Abstract
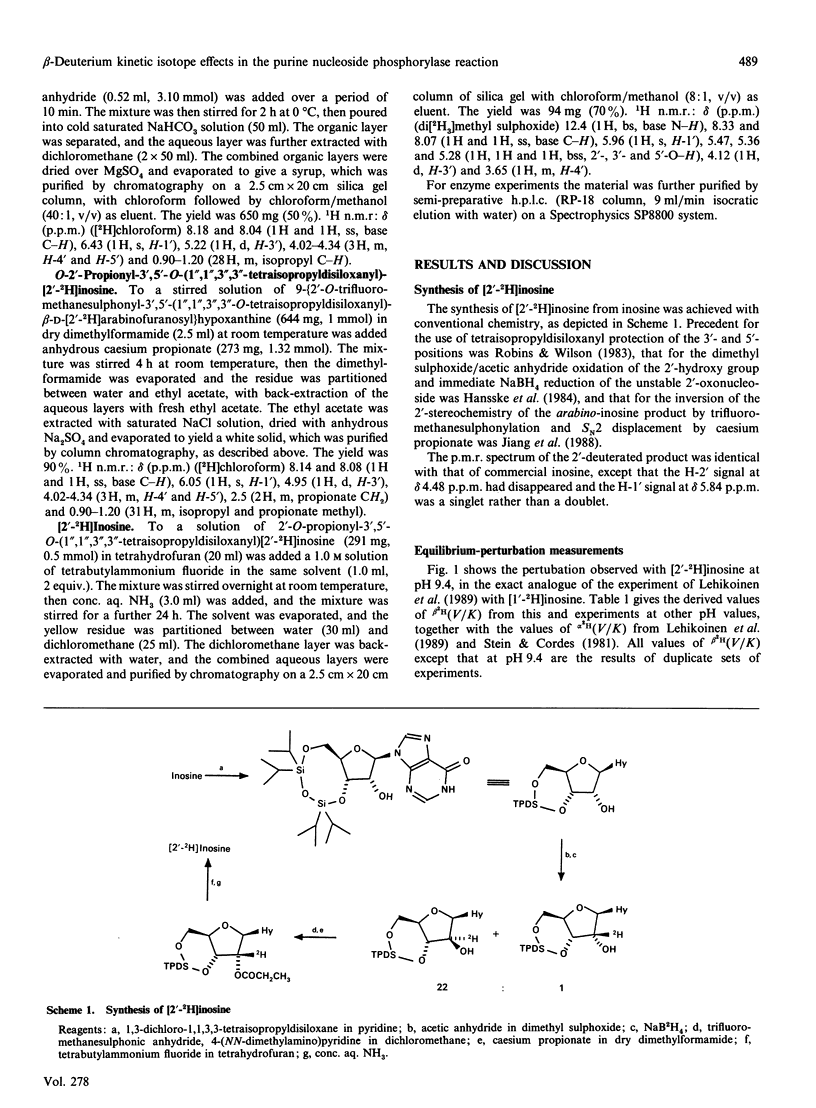
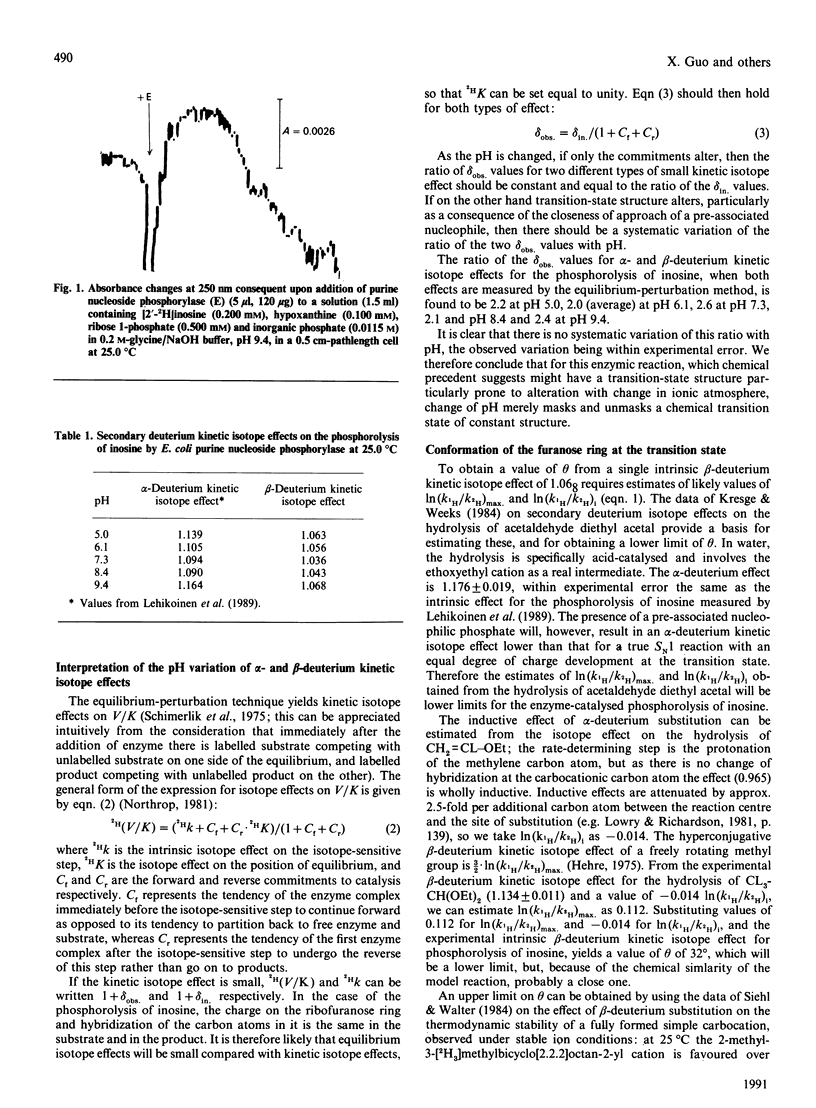
1. [2'-2H]Inosine was made from inosine by tetraisopropyldisiloxanyl protection of the 3'- and 5'-positions, oxidation with dimethyl sulphoxide and acetic anhydride, immediate NaB2H4 reduction of the oxo sugar product and inversion at C-2' of the resultant protected [2'-2H]arabino-inosine by trifluoromethanesulphonylation and reaction with caesium propionate, followed by deprotection. 2. The equilibrium-perturbation technique was used to measure beta 2H(V/K) for phosphorolysis of this compound by the purine nucleoside phosphorylase of Escherichia coli as a function of pH. 3. The pH variation indicates an intrinsic effect of 1.068 masked by isotopically silent steps near the pH optimum. 4. The similar pH variation of these beta-deuterium effects and the alpha-deuterium effects measured previously [Stein & Cordes (1981) J. Biol. Chem. 256, 767-772; Lehikoinen, Sinnott & Krenitsky (1989) Biochem. J. 257, 355-359] for this reaction provides the first experimental reassurance for the common assumption that pH changes merely mask and unmask the chemical steps in an enzyme-catalysed reaction, and do not detectably alter transition-state structure. 5. The dihedral angle between the C-H-2' bond and the electron-deficient p-orbital at the transition state is in the range 32-48 degrees, in accord with an essentially planar furanose ring.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cleland W. W. Determination of equilibrium isotope effects by the equilibrium perturbation method. Methods Enzymol. 1982;87:641–646. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)87034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ealick S. E., Rule S. A., Carter D. C., Greenhough T. J., Babu Y. S., Cook W. J., Habash J., Helliwell J. R., Stoeckler J. D., Parks R. E., Jr Three-dimensional structure of human erythrocytic purine nucleoside phosphorylase at 3.2 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1812–1820. doi: 10.2210/pdb2pnp/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehikoinen P. K., Sinnott M. L., Krenitsky T. A. Investigation of alpha-deuterium kinetic isotope effects on the purine nucleoside phosphorylase reaction by the equilibrium-perturbation technique. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):355–359. doi: 10.1042/bj2570355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B. F., Holdup D., Morton C. A., Sinnott M. L. The catalytic consequences of experimental evolution. Transition-state structure during catalysis by the evolved beta-galactosidases of Escherichia coli (ebg enzymes) changed by a single mutational event. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):109–114. doi: 10.1042/bj2600109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimerlik M. I., Rife J. E., Cleland W. W. Equilibrium perturbation by isotope substitution. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 2;14(24):5347–5354. doi: 10.1021/bi00695a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. L., Cordes E. H. Kinetic alpha-deuterium isotope effects for Escherichia coli purine nucleoside phosphorylase-catalyzed phosphorolysis of adenosine and inosine. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):767–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanoni M. A., Wong K. K., Ballou D. P., Blanchard J. S. Glutathione reductase: comparison of steady-state and rapid reaction primary kinetic isotope effects exhibited by the yeast, spinach, and Escherichia coli enzymes. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5790–5796. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M. R., Cook W. J., Cole L. B., Short S. A., Koszalka G. W., Krenitsky T. A., Ealick S. E. Three-dimensional structure of thymidine phosphorylase from Escherichia coli at 2.8 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):14016–14022. doi: 10.2210/pdb1tpt/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



