Abstract
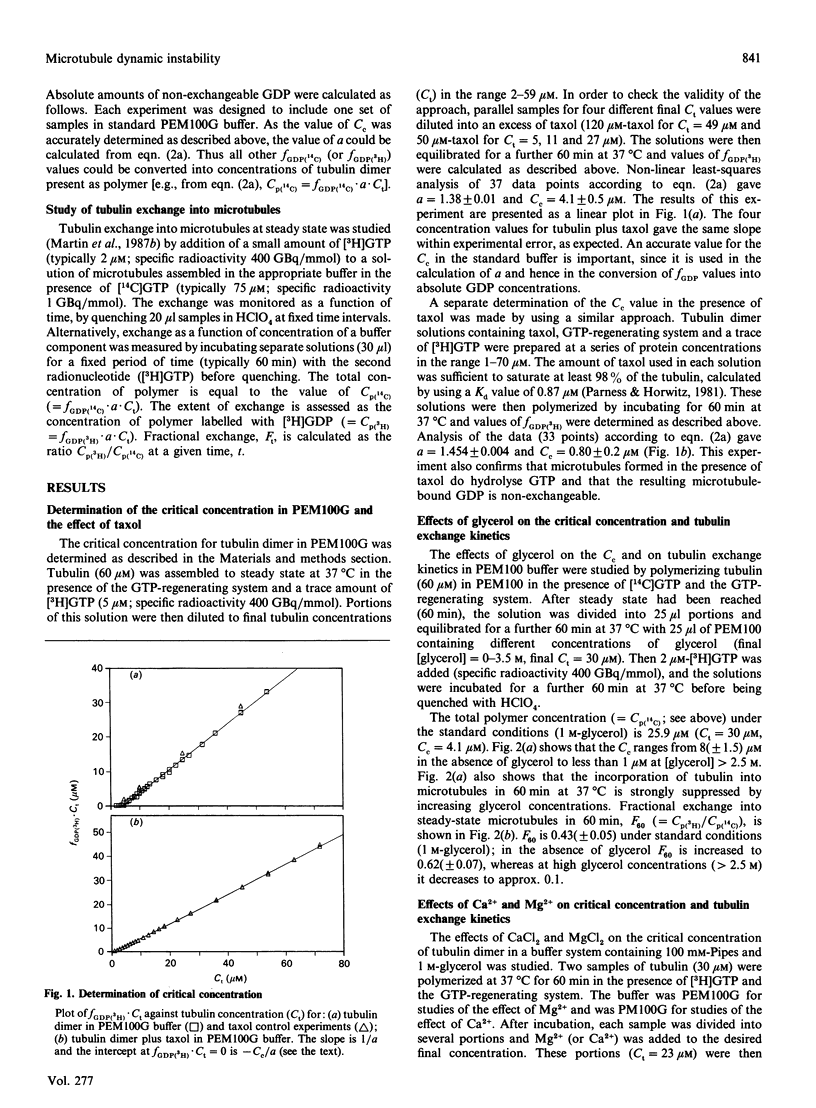
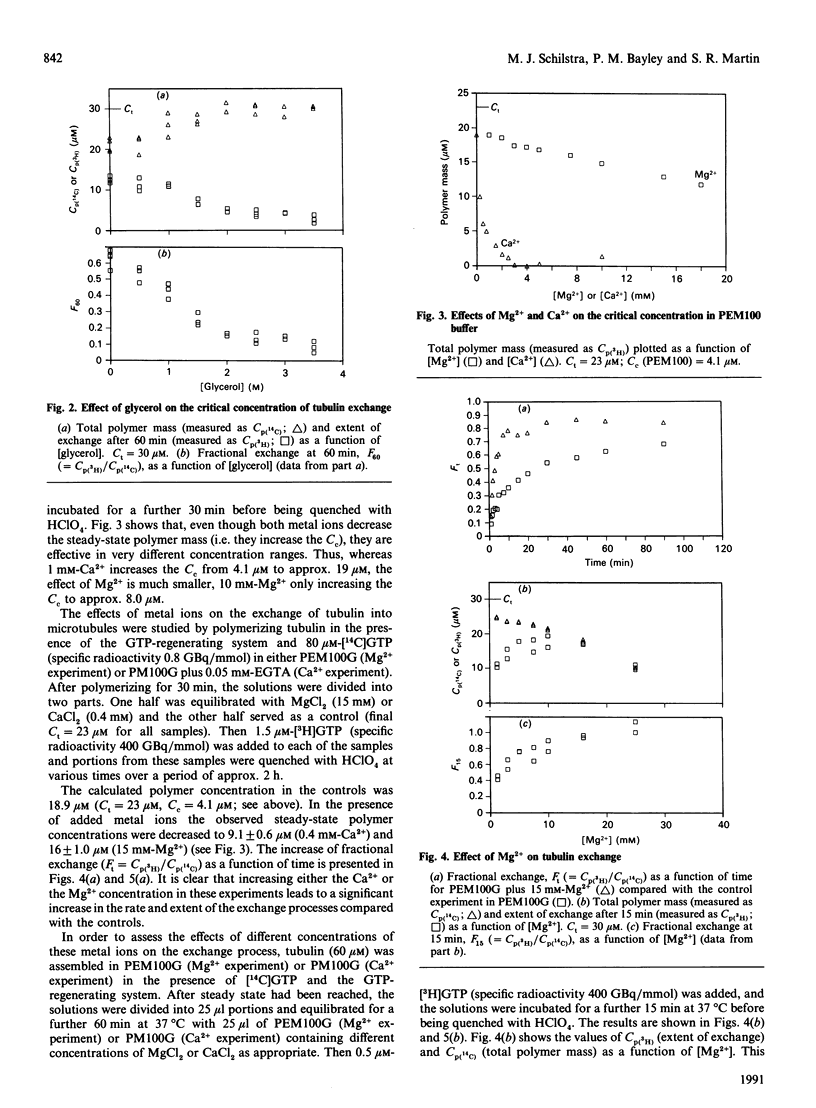
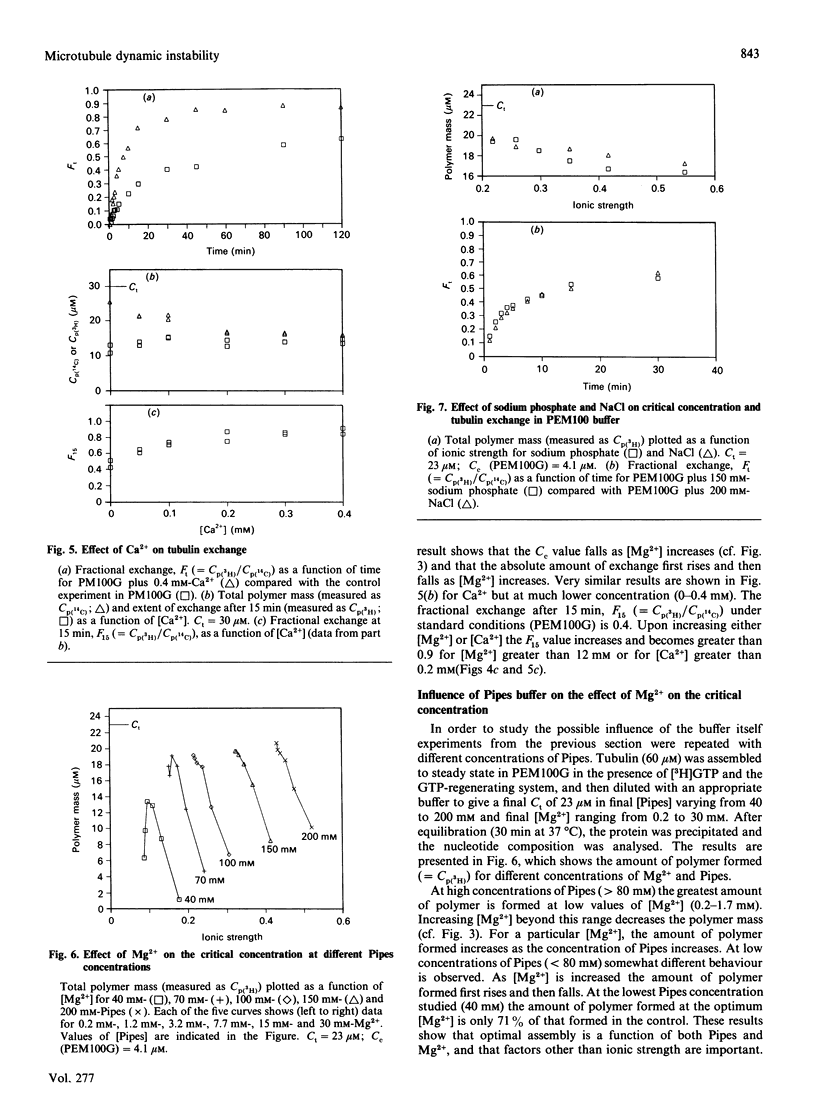
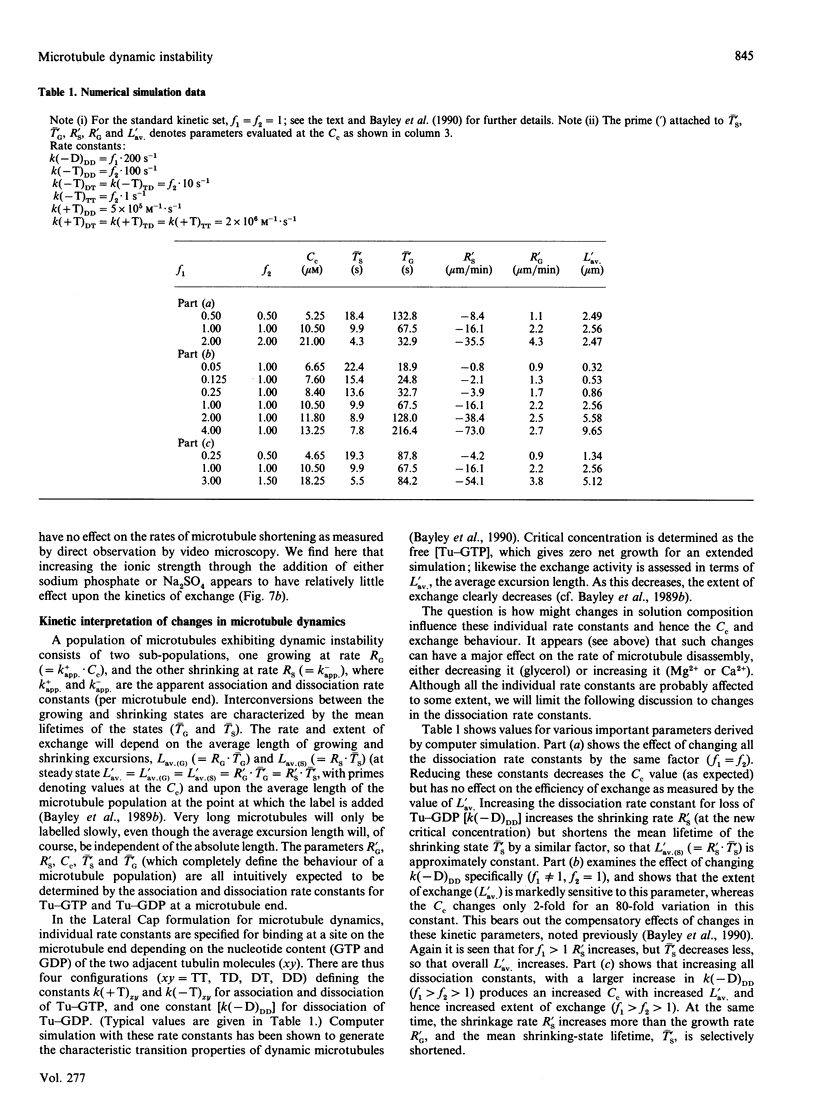
The exchange of tubulin dimer into steady-state microtubules was studied over a range of solution conditions, in order to assess the effects of various common buffer components on the dynamic instability of microtubules. In comparison with standard buffer conditions (100 mM-Pipes buffer, pH 6.5, containing 0.1 mM-EGTA, 1.8 mM-MgC12 and 1 M-glycerol), the rate and extent of exchange, and thus of dynamic instability, are suppressed by increasing the concentration of glycerol above 2 M. Exchange is enhanced by the addition of further Mg2+ (up to 17 mM) or by the addition of Ca2+ (up to 0.4 mM). Phosphate ion (150 mM) has relatively little effect on the dynamic behaviour of microtubules, as judged by the exchange method. The findings are interpreted within the framework of the Lateral Cap model for microtubule dynamic instability, in terms of the effects of these changes on the intrinsic rate constants of the system. By contrast, the extent of tubulin exchange depends selectively on the value of the dissociation rate constant for tubulin-GDP. A decrease in the extent of exchange, and hence in dynamic activity, is associated with a decreased value for this rate constant, and vice versa. The results also show good agreement of predictions of the model in treating the observed variations in the dynamic properties of individual microtubules, induced by different solution conditions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayley P. M., Butler F. M., Clark D. C., Manser E. J., Martin S. R. The assembly of microtubule protein in vitro. The kinetic role in microtubule elongation of oligomeric fragments containing microtubule-associated proteins. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 15;227(2):439–455. doi: 10.1042/bj2270439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley P. M., Schilstra M. J., Martin S. R. A simple formulation of microtubule dynamics: quantitative implications of the dynamic instability of microtubule populations in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jun;93(Pt 2):241–254. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley P. M., Schilstra M. J., Martin S. R. Microtubule dynamic instability: numerical simulation of microtubule transition properties using a Lateral Cap model. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jan;95(Pt 1):33–48. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley P. M. What makes microtubules dynamic? J Cell Sci. 1990 Mar;95(Pt 3):329–334. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley P., Schilstra M., Martin S. A lateral cap model of microtubule dynamic instability. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81523-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplow M., Ruhlen R., Shanks J., Walker R. A., Salmon E. D. Stabilization of microtubules by tubulin-GDP-Pi subunits. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 3;28(20):8136–8141. doi: 10.1021/bi00446a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplow M., Shanks J., Brylawski B. P. Differentiation between dynamic instability and end-to-end annealing models for length changes of steady-state microtubules. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16233–16240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Didry D., Melki R., Chabre M., Pantaloni D. Stabilization of microtubules by inorganic phosphate and its structural analogues, the fluoride complexes of aluminum and beryllium. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3555–3559. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Didry D., Pantaloni D. Microtubule elongation and guanosine 5'-triphosphate hydrolysis. Role of guanine nucleotides in microtubule dynamics. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4428–4437. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Didry D., Simon C., Pantaloni D. Mechanism of GTP hydrolysis in tubulin polymerization: characterization of the kinetic intermediate microtubule-GDP-Pi using phosphate analogues. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1783–1791. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D. Kinetic analysis of guanosine 5'-triphosphate hydrolysis associated with tubulin polymerization. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1918–1924. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassimeris L., Pryer N. K., Salmon E. D. Real-time observations of microtubule dynamic instability in living cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2223–2231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. D., Hill T. L. Monte Carlo study of the GTP cap in a five-start helix model of a microtubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1131–1135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Hill T. L. Theoretical treatment of microtubules disappearing in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4127–4131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. C., Martin S. R., Bayley P. M. Conformation and assembly characteristics of tubulin and microtubule protein from bovine brain. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1924–1932. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal V., Martin S., Bayley P. Fast disassembly of microtubules induced by Mg2+ or Ca2+. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 30;155(3):1464–1470. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L. Introductory analysis of the GTP-cap phase-change kinetics at the end of a microtubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6728–6732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horio T., Hotani H. Visualization of the dynamic instability of individual microtubules by dark-field microscopy. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):605–607. doi: 10.1038/321605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard W. D., Timasheff S. N. GDP state of tubulin: stabilization of double rings. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8292–8300. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr T. L., Kristofferson D., Purich D. L. Calcium ion induces endwise depolymerization of bovine brain microtubules. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11853–11856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keates R. A. Effects of glycerol on microtubule polymerization kinetics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 16;97(3):1163–1169. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keates R. A. Stabilization of microtubule protein in glycerol solutions. Can J Biochem. 1981 May;59(5):353–360. doi: 10.1139/o81-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M. W. Biological implications of microtubule dynamics. Harvey Lect. 1987;83:1–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M., Mitchison T. Beyond self-assembly: from microtubules to morphogenesis. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):329–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90318-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristofferson D., Mitchison T., Kirschner M. Direct observation of steady-state microtubule dynamics. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1007–1019. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. R., Butler F. M., Clark D. C., Zhou J. M., Bayley P. M. Magnesium ion effects on microtubule nucleation in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 24;914(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. R., Schilstra M. J., Bayley P. M. Dynamic properties of microtubules at steady state of polymerisation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):461–467. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. R., Schilstra M. J., Bayley P. M. Opposite-end behaviour of dynamic microtubules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 9;1073(3):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90230-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T., Kirschner M. Dynamic instability of microtubule growth. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):237–242. doi: 10.1038/312237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. T., Salmon E. D., Walker R. A., Erickson H. P. Effects of magnesium on the dynamic instability of individual microtubules. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6648–6656. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. T., Voter W. A., Erickson H. P. GTP hydrolysis during microtubule assembly. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):4148–4156. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B., Borisy G. G. Ionic and nucleotide requirements for microtubule polymerization in vitro. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2996–3005. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parness J., Horwitz S. B. Taxol binds to polymerized tubulin in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):479–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammak P. J., Borisy G. G. Direct observation of microtubule dynamics in living cells. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):724–726. doi: 10.1038/332724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilstra M. J., Martin S. R., Bayley P. M. On the relationship between nucleotide hydrolysis and microtubule assembly: studies with a GTP-regenerating system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):588–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90971-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilstra M. J., Martin S. R., Bayley P. M. The effect of podophyllotoxin on microtubule dynamics. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8827–8834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze E., Kirschner M. New features of microtubule behaviour observed in vivo. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):356–359. doi: 10.1038/334356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. J., Farrell K. W., Wilson L. Role of GTP hydrolysis in microtubule polymerization: evidence for a coupled hydrolysis mechanism. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 10;29(27):6489–6498. doi: 10.1021/bi00479a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., O'Brien E. T., Pryer N. K., Soboeiro M. F., Voter W. A., Erickson H. P., Salmon E. D. Dynamic instability of individual microtubules analyzed by video light microscopy: rate constants and transition frequencies. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1437–1448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wani M. C., Taylor H. L., Wall M. E., Coggon P., McPhail A. T. Plant antitumor agents. VI. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from Taxus brevifolia. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 May 5;93(9):2325–2327. doi: 10.1021/ja00738a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


