Abstract
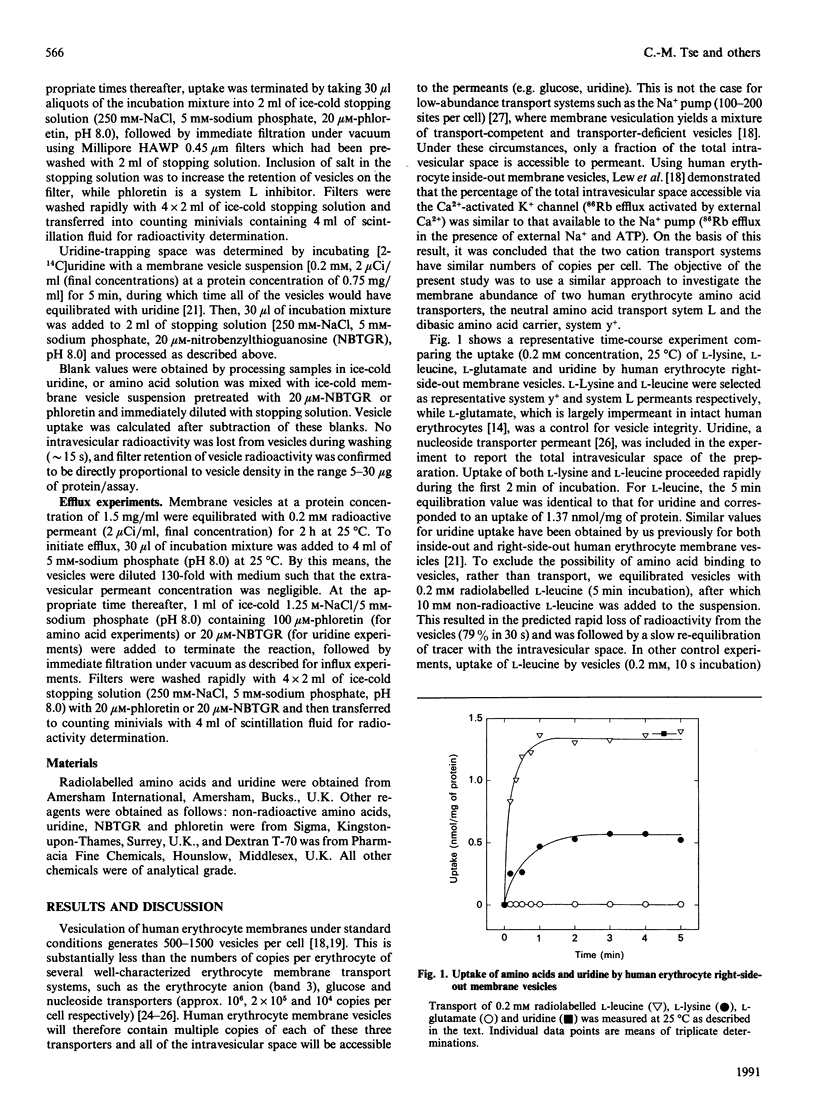
We have used equilibrium values for L-leucine and L-lysine uptake by right-side-out vesicles to estimate the membrane abundance (sites/cell) of Na(+)-dependent amino acid transport systems L and y+ in human erythrocytes. All of the intravesicular space was accessible to L-leucine, as judged by comparisons with uridine uptake via the equilibrative nucleoside transporter (10(4) sites/cell). In contrast, only 28% of the total intravesicular space was accessible to L-lysine uptake via system y+. Since human erythrocyte membranes generate an average of approximately 1000 vesicles/cell, these data provide evidence that system L is a relatively high-abundance membrane transport protein in human erythrocytes, while system y+ is present in smaller amounts (approximately 300 copies/cell). Calculated turnover numbers for L-lysine transport by system y+ at 37 degrees C are 24 s-1 for zero-trans influx and 150 s-1 for equilibrium-exchange influx.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonioli J. A., Christensen H. N. Differences in schedules of regression of transport systems during reticulocyte maturation. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1505–1509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Exploiting amino acid structure to learn about membrane transport. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1979;49:41–101. doi: 10.1002/9780470122945.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Organic ion transport during seven decades. The amino acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 3;779(3):255–269. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Levy A. G. Transport of dibasic amino acids by human erythrocytes. Metabolism. 1972 May;21(5):413–431. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guastella J., Nelson N., Nelson H., Czyzyk L., Keynan S., Miedel M. C., Davidson N., Lester H. A., Kanner B. I. Cloning and expression of a rat brain GABA transporter. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.1975955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey C. M., Ellory J. C. Identification of amino acid transporters in the red blood cell. Methods Enzymol. 1989;173:122–160. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)73010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoare D. G. The temperature dependence of the transport of L-leucine in human erythrocytes. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(2):331–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis S. M., Young J. D. Nucleoside transport in human and sheep erythrocytes. Evidence that nitrobenzylthioinosine binds specifically to functional nucleoside-transport sites. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 15;190(2):377–383. doi: 10.1042/bj1900377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Muallem S., Seymour C. A. Properties of the Ca2+-activated K+ channel in one-step inside-out vesicles from human red cell membranes. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):742–744. doi: 10.1038/296742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Muallem S., Seymour C. A. Properties of the Ca2+-activated K+ channel in one-step inside-out vesicles from human red cell membranes. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):742–744. doi: 10.1038/296742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S., Spudich J. A. Biochemical studies on the mode of action of cytochalasin B. Cytochalasin B binding to red cell membrane in relation to glucose transport. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5778–5783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macintyre J. D., Gunn R. B. Activation and deactivation kinetics of Ca transport in inside-out erythrocyte membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 22;644(2):351–362. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90393-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. I., Johnstone R. M. Simple and effective purification of a Na+-dependent amino acid transport system from Ehrlich ascites cell plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7877–7881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radian R., Bendahan A., Kanner B. I. Purification and identification of the functional sodium- and chloride-coupled gamma-aminobutyric acid transport glycoprotein from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15437–15441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L-Leucine transport in human red blood cells: a detailed kinetic analysis. J Membr Biol. 1981;62(1-2):79–93. doi: 10.1007/BF01870202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. K. Ca binding to the human red cell membrane: characterization of membrane preparations and binding sites. J Membr Biol. 1976 Nov 29;29(4):345–372. doi: 10.1007/BF01868970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Wu J. S., Young J. D. Evidence for the asymmetrical binding of p-chloromercuriphenyl sulphonate to the human erythrocyte nucleoside transporter. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 10;818(3):316–324. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. G., CHRISTENSEN H. N. MIGRATION OF AMINO ACIDS ACROSS THE MEMBRANE OF THE HUMAN ERYTHROCYTE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:872–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieth J. O. Bicarbonate exchange through the human red cell membrane determined with [14C] bicarbonate. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:521–539. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., Peerce B. E. Identification and conformational changes of the intestinal proline carrier. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):14993–14996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Jones S. E., Ellory J. C. Amino acid transport in human and in sheep erythrocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Sep 26;209(1176):355–375. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


