Abstract
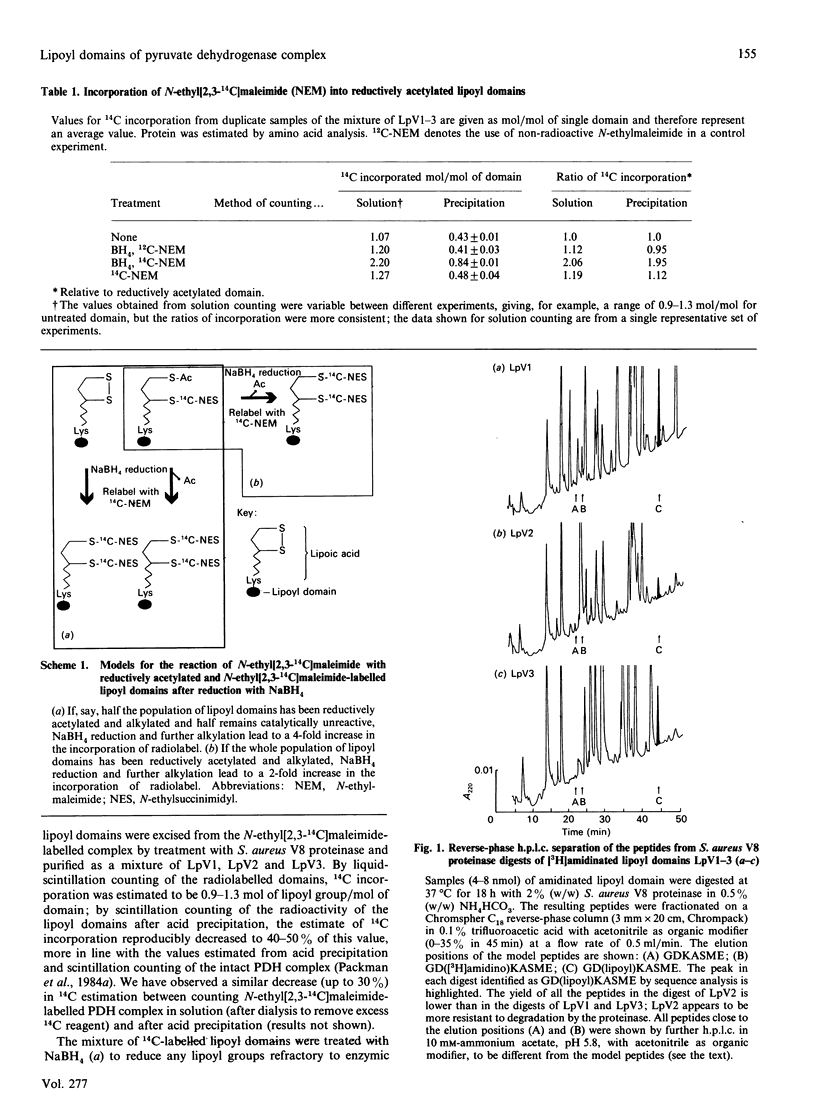
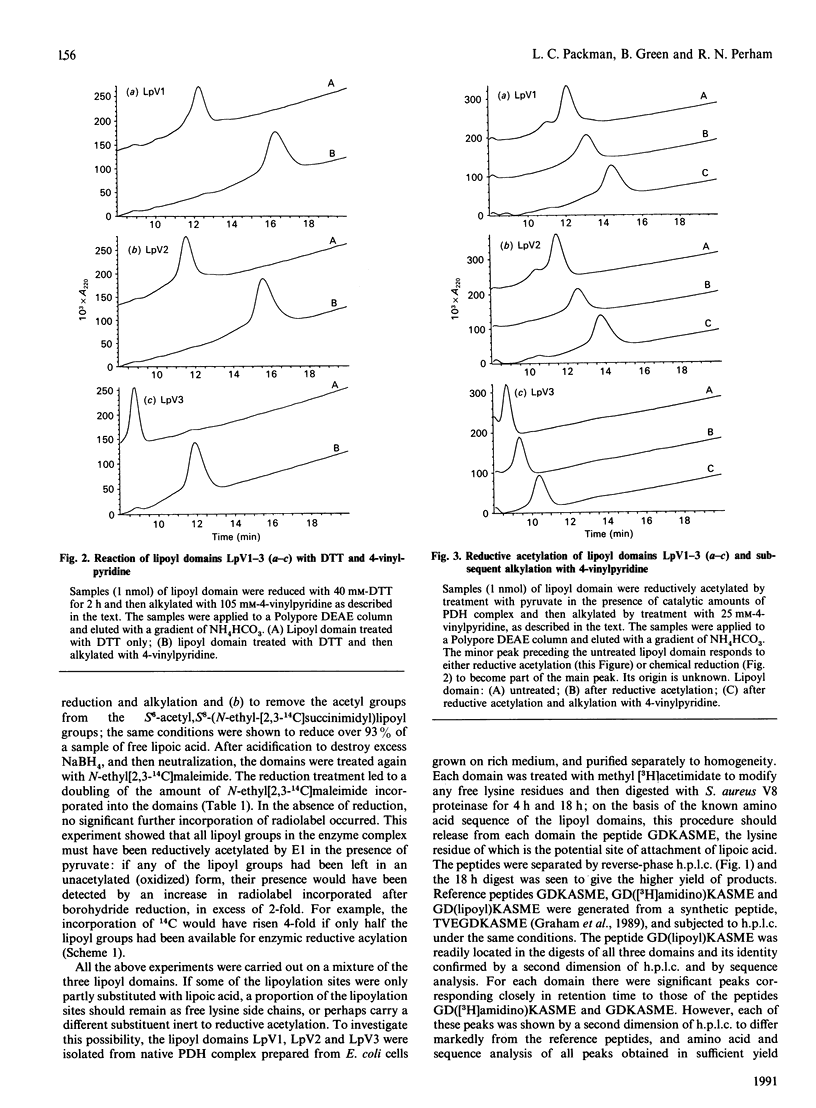
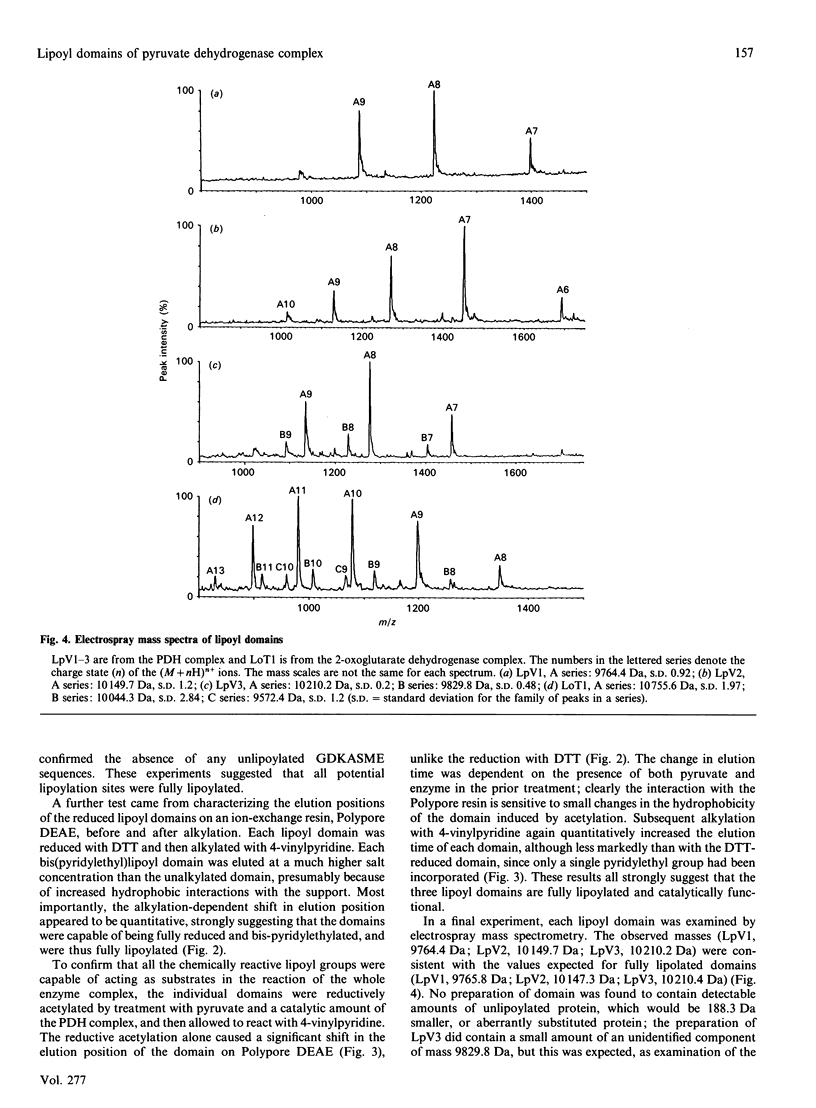
The number of functional lipoyl groups in the dihydrolipoyl acetyltransferase (E2) chain of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from Escherichia coli has been re-assessed by means of a combination of protein-chemical and mass-spectrometric techniques. (1) After the complex had been treated with N-ethyl[2,3-14C]maleimide in the presence of pyruvate, the lipoyl domains were excised from the complex, treated with NaBH4 and re-exposed to N-ethyl[2,3-14C]maleimide. All the chemically reactive lipoyl groups in the native complex were found to be catalytically active. (2) Proteolytic digests of the separated lipoyl domains were examined for the presence of the lipoylation-site peptide, GDKASME, with and without the lipoyl group in N6-linkage to the lysine residue. Only the lipoylated form of the peptide was detected, suggesting that all three lipoyl domains are fully substituted at this site. (3) The behaviour of each lipoyl domain was examined on ion-exchange chromatography in response to alkylation with 4-vinylpyridine after either chemical reduction of the lipoyl group with dithiothreitol or reductive acetylation by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in the presence of pyruvate. All three domains exhibited a quantitative shift in retention time, confirming that each domain was fully substituted by an enzymically reactive lipoyl group. (4) When subjected to electrospray mass spectrometry, each domain gave a mass consistent with a fully lipoylated domain, and no aberrant substitution of the target lysine residue was detected. The same result was obtained for the lipoyl domain from the E. coli 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. (5) Previous widespread attempts to assess the number of functional lipoyl groups in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex, which have led to the view that a maximum of two lipoyl groups per E2 chain may be involved in the catalytic mechanism, are in error.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S. T., Moir A. J., Ashton P. R., Engel P. C., Guest J. R. Octanoylation of the lipoyl domains of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in a lipoyl-deficient strain of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jun;4(6):943–950. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen A. G., Perham R. N., Allison N., Miles J. S., Guest J. R. Reductive acetylation of tandemly repeated lipoyl domains in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli is random order. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):623–633. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J., Leadlay P. F., Perham R. N. Synthesis of methyl[3H]acetimidate of high specific radioactivity, a reagent for radiolabeling proteins. Anal Biochem. 1980 Dec;109(2):410–413. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90669-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. L., Danson M. J., Hale G., Hooper E. A., Perham R. N. Self-assembly and catalytic activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1977 Jul 28;268(5618):313–316. doi: 10.1038/268313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Reed L. J. Acyl group and electron pair relay system: a network of interacting lipoyl moieties in the pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4223–4227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Hale G., Johnson P., Perham R. N., Smith J., Spragg P. Molecular weight and symmetry of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 25;129(4):603–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Perham R. N. Evidence for two lipoic acid residues per lipoate acetyltransferase chain in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):677–682. doi: 10.1042/bj1590677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardel F., Packman L. C., Perham R. N. Expression in Escherichia coli of a sub-gene encoding the lipoyl domain of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 21;264(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80249-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. D., Packman L. C., Perham R. N. Kinetics and specificity of reductive acylation of lipoyl domains from 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1574–1581. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Angier S. J., Russell G. C. Structure, expression, and protein engineering of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;573:76–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb14988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Hooper E. A., Perham R. N. Amidination of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli under denaturing conditions. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):136–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1770136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Perham R. N. Polypeptide-chain stoicheiometry and lipoic acid content of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):129–136. doi: 10.1042/bj1770129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Borges A., Perham R. N. Amino acid sequence analysis of the lipoyl and peripheral subunit-binding domains in the lipoate acetyltransferase component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):79–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2520079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Hale G., Perham R. N. Repeating functional domains in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1315–1319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01969.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Perham R. N. Limited proteolysis and sequence analysis of the 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complexes from Escherichia coli. Cleavage sites and domains in the dihydrolipoamide acyltransferase components. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):531–538. doi: 10.1042/bj2420531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Perham R. N., Roberts G. C. Domain structure and 1H-n.m.r. spectroscopy of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):219–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2170219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M. S., Roche T. E. Molecular biology and biochemistry of pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes. FASEB J. 1990 Nov;4(14):3224–3233. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.14.2227213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Packman L. C. 2-Oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes: domains, dynamics, and design. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;573:1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb14983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Packman L. C., Radford S. E. 2-Oxo acid dehydrogenase multi-enzyme complexes: in the beginning and halfway there. Biochem Soc Symp. 1987;54:67–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Roberts G. C. Limited proteolysis and proton n.m.r. spectroscopy of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):733–740. doi: 10.1042/bj1990733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed L. J., Hackert M. L. Structure-function relationships in dihydrolipoamide acyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):8971–8974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Darlison M. G., Lewis H. M., Guest J. R. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleotide sequence encoding the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase component. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;133(3):481–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. H., Bleile D. M., Reed L. J. Lipoic acid content of dihydrolipoyl transacylases determined by isotope dilution analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):78–84. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


