel P. A. Regulation of the atrial natriuretic peptide receptor on a smooth muscle cell. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C809–C816. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Andresen J. W., Kamisaki Y., Waldman S. A., Chang L. Y., Saheki S., Leitman D. C., Nakane M., Murad F. Co-purification of an atrial natriuretic factor receptor and particulate guanylate cyclase from rat lung. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5817–5823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitman D. C., Murad F. Comparison of binding and cyclic GMP accumulation by atrial natriuretic peptides in endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 23;885(1):74–79. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maack T., Suzuki M., Almeida F. A., Nussenzveig D., Scarborough R. M., McEnroe G. A., Lewicki J. A. Physiological role of silent receptors of atrial natriuretic factor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.2823385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloche S., McNicoll N., Liu B., Ong H., De Léan A. Atrial natriuretic factor R1 receptor from bovine adrenal zona glomerulosa: purification, characterization, and modulation by amiloride. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8151–8158. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel G., Belles-Isles M., Heisler S. Internalization of atrial natriuretic factor by AtT-20 corticotropin-secreting cells. Biol Cell. 1987;59(3):233–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1987.tb00535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel G., Chabot J. G., Belles-Isles M., Heisler S. Synthesis and internalization of atrial natriuretic factor in anterior pituitary cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988 Feb;55(2-3):219–231. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(88)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel G., Chabot J. G., Garcia-Caballero T., Gossard F., Dihl F., Belles-Isles M., Heisler S. Synthesis, internalization, and localization of atrial natriuretic peptide in rat adrenal medulla. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):149–158. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murad F. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate as a mediator of vasodilation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI112536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul A. K., Marala R. B., Jaiswal R. K., Sharma R. K. Coexistence of guanylate cyclase and atrial natriuretic factor receptor in a 180-kD protein. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1224–1226. doi: 10.1126/science.2881352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter J. G., Scarborough R. M., Wang Y., Schenk D., McEnroe G. A., Kang L. L., Lewicki J. A. Recombinant expression of a secreted form of the atrial natriuretic peptide clearance receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14179–14184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter J. G., Wang Y., Schwartz K., Arfsten A., Loffredo A., Spratt K., Schenk D. B., Fuller F., Scarborough R. M., Lewicki J. A. Characterization of the atrial natriuretic peptide clearance receptor using a vaccinia virus expression vector. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18827–18833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathinavelu A., Isom G. E. High affinity receptors for atrial natriuretic factor in PC12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):78–85. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80807-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi R., Inagami T., Snajdar R. M., Imada T., Tamura M., Misono K. S. Two distinct forms of receptors for atrial natriuretic factor in bovine adrenocortical cells. Purification, ligand binding, and peptide mapping. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12104–12113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Atrial natriuretic factor selectively activates particulate guanylate cyclase and elevates cyclic GMP in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14332–14334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Faison E. P., Waldman S. A., Schwartz K., Murad F., Rapoport R. M. Atrial natriuretic factor elicits an endothelium-independent relaxation and activates particulate guanylate cyclase in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7661–7664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]